Wide-Range Color-Tunable Organic Phosphorescence Materials for Printable and Writable Security Inks
Yunxiang Lei
Beijing Key Laboratory of Construction Tailorable Advanced Functional Materials and Green Applications, School of Materials Science & Engineering, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing, 100081 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorWenbo Dai
Beijing Key Laboratory of Construction Tailorable Advanced Functional Materials and Green Applications, School of Materials Science & Engineering, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing, 100081 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorJianxin Guan
Beijing National Laboratory for Molecular Sciences, College of Chemistry and Molecular Engineering, Peking University, Beijing, 100871 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorShuai Guo
Beijing Key Laboratory of Construction Tailorable Advanced Functional Materials and Green Applications, School of Materials Science & Engineering, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing, 100081 China
Search for more papers by this authorFei Ren
Beijing Key Laboratory of Construction Tailorable Advanced Functional Materials and Green Applications, School of Materials Science & Engineering, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing, 100081 China
Search for more papers by this authorYudai Zhou
Beijing Key Laboratory of Construction Tailorable Advanced Functional Materials and Green Applications, School of Materials Science & Engineering, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing, 100081 China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Jianbing Shi
Beijing Key Laboratory of Construction Tailorable Advanced Functional Materials and Green Applications, School of Materials Science & Engineering, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing, 100081 China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Bin Tong
Beijing Key Laboratory of Construction Tailorable Advanced Functional Materials and Green Applications, School of Materials Science & Engineering, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing, 100081 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Zhengxu Cai
Beijing Key Laboratory of Construction Tailorable Advanced Functional Materials and Green Applications, School of Materials Science & Engineering, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing, 100081 China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Junrong Zheng
Beijing National Laboratory for Molecular Sciences, College of Chemistry and Molecular Engineering, Peking University, Beijing, 100871 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Yuping Dong
Beijing Key Laboratory of Construction Tailorable Advanced Functional Materials and Green Applications, School of Materials Science & Engineering, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing, 100081 China
Search for more papers by this authorYunxiang Lei
Beijing Key Laboratory of Construction Tailorable Advanced Functional Materials and Green Applications, School of Materials Science & Engineering, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing, 100081 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorWenbo Dai
Beijing Key Laboratory of Construction Tailorable Advanced Functional Materials and Green Applications, School of Materials Science & Engineering, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing, 100081 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorJianxin Guan
Beijing National Laboratory for Molecular Sciences, College of Chemistry and Molecular Engineering, Peking University, Beijing, 100871 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorShuai Guo
Beijing Key Laboratory of Construction Tailorable Advanced Functional Materials and Green Applications, School of Materials Science & Engineering, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing, 100081 China
Search for more papers by this authorFei Ren
Beijing Key Laboratory of Construction Tailorable Advanced Functional Materials and Green Applications, School of Materials Science & Engineering, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing, 100081 China
Search for more papers by this authorYudai Zhou
Beijing Key Laboratory of Construction Tailorable Advanced Functional Materials and Green Applications, School of Materials Science & Engineering, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing, 100081 China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Jianbing Shi
Beijing Key Laboratory of Construction Tailorable Advanced Functional Materials and Green Applications, School of Materials Science & Engineering, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing, 100081 China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Bin Tong
Beijing Key Laboratory of Construction Tailorable Advanced Functional Materials and Green Applications, School of Materials Science & Engineering, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing, 100081 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Zhengxu Cai
Beijing Key Laboratory of Construction Tailorable Advanced Functional Materials and Green Applications, School of Materials Science & Engineering, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing, 100081 China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Junrong Zheng
Beijing National Laboratory for Molecular Sciences, College of Chemistry and Molecular Engineering, Peking University, Beijing, 100871 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Yuping Dong
Beijing Key Laboratory of Construction Tailorable Advanced Functional Materials and Green Applications, School of Materials Science & Engineering, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing, 100081 China
Search for more papers by this authorGraphical Abstract
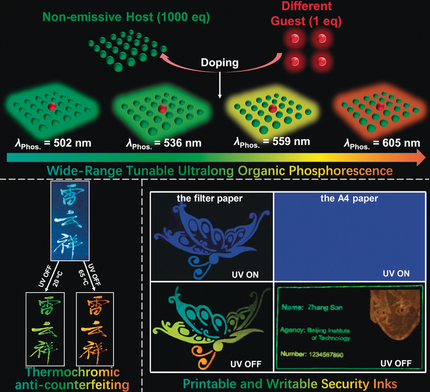
Multicolor swap shop: A facile doping approach for color-tunable organic phosphorescence materials is enabled through hosts that not only restrict the molecular motion and avoid the triplet quenching from the oxygen, but also interact with the guests for the realization of phosphorescence. Color tunable, temperature dependent, and time-resolved anti-counterfeiting techniques are achieved by the printable and writable materials.
