Design Strategies for High-Energy-Density Aqueous Zinc Batteries
Pengchao Ruan
School of Materials Science and Engineering, Key Laboratory of Electronic Packaging and Advanced Functional Materials of Hunan Province, Central South University, Changsha, 410083 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Shuquan Liang
School of Materials Science and Engineering, Key Laboratory of Electronic Packaging and Advanced Functional Materials of Hunan Province, Central South University, Changsha, 410083 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Bingan Lu
School of Physics and Electronics, Hunan University, Changsha, 410082 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Hong Jin Fan
School of Physical and Mathematical Sciences, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore, 637371 Singapore
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Jiang Zhou
School of Materials Science and Engineering, Key Laboratory of Electronic Packaging and Advanced Functional Materials of Hunan Province, Central South University, Changsha, 410083 P. R. China
College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Jishou University, Jishou, Hunan, 416000 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorPengchao Ruan
School of Materials Science and Engineering, Key Laboratory of Electronic Packaging and Advanced Functional Materials of Hunan Province, Central South University, Changsha, 410083 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Shuquan Liang
School of Materials Science and Engineering, Key Laboratory of Electronic Packaging and Advanced Functional Materials of Hunan Province, Central South University, Changsha, 410083 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Bingan Lu
School of Physics and Electronics, Hunan University, Changsha, 410082 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Hong Jin Fan
School of Physical and Mathematical Sciences, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore, 637371 Singapore
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Jiang Zhou
School of Materials Science and Engineering, Key Laboratory of Electronic Packaging and Advanced Functional Materials of Hunan Province, Central South University, Changsha, 410083 P. R. China
College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Jishou University, Jishou, Hunan, 416000 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorGraphical Abstract
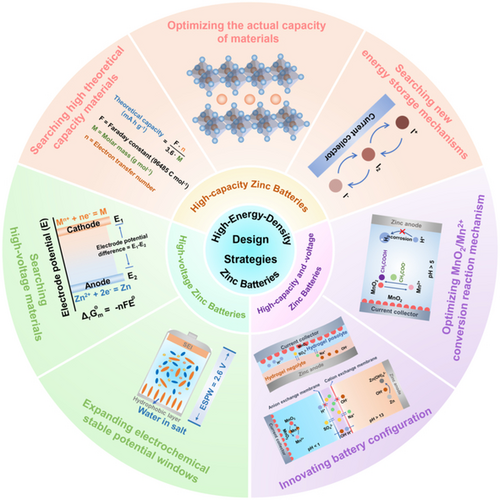
Safe, inexpensive aqueous zinc batteries are expected to play a vital role in the next-generation energy storage systems, but they currently display insufficient energy density. This Review articulates the design strategies effective in boosting the capacity, voltage, or both, highlights the challenges, and finally makes suggestions for future research directions.
Abstract
In recent years, the increasing demand for high-capacity and safe energy storage has focused attention on zinc batteries featuring high voltage, high capacity, or both. Despite extensive research progress, achieving high-energy-density zinc batteries remains challenging and requires the synergistic regulation of multiple factors including reaction mechanisms, electrodes, and electrolytes. In this Review, we comprehensively summarize the rational design strategies of high-energy-density zinc batteries and critically analyze the positive effects and potential issues of these strategies in optimizing the electrochemistry, cathode materials, electrolytes, and device architecture. Finally, the challenges and perspectives for the further development of high-energy-density zinc batteries are outlined to guide research towards new-generation batteries for household appliances, low-speed electric vehicles, and large-scale energy storage systems.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Supporting Information
As a service to our authors and readers, this journal provides supporting information supplied by the authors. Such materials are peer reviewed and may be re-organized for online delivery, but are not copy-edited or typeset. Technical support issues arising from supporting information (other than missing files) should be addressed to the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| anie202200598-sup-0001-misc_information.pdf10.9 KB | Supporting Information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1
- 1aD. Larcher, J. M. Tarascon, Nat. Chem. 2015, 7, 19;
- 1bS. Chu, Y. Cui, N. Liu, Nat. Mater. 2017, 16, 16;
- 1cR. Fang, S. Zhao, Z. Sun, D. Wang, H. Cheng, F. Li, Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1606823;
- 1dX. Gao, H. Yang, Energy Environ. Sci. 2010, 3, 174.
