Hypoxia-Responsive Platinum Supernanoparticles for Urinary Microfluidic Monitoring of Tumors
Qin Xu
College of Engineering and Applied Sciences, Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Artificial Functional Materials, State Key Laboratory of Analytical Chemistry for Life Science, Nanjing University, Nanjing, 210023 China
Search for more papers by this authorYongchun Pan
College of Engineering and Applied Sciences, Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Artificial Functional Materials, State Key Laboratory of Analytical Chemistry for Life Science, Nanjing University, Nanjing, 210023 China
Search for more papers by this authorXinli Liu
Life Science Institute, Guangxi Medical University, Nanning, 530021 China
Search for more papers by this authorYanfeng Gao
College of Engineering and Applied Sciences, Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Artificial Functional Materials, State Key Laboratory of Analytical Chemistry for Life Science, Nanjing University, Nanjing, 210023 China
Search for more papers by this authorXiaowei Luan
College of Engineering and Applied Sciences, Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Artificial Functional Materials, State Key Laboratory of Analytical Chemistry for Life Science, Nanjing University, Nanjing, 210023 China
Search for more papers by this authorFei Zeng
College of Engineering and Applied Sciences, Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Artificial Functional Materials, State Key Laboratory of Analytical Chemistry for Life Science, Nanjing University, Nanjing, 210023 China
Search for more papers by this authorDongtao Zhou
College of Engineering and Applied Sciences, Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Artificial Functional Materials, State Key Laboratory of Analytical Chemistry for Life Science, Nanjing University, Nanjing, 210023 China
Search for more papers by this authorWenxiu Long
Key Laboratory of Flexible Electronics & Institute of Advanced Materials, Jiangsu National Synergistic Innovation Center for Advanced Materials, Nanjing Tech University, Nanjing, 211816 China
Search for more papers by this authorYuzhen Wang
Key Laboratory of Flexible Electronics & Institute of Advanced Materials, Jiangsu National Synergistic Innovation Center for Advanced Materials, Nanjing Tech University, Nanjing, 211816 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Yujun Song
College of Engineering and Applied Sciences, Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Artificial Functional Materials, State Key Laboratory of Analytical Chemistry for Life Science, Nanjing University, Nanjing, 210023 China
Search for more papers by this authorQin Xu
College of Engineering and Applied Sciences, Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Artificial Functional Materials, State Key Laboratory of Analytical Chemistry for Life Science, Nanjing University, Nanjing, 210023 China
Search for more papers by this authorYongchun Pan
College of Engineering and Applied Sciences, Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Artificial Functional Materials, State Key Laboratory of Analytical Chemistry for Life Science, Nanjing University, Nanjing, 210023 China
Search for more papers by this authorXinli Liu
Life Science Institute, Guangxi Medical University, Nanning, 530021 China
Search for more papers by this authorYanfeng Gao
College of Engineering and Applied Sciences, Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Artificial Functional Materials, State Key Laboratory of Analytical Chemistry for Life Science, Nanjing University, Nanjing, 210023 China
Search for more papers by this authorXiaowei Luan
College of Engineering and Applied Sciences, Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Artificial Functional Materials, State Key Laboratory of Analytical Chemistry for Life Science, Nanjing University, Nanjing, 210023 China
Search for more papers by this authorFei Zeng
College of Engineering and Applied Sciences, Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Artificial Functional Materials, State Key Laboratory of Analytical Chemistry for Life Science, Nanjing University, Nanjing, 210023 China
Search for more papers by this authorDongtao Zhou
College of Engineering and Applied Sciences, Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Artificial Functional Materials, State Key Laboratory of Analytical Chemistry for Life Science, Nanjing University, Nanjing, 210023 China
Search for more papers by this authorWenxiu Long
Key Laboratory of Flexible Electronics & Institute of Advanced Materials, Jiangsu National Synergistic Innovation Center for Advanced Materials, Nanjing Tech University, Nanjing, 211816 China
Search for more papers by this authorYuzhen Wang
Key Laboratory of Flexible Electronics & Institute of Advanced Materials, Jiangsu National Synergistic Innovation Center for Advanced Materials, Nanjing Tech University, Nanjing, 211816 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Yujun Song
College of Engineering and Applied Sciences, Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Artificial Functional Materials, State Key Laboratory of Analytical Chemistry for Life Science, Nanjing University, Nanjing, 210023 China
Search for more papers by this authorGraphical Abstract
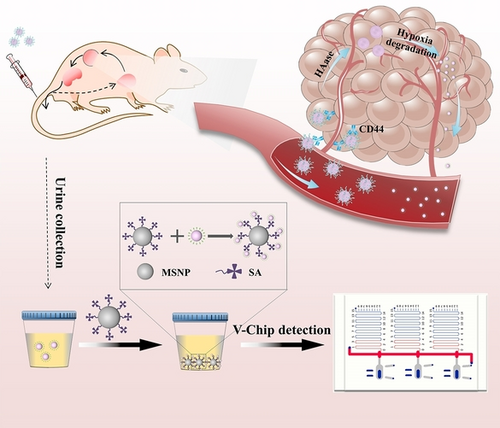
Hypoxia-triggered platinum supernanoparticles dissociated into ultrasmall platinum nanoclusters, which could be cleared by the kidney through urine, in response to the tumor microenvironment. After collection of the excreted nanosensors, the disease status was monitored visually and quantitatively by using a microfluidic chip.
