Photo-Induced Polymer Cyclization via Supramolecular Confinement of Cyanostilbenes
Yuncong Xue
CAS Key Laboratory of Soft Matter Chemistry, Department of Polymer Science and Engineering, Hefei National Laboratory for Physical Science at the Microscale, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, Anhui, 230026 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorSixun Jiang
CAS Key Laboratory of Soft Matter Chemistry, Department of Polymer Science and Engineering, Hefei National Laboratory for Physical Science at the Microscale, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, Anhui, 230026 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorHua Zhong
CAS Key Laboratory of Soft Matter Chemistry, Department of Polymer Science and Engineering, Hefei National Laboratory for Physical Science at the Microscale, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, Anhui, 230026 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorZe Chen
CAS Key Laboratory of Soft Matter Chemistry, Department of Polymer Science and Engineering, Hefei National Laboratory for Physical Science at the Microscale, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, Anhui, 230026 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. Feng Wang
CAS Key Laboratory of Soft Matter Chemistry, Department of Polymer Science and Engineering, Hefei National Laboratory for Physical Science at the Microscale, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, Anhui, 230026 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorYuncong Xue
CAS Key Laboratory of Soft Matter Chemistry, Department of Polymer Science and Engineering, Hefei National Laboratory for Physical Science at the Microscale, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, Anhui, 230026 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorSixun Jiang
CAS Key Laboratory of Soft Matter Chemistry, Department of Polymer Science and Engineering, Hefei National Laboratory for Physical Science at the Microscale, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, Anhui, 230026 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorHua Zhong
CAS Key Laboratory of Soft Matter Chemistry, Department of Polymer Science and Engineering, Hefei National Laboratory for Physical Science at the Microscale, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, Anhui, 230026 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorZe Chen
CAS Key Laboratory of Soft Matter Chemistry, Department of Polymer Science and Engineering, Hefei National Laboratory for Physical Science at the Microscale, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, Anhui, 230026 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. Feng Wang
CAS Key Laboratory of Soft Matter Chemistry, Department of Polymer Science and Engineering, Hefei National Laboratory for Physical Science at the Microscale, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, Anhui, 230026 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorGraphical Abstract
Abstract
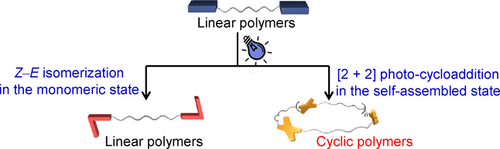
Efficient synthesis of cyclic polymers has received much attention in polymer chemistry field. Although photochemical cycloaddition of terminal π-bonded units provides a plausible way toward cyclic polymerization, it remains challenging to avoid side reactions by manipulating the reaction selectivity. Herein supramolecular confinement has been developed as a promising strategy to address this issue, by introducing highly directional hydrogen bonds to the photo-reactive cyanostilbenes. The cyanostilbenes units on both ends of a telechelic macromonomer are orientationally aligned with high local concentrations, yielding [2+2] photo-cycloaddition products upon 430 nm light irradiation. It leads to the formation of cyclic polymers in the self-assembled state, in stark contrast to Z-E isomerization of cyanostilbenes in the monomeric state. Overall, supramolecular confinement effect exemplified in the current study provides new avenues toward cyclic topological polymers with high synthetic efficiency.
Supporting Information
As a service to our authors and readers, this journal provides supporting information supplied by the authors. Such materials are peer reviewed and may be re-organized for online delivery, but are not copy-edited or typeset. Technical support issues arising from supporting information (other than missing files) should be addressed to the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| anie202110766-sup-0001-misc_information.pdf3 MB | Supporting Information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1
- 1aB. A. Laurent, S. M. Grayson, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 2202–2213;
- 1bF. M. Haque, S. M. Grayson, Nat. Chem. 2020, 12, 433–444;
- 1cR. Liénard, J. De Winter, O. Coulembier, J. Polym. Sci. 2020, 58, 1481–1502.
- 2
- 2aT. Yamamoto, Y. Tezuka, Polym. Chem. 2011, 2, 1930–1941;
- 2bT. Josse, J. D. Winter, P. Gerbaux, O. Coulembier, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 13944–13958; Angew. Chem. 2016, 128, 14150–14164.
- 3
- 3aY. Tezuka, R. Komiya, Macromolecules 2002, 35, 8667–8669;
- 3bM. Schulz, S. Tanner, H. Barqawi, W. H. Binder, J. Polym. Sci. Part A 2010, 48, 671–680;
- 3cR. P. Quirk, S. F. Wang, M. D. Foster, Macromolecules 2011, 44, 7538–7545.
- 4
- 4aZ. Ge, Y. Zhou, J. Xu, H. Liu, D. Chen, S. Liu, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 1628–1629;
- 4bH. Misaka, R. Kakuchi, C. Zhang, R. Sakai, T. Satoh, T. Kakuchi, Macromolecules 2009, 42, 5091–5096;
- 4cM. B. Koo, S. W. Lee, J. M. Lee, K. T. Kim, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 14028–14032.