- 2
- 2aH. Ao, Y. Zhao, J. Zhou, W. Cai, X. Zhang, Y. Zhu, Y. Qian, J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 18708;
- 2bA. Zhou, Y. Liu, X. Zhu, X. Li, J. Yue, X. Ma, L. Gu, Y.-S. Hu, H. Li, X. Huang, L. Chen, L. Suo, Energy Stor. Mater. 2021, 42, 438;
- 2cX. Xu, F. Xiong, J. Meng, X. Wang, C. Niu, Q. An, L. Mai, Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1904398;
- 2dF. Wu, X. Gao, X. Xu, Y. Jiang, X. Gao, R. Yin, W. Shi, W. Liu, G. Lu, X. Cao, ChemSusChem 2020, 13, 1537.
- 3
- 3aF. Wan, Z. Hao, S. Wang, Y. Ni, J. Zhu, Z. Tie, S. Bi, Z. Niu, J. Chen, Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2102701;
- 3bC. Li, X. Shi, S. Liang, X. Ma, M. Han, X. Wu, J. Zhou, Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 379, 122248;
- 3cP. He, Y. Quan, X. Xu, M. Yan, W. Yang, Q. An, L. He, L. Mai, Small 2017, 13, 1702551;
- 3dX. Xu, Y. Chen, D. Zheng, P. Ruan, Y. Cai, X. Dai, X. Niu, C. Pei, W. Shi, W. Liu, F. Wu, Z. Pan, H. Li, X. Cao, Small 2021, 17, 2101901;
- 3eB. Li, X. Zhang, T. Wang, Z. He, B. Lu, S. Liang, J. Zhou, Nano-Micro Lett. 2022, 14, 6.
- 4
- 4aD. Chao, S.-Z. Qiao, Joule 2020, 4, 1846;
- 4bX. Guo, J. Zhou, C. Bai, X. Li, G. Fang, S. Liang, Mater. Today Energy 2020, 16, 100396;
- 4cZ. Liu, Y. Huang, Y. Huang, Q. Yang, X. Li, Z. Huang, C. Zhi, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 180;
- 4dV. Verma, S. Kumar, W. Manalastas, M. Srinivasan, ACS Energy Lett. 2021, 6, 1773;
- 4eX. Wang, Z. Zhang, B. Xi, W. Chen, Y. Jia, J. Feng, S. Xiong, ACS Nano 2021, 15, 9244;
- 4fY. Fang, X. Xie, B. Zhang, Y. Chai, B. Lu, M. Liu, J. Zhou, S. Liang, Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 2109671.
- 5
- 5aJ. Song, K. Xu, N. Liu, D. Reed, X. Li, Mater. Today 2021, 45, 191;
- 5bJ. Yan, E. H. Ang, Y. Yang, Y. Zhang, M. Ye, W. Du, C. C. Li, Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2010213;
- 5cP. Ruan, X. Xu, J. Feng, L. Yu, X. Gao, W. Shi, F. Wu, W. Liu, X. Zang, F. Ma, X. Cao, Mater. Res. Bull. 2021, 133, 111077.
- 6N. Fan, C. Sun, D. Kong, Y. Qian, J. Power Sources 2014, 254, 323.
- 7S. Ovshinsky, M. Fetcenko, Science 1993, 260, 176.
- 8K. Mizushima, P. C. Jones, P. J. Wiseman, J. B. Goodenough, Mater. Res. Bull. 1980, 15, 783.
- 9
- 9aD. Kundu, B. D. Adams, V. Duffort, S. H. Vajargah, L. F. Nazar, Nat. Energy 2016, 1, 16119;
- 9bC. Li, X. Xie, H. Liu, P. Wang, C. Deng, B. Lu, J. Zhou, S. Liang, Natl. Sci. Rev. 2021, nwab177.
- 10Y. Lu, Y. Lu, Z. Niu, J. Chen, Adv. Energy Mater. 2018, 8, 1702469.