Abstract
Cancer has become a leading cause of morbidity and mortality, and there is an increasing need for versatile tools to enable sensitive, simple and early cancer monitoring. Here, we report platinum supernanoparticles as an exogenous nanosensor which can dissociate into ultrasmall platinum nanoclusters (PtNCs) under tumor-specific hypoxia conditions. The resulting PtNCs can be filtered through the kidney as urinary reporters to be quantified by a companion volumetric bar-chart chip (V-Chip) for point-of-care analysis. The V-Chip signals of triple-negative breast cancer and its lung metastasis mouse model showed a significant increase compared to healthy mice. Our nanosensor can also noninvasively monitor the course of treatment, which is significant for screening tumor recurrence and individualized evaluation of pharmacological and follow-up efficacy. Importantly, this strategy could be adapted for various diseases to form a common diagnostic platform by changing responsive linkers.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Open Research
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Supporting Information
As a service to our authors and readers, this journal provides supporting information supplied by the authors. Such materials are peer reviewed and may be re-organized for online delivery, but are not copy-edited or typeset. Technical support issues arising from supporting information (other than missing files) should be addressed to the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| anie202114239-sup-0001-misc_information.pdf2.1 MB | Supporting Information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1
- 1aK. Hill, K. Thomas, C. AbouZahr, N. Walker, L. Say, M. Inoue, E. Suzuki, Lancet 2007, 370, 1311–1319;
- 1bC. D. Mathers, D. Loncar, PLoS Med. 2006, 3, e442;
- 1cF. Selmouni, A. Zidouh, L. Belakhel, C. Sauvaget, M. Bennani, Y. C. Khazraji, A. Benider, C. P. Wild, R. Bekkali, I. Fadhil, R. Sankaranarayanan, Lancet Oncol. 2018, 19, e93–e101;
- 1dP. Kanavos, Ann. Oncol. 2006, 17, viii15–viii23.
- 2
- 2aC. Liu, J. Zhao, F. Tian, L. Cai, W. Zhang, Q. Feng, J. Chang, F. Wan, Y. Yang, B. Dai, Y. Cong, B. Ding, J. Sun, W. Tan, Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2019, 3, 183–193;
- 2bC. J. A. Punt, M. Koopman, L. Vermeulen, Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 14, 235–246;
- 2cE. J. Kwon, J. H. Lo, S. N. Bhatia, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 14460;
- 2dF. Tian, S. Zhang, C. Liu, Z. Han, Y. Liu, J. Deng, Y. Li, X. Wu, L. Cai, L. Qin, Q. Chen, Y. Yuan, Y. Liu, Y. Cong, B. Ding, Z. Jiang, J. Sun, Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2536.
- 3
- 3aA. K. Siriwardena, J. M. Mason, S. Mullamitha, H. C. Hancock, S. Jegatheeswaran, Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 11, 446–459;
- 3bA. M. Lennon, A. H. Buchanan, I. Kinde, A. Warren, A. Honushefsky, A. T. Cohain, D. H. Ledbetter, F. Sanfilippo, K. Sheridan, D. Rosica, C. S. Adonizio, H. J. Hwang, K. Lahouel, J. D. Cohen, C. Douville, A. A. Patel, L. N. Hagmann, D. D. Rolston, N. Malani, S. Zhou, C. Bettegowda, D. L. Diehl, B. Urban, C. D. Still, L. Kann, J. I. Woods, Z. M. Salvati, J. Vadakara, R. Leeming, P. Bhattacharya, C. Walter, A. Parker, C. Lengauer, A. Klein, C. Tomasetti, E. K. Fishman, R. H. Hruban, K. W. Kinzler, B. Vogelstein, N. Papadopoulos, Science 2020, 369, eabb9601.
- 4K. Cheng, M. Yang, R. Zhang, C. Qin, X. Su, Z. Cheng, ACS Nano 2014, 8, 9884–9896.
- 5P. B. Bach, J. N. Mirkin, T. K. Oliver, C. G. Azzoli, D. A. Berry, O. W. Brawley, T. Byers, G. A. Colditz, M. K. Gould, J. R. Jett, A. L. Sabichi, R. Smith-Bindman, D. E. Wood, A. Qaseem, F. C. Detterbeck, JAMA J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2012, 307, 2418–2429.