- 5
- 5aH. Wang, L. Zhang, B. Liu, B. Han, Z. Duan, C. Qi, D. W. Park, I. Kim, Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2015, 36, 1646–1650;
- 5bT. Yamamoto, S. Yagyu, Y. Tezuka, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 3904–3911;
- 5cH. Frisch, F. B. Bloesser, C. Barner-Kowollik, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 3604–3609; Angew. Chem. 2019, 131, 3642–3648;
- 5dH.-L. Zhang, W. Xu, C. Liu, C.-Y. Hong, Polym. Chem. 2021, 12, 5357–5363.
- 6
- 6aM. Klaper, T. Linker, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 11896–11899; Angew. Chem. 2013, 125, 12112–12115;
- 6bZ. Gao, Y. Han, F. Wang, Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3977;
- 6cA. B. Grommet, L. M. Lee, R. Klajn, Acc. Chem. Res. 2020, 53, 2600–2610.
- 7
- 7aL. Zhu, X. Li, Q. Zhang, X. Ma, M. Li, H. Zhang, Z. Luo, H. Ågren, Y. Zhao, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 5175–5182;
- 7bJ. W. Chung, S. J. Yoon, B. K. An, S. Y. Park, J. Phys. Chem. C 2013, 117, 11285–11291;
- 7cM. Martínez-Abadía, R. Giménez, M. B. Ros, Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1704161.
- 8
- 8aJ. W. Chung, Y. You, H. S. Huh, B. K. An, S. J. Yoon, S. H. Kim, S. W. Lee, S. Y. Park, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 8163–8172;
- 8bP. Wei, J. X. Zhang, Z. Zhao, Y. Chen, X. He, M. Chen, J. Gong, H. H. Y. Sung, I. D. Williams, J. W. L. Lam, B. Tang, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 1966–1975;
- 8cK. Y. Kim, S. H. Jung, S. Lee, C. J. Moon, Y. Choi, M. Y. Choi, J. H. Jung, J. Phys. Chem. C 2018, 122, 22143–22149;
- 8dT. Dünnebacke, K. K. Kartha, J. M. Wiest, R. Q. Albuquerque, G. Fernández, Chem. Sci. 2020, 11, 10405–10413.
- 9
- 9aG. M. Schmidt, J. Pure Appl. Chem. 1971, 27, 647–678;
- 9bH. Wang, P. Chen, Z. Wu, J. Zhao, J. Sun, R. Lu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 9463–9467; Angew. Chem. 2017, 129, 9591–9595.
- 10
- 10aK. Kinjo, T. Hirao, S. Kihara, Y. Katsumoto, T. Haino, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 14830–14834; Angew. Chem. 2015, 127, 15043–15047;
- 10bS. Das, N. Okamura, S. Yagi, A. Ajayaghosh, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 5635–5639.
- 11
- 11aX. Wang, Y. Han, Y. Liu, G. Zou, Z. Gao, F. Wang, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 12466–12470; Angew. Chem. 2017, 129, 12640–12644;
- 11bS. Sarkar, A. Sarkar, S. J. George, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 19841–19845; Angew. Chem. 2020, 132, 20013–20017;
- 11cJ. Matern, N. Bäumer, G. Fernández, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 7164–7175;
- 11dI. Helmers, G. Ghosh, R. Q. Albuquerque, G. Fernández, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 4368–4376; Angew. Chem. 2021, 133, 4414–4423;
- 11eY. Han, Y. Yin, F. Wang, F. Wang, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 14076–14082; Angew. Chem. 2021, 133, 14195–14201.
- 12
- 12aJ. Roosma, T. Mes, P. Leclère, A. R. A. Palmans, E. W. Meijer, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 1120–1121;
- 12bY. Uemura, K. Yamato, R. Sekiya, T. Haino, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 4960–4964; Angew. Chem. 2018, 130, 5054–5058.
- 13R. H. Zha, B. F. M. de Waal, M. Lutz, A. J. P. Teunissen, E. W. Meijer, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 5693–5698.
- 14B. A. G. Lamers, B. F. M. de Waal, E. W. Meijer, J. Polym. Sci. 2020, 59, 1142–1150.
- 15M. Wolffs, S. J. George, Ž. Tomović, S. C. J. Meskers, A. P. H. J. Schenning, E. W. Meijer, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 8203–8205; Angew. Chem. 2007, 119, 8351–8353.
- 16
- 16aT. F. A. De Greef, M. M. J. Smulders, M. Wolffs, A. P. H. J. Schenning, R. P. Sijbesma, E. W. Meijer, Chem. Rev. 2009, 109, 5687–5754;
- 16bC. Rest, R. Kandanelli, G. Fernández, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 2543–2572;
- 16cM. Wehner, F. Würthner, Nat. Rev. Chem. 2020, 4, 38–53.