Abstract
Organic materials with long-lived, color-tunable phosphorescence are potentially useful for optical recording, anti-counterfeiting, and bioimaging. Herein, we develop a series of novel host–guest organic phosphors allowing dynamic color tuning from the cyan (502 nm) to orange red (608 nm). Guest materials are employed to tune the phosphorescent color, while the host materials interact with the guest to activate the phosphorescence emission. These organic phosphors have an ultra-long lifetime of 0.7 s and a maximum phosphorescence efficiency of 18.2 %. Although color-tunable inks have already been developed using visible dyes, solution-processed security inks that are temperature dependent and display time-resolved printed images are unprecedented. This strategy can provide a crucial step towards the next-generation of security technologies for information handling.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Supporting Information
As a service to our authors and readers, this journal provides supporting information supplied by the authors. Such materials are peer reviewed and may be re-organized for online delivery, but are not copy-edited or typeset. Technical support issues arising from supporting information (other than missing files) should be addressed to the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| anie202003585-sup-0001-misc_information.pdf3.7 MB | Supplementary |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1
- 1aO. Bolton, K. Lee, H. J. Kim, K. Y. Lin, J. Kim, Nat. Chem. 2011, 3, 205–210;
- 1bL. Gu, H. Shi, L. Bian, M. Gu, K. Ling, X. Wang, H. Ma, S. Cai, W. Ning, L. Fu, H. Wang, S. Wang, Y. Gao, W. Yao, F. Huo, Y. Tao, Z. An, X. Liu, W. Huang, Nat. Photonics 2019, 13, 406–411;
- 1cY. Xiong, Z. Zhao, W. Zhao, H. Ma, Q. Peng, Z. He, X. Zhang, Y. Chen, X. He, J. W. Y. Lam, B. Z. Tang, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 7997–8001; Angew. Chem. 2018, 130, 8129–8133;
- 1dZ. An, C. Zheng, Y. Tao, R. Chen, H. Shi, T. Chen, Z. Wang, H. Li, R. Deng, X. Liu, W. Huang, Nat. Mater. 2015, 14, 685–690;
- 1eZ. He, H. Gao, S. Zhang, S. Zheng, Y. Wang, Z. Zhao, D. Ding, B. Yang, Y. Zhang, W. Z. Yuan, Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1807222;
- 1fW. Zhao, Z. He, J. W. Y. Lam, Q. Peng, H. Ma, Z. Shuai, G. Bai, J. Hao, B. Z. Tang, Chem 2016, 1, 592–602;
- 1gG. Zhang, G. M. Palmer, M. W. Dewhirst, C. L. Fraser, Nat. Mater. 2009, 8, 747–751;
- 1hJ. Zhao, W. Wu, J. Sun, S. Guo, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 5323–5351.
- 2
- 2aH. Ma, Q. Peng, Z. An, W. Huang, Z. Shuai, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 1010–1015;
- 2bY. Xie, Y. Ge, Q. Peng, C. Li, Q. Li, Z. Li, Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1606829.
- 3
- 3aT. Wang, X. Su, X. Zhang, X. Nie, L. Huang, X. Zhang, X. Sun, Y. Luo, G. Zhang, Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1904273;
- 3bJ. Wang, Z. Chai, J. Wang, C. Wang, M. Han, Q. Liao, A. Huang, P. Lin, C. Li, Q. Li, Z. Li, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 17297–17302; Angew. Chem. 2019, 131, 17457–17462;
- 3cY. Gong, G. Chen, Q. Peng, W. Z. Yuan, Y. Xie, S. Li, Y. Zhang, B. Z. Tang, Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 6195–6201;
- 3dC. J. Chen, R. J. Huang, A. S. Batsanov, P. Pander, Y. T. Hsu, Z. G. Chi, F. B. Dias, M. R. Bryce, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 16407–16411; Angew. Chem. 2018, 130, 16645–16649.
- 4
- 4aY. Lei, W. Dai, Z. Liu, S. Guo, Z. Cai, J. Shi, X. Zheng, J. Zhi, B. Tong, Y. Dong, Mater. Chem. Front. 2019, 3, 284–291;
- 4bY. Gong, L. Zhao, Q. Peng, D. Fan, W. Z. Yuan, Y. Zhang, B. Z. Tang, Chem. Sci. 2015, 6, 4438–4444.
- 5
- 5aY. Shoji, Y. Ikabata, Q. Wang, D. Nemoto, A. Sakamoto, N. Tanaka, J. Seino, H. Nakai, T. Fukushima, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 2728–2733;
- 5bZ. He, W. Zhao, J. W. Y. Lam, Q. Peng, H. Ma, G. Liang, Z. Shuai, B. Z. Tang, Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 416;
- 5cW. Zhao, T. S. Cheung, N. Jiang, W. Huang, J. W. Y. Lam, X. Zhang, Z. He, B. Z. Tang, Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1595.