- 6
- 6aA. Aalipour, H.-Y. Chuang, S. Murty, A. L. D'Souza, S.-m. Park, G. S. Gulati, C. B. Patel, C. Beinat, F. Simonetta, I. Martinić, G. Gowrishankar, E. R. Robinson, E. Aalipour, Z. Zhian, S. S. Gambhir, Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 531–539;
- 6bJ. D. Kirkpatrick, A. D. Warren, A. P. Soleimany, P. M. K. Westcott, J. C. Voog, C. Martin-Alonso, H. E. Fleming, T. Tammela, T. Jacks, S. N. Bhatia, Sci. Transl. Med. 2020, 12, eaaw0262.
- 7
- 7aY. Song, Y.-Y. Huang, X. Liu, X. Zhang, M. Ferrari, L. Qin, Trends Biotechnol. 2014, 32, 132–139;
- 7bK. Liang, F. Liu, J. Fan, D. Sun, C. Liu, C. J. Lyon, D. W. Bernard, Y. Li, K. Yokoi, M. H. Katz, E. J. Koay, Z. Zhao, Y. Hu, Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2017, 1, 0021.
- 8
- 8aS. Gutman, L. G. Kessler, Nat. Rev. Cancer 2006, 6, 565–571;
- 8bS. M. Hanash, S. J. Pitteri, V. M. Faca, Nature 2008, 452, 571–579;
- 8cJ. D. Brooks, Genome Res. 2012, 22, 183–187;
- 8dY. Liu, J. Fan, T. Xu, N. Ahmadinejad, K. Hess, S. H. Lin, J. Zhang, X. Liu, L. Liu, B. Ning, Z. Liao, T. Y. Hu, Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaaz6162.
- 9C. N. Loynachan, A. P. Soleimany, J. S. Dudani, Y. Lin, A. Najer, A. Bekdemir, Q. Chen, S. N. Bhatia, M. M. Stevens, Nat. Nanotechnol. 2019, 14, 883–890.
- 10
- 10aD. K. Nomura, M. M. Dix, B. F. Cravatt, Nat. Rev. Cancer 2010, 10, 630–638;
- 10bL. E. Edgington, M. Verdoes, M. Bogyo, Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2011, 15, 798–805;
- 10cS. A. Hilderbrand, R. Weissleder, Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2010, 14, 71–79.
- 11R. Polsky, R. Gill, L. Kaganovsky, I. Willner, Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 2268–2271.
- 12J. Fan, J. J. Yin, B. Ning, X. Wu, Y. Hu, M. Ferrari, G. J. Anderson, J. Wei, Y. Zhao, G. Nie, Biomaterials 2011, 32, 1611–1618.
- 13Y. Song, X. Xia, X. Wu, P. Wang, L. Qin, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 12451–12455; Angew. Chem. 2014, 126, 12659–12663.
- 14
- 14aW. Li, M. Khan, L. Lin, Q. Zhang, S. Feng, Z. Wu, J. M. Lin, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 9282–9287; Angew. Chem. 2020, 132, 9368–9373;
- 14bQ. Zhang, S. Feng, W. Li, T. Xie, W. Zhang, J. M. Lin, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 8483–8487; Angew. Chem. 2021, 133, 8564–8568.
- 15
- 15aZ. Wang, Y. Zhang, E. Ju, Z. Liu, F. Cao, Z. Chen, J. Ren, X. Qu, Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3334;
- 15bY. Huang, Z. Liu, C. Liu, E. Ju, Y. Zhang, J. Ren, X. Qu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 6646–6650; Angew. Chem. 2016, 128, 6758–6762.
- 16
- 16aA. Challapalli, L. Carroll, E. O. Aboagye, Clin. Transl. Imaging 2017, 5, 225–253;
- 16bX. Li, Y. Pan, C. Chen, Y. Gao, X. Liu, K. Yang, X. Luan, D. Zhou, F. Zeng, X. Han, Y. Song, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 21200–21204; Angew. Chem. 2021, 133, 21370–21374.
- 17
- 17aH. S. Choi, W. Liu, P. Misra, E. Tanaka, J. P. Zimmer, B. Itty Ipe, M. G. Bawendi, J. V. Frangioni, Nat. Biotechnol. 2007, 25, 1165–1170;
- 17bM. Yu, J. Zhou, B. Du, X. Ning, C. Authement, L. Gandee, P. Kapur, J.-T. Hsieh, J. Zheng, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 2787–2791; Angew. Chem. 2016, 128, 2837–2841.
- 18W.-C. Geng, S. Jia, Z. Zheng, Z. Li, D. Ding, D.-S. Guo, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 2377–2381; Angew. Chem. 2019, 131, 2399–2403.
- 19P. Y. Chu, S. C. Tsai, H. Y. Ko, C. C. Wu, Y. H. Lin, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 23880–23892.
- 20
- 20aL. Hnormao, N. Rohani, R. T. Zhao, E. M. Pulver, H. Mak, O. J. Kelada, H. Ko, H. E. Fleming, F. B. Gertler, S. N. Bhatia, Nat. Mater. 2021, 20, 1440–1448;
- 20bP. Sidaway, Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 15, 68–68.