- 11
- 11aQ. Li, Q. Zhang, C. Liu, Z. Zhou, C. Li, B. He, P. Man, X. Wang, Y. Yao, J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 12997;
- 11bX. Wang, Y. Li, S. Wang, F. Zhou, P. Das, C. Sun, S. Zheng, Z. Wu, Adv. Energy Mater. 2020, 10, 2000081.
- 12
- 12aY. Xu, P. Cai, K. Chen, Y. Ding, L. Chen, W. Chen, Z. Wen, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 23593; Angew. Chem. 2020, 132, 23799;
- 12bQ. Ni, H. Jiang, S. Sandstrom, Y. Bai, H. Ren, X. Wu, Q. Guo, D. Yu, C. Wu, X. Ji, Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 2003511.
- 13
- 13aD. Chao, C. Ye, F. Xie, W. Zhou, Q. Zhang, Q. Gu, K. Davey, L. Gu, S. Z. Qiao, Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 2001894;
- 13bC. Zhong, B. Liu, J. Ding, X. Liu, Y. Zhong, Y. Li, C. Sun, X. Han, Y. Deng, N. Zhao, W. Hu, Nat. Energy 2020, 5, 440.
- 14
- 14aY. Yang, Y. Tang, G. Fang, L. Shan, J. Guo, W. Zhang, C. Wang, L. Wang, J. Zhou, S. Liang, Energy Environ. Sci. 2018, 11, 3157;
- 14bY. Wu, Z. Zhu, Y. Li, D. Shen, L. Chen, T. Kang, X. Lin, Z. Tong, H. Wang, C. S. Lee, Small 2021, 17, 2008182;
- 14cX. Liu, G. Xu, Q. Zhang, S. Huang, L. Li, X. Wei, J. Cao, L. Yang, P. K. Chu, J. Power Sources 2020, 463, 228223;
- 14dF. Wu, Y. Wang, P. Ruan, X. Niu, D. Zheng, X. Xu, X. Gao, Y. Cai, W. Liu, W. Shi, X. Cao, Mater. Today Energy 2021, 21, 100842;
- 14eL. Shan, Y. Wang, S. Liang, B. Tang, Y. Yang, Z. Wang, B. Lu, J. Zhou, InfoMat 2021, 3, 1028;
- 14fX. Ma, X. Cao, M. Yao, L. Shan, X. Shi, G. Fang, A. Pan, B. Lu, J. Zhou, S. Liang, Adv. Mater. 2021, 34, 2105452.
- 15P. He, J. Liu, X. Zhao, Z. Ding, P. Gao, L.-Z. Fan, J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 10370.
- 16
- 16aJ. Ding, H. Zheng, H. Gao, Q. Liu, Z. Hu, L. Han, S. Wang, S. Wu, S. Fang, S. Chou, Adv. Energy Mater. 2021, 11, 2100973;
- 16bH. Luo, B. Wang, F. Wang, J. Yang, F. Wu, Y. Ning, Y. Zhou, D. Wang, H. Liu, S. Dou, ACS Nano 2020, 14, 7328;
- 16cK. Zhu, T. Wu, K. Huang, Energy Stor. Mater. 2021, 38, 473;
- 16dS. Wei, S. Chen, X. Su, Z. Qi, C. Wang, B. Ganguli, P. Zhang, K. Zhu, Y. Cao, Q. He, D. Cao, X. Guo, W. Wen, X. Wu, P. M. Ajayan, L. Song, Energy Environ. Sci. 2021, 14, 3954;
- 16eJ. Ding, Z. Du, B. Li, L. Wang, S. Wang, Y. Gong, S. Yang, Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1904369.
- 17
- 17aX. Wang, L. Chen, F. Lu, J. Liu, X. Chen, G. Shao, ChemElectroChem 2019, 6, 3644;
- 17bJ. Cui, Z. Guo, J. Yi, X. Liu, K. Wu, P. Liang, Q. Li, Y. Liu, Y. Wang, Y. Xia, J. Zhang, ChemSusChem 2020, 13, 2160.