- 6
- 6aJ. Wei, B. Liang, R. Duan, Z. Cheng, C. Li, T. Zhou, Y. Yi, Y. Wang, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 15589–15593; Angew. Chem. 2016, 128, 15818–15822;
- 6bM. S. Kwon, D. Lee, S. Seo, J. Jung, J. Kim, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 11177–11181; Angew. Chem. 2014, 126, 11359–11363;
- 6cD. Li, F. Lu, J. Wang, W. Hu, X. M. Cao, X. Ma, H. Tian, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 1916–1923;
- 6dZ. Y. Zhang, Y. Liu, Chem. Sci. 2019, 10, 7773–7778;
- 6eS. Hirata, K. Totani, J. Zhang, T. Yamashita, H. Kaji, S. R. Marder, T. Watanabe, C. Adachi, Adv. Funct. Mater. 2013, 23, 3386–3397;
- 6fY. Su, Y. Zhang, Z. Wang, W. Gao, P. Jia, D. Zhang, C. Yang, Y. Li, Y. Zhao, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 9967–9971; Angew. Chem. 2020, 132, 10053–10057;
- 6gZ. Wang, Y. Zhang, C. Wang, X. Zheng, Y. Zheng, L. Gao, C. Yang, Y. Li, L. Qu, Y. Zhao, Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 201907355;
- 6hY. X. Lei, W. B. Dai, Y. Tian, J. H. Yang, P. F. Li, J. B. Shi, B. Tong, Z. X. Cai, Y. P. Dong, J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2019, 10, 6019–6025.
- 7
- 7aX. Wang, H. L. Ma, M. X. Gu, C. Q. Lin, N. Gan, Z. L. Xie, H. Wang, L. F. Bian, L. S. Fu, S. Z. Cai, Z. G. Chi, W. Yao, Z. F. An, H. F. Shi, W. Huang, Chem. Mater. 2019, 31, 5584–5591;
- 7bQ. Mei, Z. Zhang, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 5602–5606; Angew. Chem. 2012, 124, 5700–5704;
- 7cC. Zhang, L. Yang, J. Zhao, B. Liu, M. Y. Han, Z. Zhang, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 11531–11535; Angew. Chem. 2015, 127, 11693–11697.
- 8S. M. A. Fateminia, Z. Mao, S. Xu, Z. Yang, Z. Chi, B. Liu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 12160–12164; Angew. Chem. 2017, 129, 12328–12332.
- 9
- 9aR. Kabe, C. Adachi, Nature 2017, 550, 384–387;
- 9bX. Zhang, L. Du, W. Zhao, Z. Zhao, Y. Xiong, X. He, P. F. Gao, P. Alam, C. Wang, Z. Li, J. Leng, J. Liu, C. Zhou, J. W. Y. Lam, D. L. Phillips, G. Zhang, B. Z. Tang, Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 5161;
- 9cZ. Lin, R. Kabe, N. Nishimura, K. Jinnai, C. Adachi, Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1803713.
- 10J. Xu, A. Takai, Y. Kobayashi, M. Takeuchi, Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 8447–8449.
- 11
- 11aH. Sun, Z. Hu, C. Zhong, X. Chen, Z. Sun, J. L. Brédas, J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2017, 8, 2393–2398;
- 11bH. Han, E. G. Kim, Chem. Mater. 2019, 31, 6925–6935;
- 11cB. L. Cotts, D. G. McCarthy, R. Noriega, S. B. Penwell, ACS Energy Lett. 2017, 2, 1526–1533.
- 12
- 12aX. Vries, P. Friederich, W. Wenzel, R. Coehoorn, P. A. Bobbert, Phys. Rev. B 2019, 99, 205201;
- 12bR. Gaoa, D. P. Yan, Chem. Sci. 2017, 8, 590–599;
- 12cK. Totani, Y. Okada, S. Hirata, M. Vacha, T. Watanabe, Adv. Opt. Mater. 2013, 1, 283–288;
- 12dX. P. Zhang, L. L. Du, W. J. Zhao, D. Phillips, G. Q. Zhang, B. Z. Tang, Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 5161.
- 13J. R. Lakowicz, Principles of Fluorescence Spectroscopy, Springer Science & Business Media, Cham, 2013.
- 14
- 14aJ. Zhang, S. Sulaiman, I. K. Madu, R. M. Laine, T. Goodson, J. Phys. Chem. C 2019, 123, 5048–5060;
- 14bA. Kushnarenko, E. Miloglyadov, M. Quack, G. Seyfang, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2018, 20, 10949–10959.
- 15
- 15aL. W. Barbour, M. Hegadorn, J. B. Asbury, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 15884–15894;
- 15bO. Varnavski, N. Abeyasinghe, J. Aragó, J. J. Serrano-Pérez, E. Ortí, J. T. López Navarrete, K. Takimiya, D. Casanova, J. Casado, T. Goodson, J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2015, 6, 1375–1384.
- 16
- 16aS. Erevelles, N. Fukawa, L. Swayne, J. Bus. Res. 2016, 69, 897–904;
- 16bX. Liu, Y. Wang, X. Li, Z. Yi, R. Deng, L. Liang, X. Xie, D. T. B. Loong, S. Song, D. Fan, A. H. All, H. Zhang, L. Huang, X. Liu, Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 899;
- 16cJ. F. Barrera, A. Mira, R. Torroba, Opt. Express 2013, 21, 5373–5378.