- 18
- 18aZ. Tie, Z. Niu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 21293; Angew. Chem. 2020, 132, 21477;
- 18bQ. Zhao, W. Huang, Z. Luo, L. Liu, Y. Lu, Y. Li, L. Li, J. Hu, H. Ma, J. Chen, Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, 1761;
- 18cT. Sun, H. J. Fan, Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2021, 30, 100799.
- 19W. Wang, V. S. Kale, Z. Cao, Y. Lei, S. Kandambeth, G. Zou, Y. Zhu, E. Abouhamad, O. Shekhah, L. Cavallo, M. Eddaoudi, H. N. Alshareef, Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2103617.
- 20Y. Zhao, Y. Huang, F. Wu, R. Chen, L. Li, Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2106469.
- 21W. Li, K. Wang, K. Jiang, Adv. Sci. 2020, 7, 2000761.
- 22
- 22aC. Dai, X. Jin, H. Ma, L. Hu, G. Sun, H. Chen, Q. Yang, M. Xu, Q. Liu, Y. Xiao, X. Zhang, H. Yang, Q. Guo, Z. Zhang, L. Qu, Adv. Energy Mater. 2021, 11, 2003982;
- 22bC. Dai, L. Hu, X. Jin, H. Chen, X. Zhang, S. Zhang, L. Song, H. Ma, M. Xu, Y. Zhao, Z. Zhang, H. Cheng, L. Qu, Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2105480;
- 22cX. Wu, A. Markir, L. Ma, Y. Xu, H. Jiang, D. P. Leonard, W. Shin, T. Wu, J. Lu, X. Ji, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 12640; Angew. Chem. 2019, 131, 12770.
- 23W. Li, Y. Ma, P. Li, X. Jing, K. Jiang, D. Wang, Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2101237.
- 24Z. Chen, F. Mo, T. Wang, Q. Yang, Z. Huang, D. Wang, G. Liang, A. Chen, Q. Li, Y. Guo, X. Li, J. Fan, C. Zhi, Energy Environ. Sci. 2021, 14, 2441.
- 25J. Shin, D. S. Choi, H. J. Lee, Y. Jung, J. W. Choi, Adv. Energy Mater. 2019, 9, 1900083.
- 26
- 26aW. Li, C. Han, Q. Gu, S. Chou, J. Wang, H. Liu, S. Dou, Adv. Energy Mater. 2020, 10, 202001852;
- 26bD. Bin, W. Huo, Y. Yuan, J. Huang, Y. Liu, Y. Zhang, F. Dong, Y. Wang, Y. Xia, Chem 2020, 6, 968;
- 26cS. Liu, H. Zhu, B. Zhang, G. Li, H. Zhu, Y. Ren, H. Geng, Y. Yang, Q. Liu, C. C. Li, Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 2001113;
- 26dT.-T. Lv, Y.-Y. Liu, H. Wang, S.-Y. Yang, C.-S. Liu, H. Pang, Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 411, 128533.
- 27
- 27aD. Bin, Y. Liu, B. Yang, J. Huang, X. Dong, X. Zhang, Y. Wang, Y. Xia, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 20796;
- 27bT. Sun, Q. Nian, S. Zheng, X. Yuan, Z. Tao, J. Power Sources 2020, 478, 228758.
- 28M. Zhang, W. Wu, J. Luo, H. Zhang, J. Liu, X. Liu, Y. Yang, X. Lu, J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 11642.
- 29T. Xiong, Z. G. Yu, H. Wu, Y. Du, Q. Xie, J. Chen, Y. W. Zhang, S. J. Pennycook, W. S. V. Lee, J. Xue, Adv. Energy Mater. 2019, 9, 1803815.
- 30
- 30aY. Wu, M. Wang, Y. Tao, K. Zhang, M. Cai, Y. Ding, X. Liu, T. Hayat, A. Alsaedi, S. Dai, Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1907120;
- 30bX. Zhu, Z. Cao, W. Wang, H. Li, J. Dong, S. Gao, D. Xu, L. Li, J. Shen, M. Ye, ACS Nano 2021, 15, 2971.
- 31
- 31aY. Zeng, X. Zhang, Y. Meng, M. Yu, J. Yi, Y. Wu, X. Lu, Y. Tong, Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1700274;
- 31bY. Fu, Q. Wei, G. Zhang, X. Wang, J. Zhang, Y. Hu, D. Wang, L. Zuin, T. Zhou, Y. Wu, S. Sun, Adv. Energy Mater. 2018, 8, 1801445;
- 31cL. Chen, Z. Yang, F. Cui, J. Meng, Y. Jiang, J. Long, X. Zeng, Mater. Chem. Front. 2020, 4, 213;
- 31dB. Wu, G. Zhang, M. Yan, T. Xiong, P. He, L. He, X. Xu, L. Mai, Small 2018, 14, 1703850;
- 31eP. Ruan, X. Xu, X. Gao, J. Feng, L. Yu, Y. Cai, X. Gao, W. Shi, F. Wu, W. Liu, X. Zang, F. Ma, X. Cao, Sustainable Mater. Technol. 2021, 28, e00254.
- 32J. Ji, H. Wan, B. Zhang, C. Wang, Y. Gan, Q. Tan, N. Wang, J. Yao, Z. Zheng, P. Liang, J. Zhang, H. Wang, L. Tao, Y. Wang, D. Chao, H. Wang, Adv. Energy Mater. 2021, 11, 2003203.
- 33Z. Luo, S. Zheng, S. Zhao, X. Jiao, Z. Gong, F. Cai, Y. Duan, F. Li, Z. Yuan, J. Mater. Chem. A 2021, 9, 6131.
- 34S. Wang, Z. Yuan, X. Zhang, S. Bi, Z. Zhou, J. Tian, Q. Zhang, Z. Niu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 7056; Angew. Chem. 2021, 133, 7132.
- 35H. Pan, Y. Shao, P. Yan, Y. Cheng, K. S. Han, Z. Nie, C. Wang, J. Yang, X. Li, P. Bhattacharya, K. T. Mueller, J. Liu, Nat. Energy 2016, 1, 16039.
- 36D. Chao, W. Zhou, C. Ye, Q. Zhang, Y. Chen, L. Gu, K. Davey, S. Z. Qiao, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 7823; Angew. Chem. 2019, 131, 7905.
- 37Y. Zou, T. Liu, Q. Du, Y. Li, H. Yi, X. Zhou, Z. Li, L. Gao, L. Zhang, X. Liang, Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 170.
- 38J. Hao, L. Yuan, B. Johannessen, Y. Zhu, Y. Jiao, C. Ye, F. Xie, S. Z. Qiao, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 25114; Angew. Chem. 2021, 133, 25318.
- 39S. Deng, Z. Yuan, Z. Tie, C. Wang, L. Song, Z. Niu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 22002; Angew. Chem. 2020, 132, 22186.
- 40D. Chen, M. Lu, B. Wang, R. Chai, L. Li, D. Cai, H. Yang, B. Liu, Y. Zhang, W. Han, Energy Stor. Mater. 2021, 35, 679.
- 41L. Hu, Z. Wu, C. Lu, F. Ye, Q. Liu, Z. Sun, Energy Environ. Sci. 2021, 14, 4095.
- 42L. Wang, Z. Cao, P. Zhuang, J. Li, H. Chu, Z. Ye, D. Xu, H. Zhang, J. Shen, M. Ye, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 13338.
- 43W. Qiu, Y. Li, A. You, Z. Zhang, G. Li, X. Lu, Y. Tong, J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 14838.
- 44L. Zhang, L. Chen, X. Zhou, Z. Liu, Adv. Energy Mater. 2015, 5, 1400930.
- 45L. Ma, S. Chen, C. Long, X. Li, Y. Zhao, Z. Liu, Z. Huang, B. Dong, J. A. Zapien, C. Zhi, Adv. Energy Mater. 2019, 9, 1902446.
- 46L. Ma, S. Chen, H. Li, Z. Ruan, Z. Tang, Z. Liu, Z. Wang, Y. Huang, Z. Pei, J. A. Zapien, C. Zhi, Energy Environ. Sci. 2018, 11, 2521.
- 47Z. Liu, Q. Yang, D. Wang, G. Liang, Y. Zhu, F. Mo, Z. Huang, X. Li, L. Ma, T. Tang, Z. Lu, C. Zhi, Adv. Energy Mater. 2019, 9, 1902473.
- 48Z. Hou, X. Zhang, X. Li, Y. Zhu, J. Liang, Y. Qian, J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 730.
- 49W. Pan, Y. Wang, X. Zhao, Y. Zhao, X. Liu, J. Xuan, H. Wang, D. Y. C. Leung, Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2008783.
- 50F. Wan, Y. Zhang, L. Zhang, D. Liu, C. Wang, L. Song, Z. Niu, J. Chen, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 7062; Angew. Chem. 2019, 131, 7136.
- 51L. Ma, N. Li, C. Long, B. Dong, D. Fang, Z. Liu, Y. Zhao, X. Li, J. Fan, S. Chen, S. Zhang, C. Zhi, Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1906142.
- 52N. Li, G. Li, C. Li, H. Yang, G. Qin, X. Sun, F. Li, H. M. Cheng, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 13790.
- 53X. Zeng, J. Liu, J. Mao, J. Hao, Z. Wang, S. Zhou, C. D. Ling, Z. Guo, Adv. Energy Mater. 2020, 10, 1904163.
- 54L. Dai, Y. Wang, L. Sun, Y. Ding, Y. Yao, L. Yao, N. E. Drewett, W. Zhang, J. Tang, W. Zheng, Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2004995.
- 55X. Shen, X. Wang, Y. Zhou, Y. Shi, L. Zhao, H. Jin, J. Di, Q. Li, Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2101579.
- 56C. Xie, T. Li, C. Deng, Y. Song, H. Zhang, X. Li, Energy Environ. Sci. 2020, 13, 135.
- 57G. Li, W. Chen, H. Zhang, Y. Gong, F. Shi, J. Wang, R. Zhang, G. Chen, Y. Jin, T. Wu, Z. Tang, Y. Cui, Adv. Energy Mater. 2020, 10, 1902085.
- 58H. Tang, Y. Yin, Y. Huang, J. Wang, L. Liu, Z. Qu, H. Zhang, Y. Li, M. Zhu, O. G. Schmidt, ACS Energy Lett. 2021, 6, 1859.
- 59G. G. Yadav, D. Turney, J. Huang, X. Wei, S. Banerjee, ACS Energy Lett. 2019, 4, 2144.
- 60C. Liu, X. Chi, C. Yang, Y. Liu, Energy Environ. Mater. 2021 https://doi.org/10.1002/EEM2.12300.
- 61M. Ulaganathan, S. Suresh, K. Mariyappan, P. Periasamy, R. Pitchai, ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 6053.
- 62S. Gu, K. Gong, E. Z. Yan, Y. Yan, Energy Environ. Sci. 2014, 7, 2986.
- 63K. Gong, X. Ma, K. M. Conforti, K. J. Kuttler, J. B. Grunewald, K. L. Yeager, M. Z. Bazant, S. Gu, Y. Yan, Energy Environ. Sci. 2015, 8, 2941.
- 64F. Yu, L. Pang, X. Wang, E. R. Waclawik, F. Wang, K. Ostrikov, H. Wang, Energy Stor. Mater. 2019, 19, 56.
- 65C. Liu, X. Chi, Q. Han, Y. Liu, Adv. Energy Mater. 2020, 10, 1903589.
- 66X. Xie, H. Fu, Y. Fang, B. Lu, J. Zhou, S. Liang, Adv. Energy Mater. 2021, 12, 2102393.
- 67Z. Liu, Y. Yang, S. Liang, B. Lu, J. Zhou, Small Struct. 2021, 2, 2100119.
- 68J. Lei, Y. Yao, Z. Wang, Y.-C. Lu, Energy Environ. Sci. 2021, 14, 4418.
- 69T. Xue, H. J. Fan, J. Energy Chem. 2021, 54, 194.
- 70J. Huang, Y. Xie, L. Yan, B. Wang, T. Kong, X. Dong, Y. Wang, Y. Xia, Energy Environ. Sci. 2021, 14, 883.
- 71C. Wang, L. Sun, M. Li, L. Zhou, Y. Cheng, X. Ao, X. Zhang, L. Wang, B. Tian, H. J. Fan, Sci. China Chem. 2022, 65, 399.