Synthesis of Chiral Aldehyde Catalysts by Pd-Catalyzed Atroposelective C−H Naphthylation
Gang Liao
Department of Chemistry, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, 310027 China
Search for more papers by this authorHao-Ming Chen
School of Chemical & Environmental Engineering, Wuyi University, Jiangmen, 529020 China
Search for more papers by this authorYu-Nong Xia
Department of Chemistry, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, 310027 China
Search for more papers by this authorBing Li
Department of Chemistry, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, 310027 China
Search for more papers by this authorQi-Jun Yao
Department of Chemistry, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, 310027 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. Bing-Feng Shi
Department of Chemistry, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, 310027 China
Search for more papers by this authorGang Liao
Department of Chemistry, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, 310027 China
Search for more papers by this authorHao-Ming Chen
School of Chemical & Environmental Engineering, Wuyi University, Jiangmen, 529020 China
Search for more papers by this authorYu-Nong Xia
Department of Chemistry, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, 310027 China
Search for more papers by this authorBing Li
Department of Chemistry, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, 310027 China
Search for more papers by this authorQi-Jun Yao
Department of Chemistry, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, 310027 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. Bing-Feng Shi
Department of Chemistry, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, 310027 China
Search for more papers by this authorGraphical Abstract
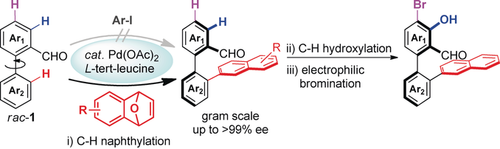
A concise synthetic route to chiral aldehyde catalysts with Pd-catalyzed atroposelective C−H naphthylation as a key reaction is reported. These chiral aldehyde catalysts were successfully employed as ligands in the asymmetric activation of glycine esters enabling a higher level of asymmetric induction and reaction activity. A wide range of enantioenriched biaryls were prepared in synthetically useful yields with excellent enantioselectivities (up to >99 % ee).
Abstract
Chiral aldehyde catalysis opens new avenues for the activation of simple amines. However, the lack of easy access to structurally diverse chiral aldehyde catalysts has hampered the development of this cutting-edge field. Herein, we report a Pd-catalyzed atroposelective C−H naphthylation with 7-oxabenzonorbornadienes for the preparation of axially chiral biaryls with excellent enantioselectivities (up to >99 % ee). This reaction is scalable and robust, which serves as a key step to provide a rapid access to axially chiral aldehyde catalysts through a three-step C−H functionalization sequence. These chiral aldehydes exhibit better activities and enantioselectivities than the previously reported organocatalysts in the asymmetric activation of glycine derived amides and dipeptides. Moreover, preliminary investigation also discloses that the aldehyde catalyst can effectively override the intrinsic facial selectivity of chiral dipeptide substrates, showcasing the strong chiral induction ability of this type of novel aldehyde catalysts.
Supporting Information
As a service to our authors and readers, this journal provides supporting information supplied by the authors. Such materials are peer reviewed and may be re-organized for online delivery, but are not copy-edited or typeset. Technical support issues arising from supporting information (other than missing files) should be addressed to the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| anie201906700-sup-0001-misc_information.pdf13.8 MB | Supplementary |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1
- 1aQ. Wang, Q. Gu, S.-L. You, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 6818;
- 1bJ. Chen, Y. E. Liu, X. Gong, L. Shi, B. Zhao, Chin. J. Chem. 2019, 37, 103;
- 1cL.-Z. Gong, Sci. China Chem. 2019, 62, 3;
- 1dS. Li, X.-Y. Chen, D. Enders, Chem. 2018, 4, 2026;
- 1eB.-J. Li, C. EI-Nachef, A. M. Beauchemin, Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 13192.
- 2
- 2aH. Kuzuhara, N. Watanabe, M. Ando, J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1987, 95;
- 2bJ. T. Koh, L. Delaude, R. Breslow, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1994, 116, 11234.
- 3
- 3aL. Shi, C. Tao, Q. Yang, Y. E. Liu, J. Chen, J. F. Chen, J. Tian, F. Liu, B. Li, Y. Du, B. Zhao, Org. Lett. 2015, 17, 5784;
- 3bJ. Chen, X. Gong, J. Li, Y. Li, J. Ma, C. Hou, G. Zhao, W. Yuan, B. Zhao, Science 2018, 360, 1438.
- 4
- 4aB. Xu, L.-L. Shi, Y.-Z. Zhang, Z.-J. Wu, L.-N. Fud, C.-Q. Luo, L.-X. Zhang, Y.-G. Peng, Q.-X. Guo, Chem. Sci. 2014, 5, 1988;
- 4bW. Wen, L. Chen, M.-J. Luo, Y. Zhang, Y.-C. Chen, Q. Ouyang, Q.-X. Guo, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 9774;
- 4cL. Chen, M.-J. Luo, F. Zhu, W. Wen, Q.-X. Guo, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 5159.
- 5For selected reviews, see:
- 5aM. C. Kozlowski, B. J. Morgan, E. C. Linton, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 3193;
- 5bJ. Clayden, W. J. Moran, P. J. Edwards, S. R. LaPlante, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 6398;
- 5cG. Bringmann, T. Gulder, T. A. M. Gulder, M. Breuning, Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 563;
- 5dS. R. LaPlante, P. J. Edwards, L. D. Fader, A. Jakalian, O. Hucke, ChemMedChem 2011, 6, 505.
- 6
- 6aR. Noyori, H. Takaya, Acc. Chem. Res. 1990, 23, 345;
- 6bY. Chen, S. Yekta, A. K. Yudin, Chem. Rev. 2003, 103, 3155;
- 6cP. Kočovský, Š. Vyskočil, M. Smrčina, Chem. Rev. 2003, 103, 3213;
- 6dJ. M. Brunel, Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, PR 1;
- 6eJ. Yu, F. Shi, L.-Z. Gong, Acc. Chem. Res. 2011, 44, 1156;
- 6f Privileged Chiral Ligands and Catalysts (Ed.: ), Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2011;
- 6gD. Parmar, E. Sugiono, S. Raja, M. Rueping, Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 9047;
- 6hC. Min, D. Seidel, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 5889.
- 7For recent reviews on the synthesis of axially chiral biaryls, see:
- 7aO. Baudoin, Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2005, 4223;
- 7bG. Bringmann, A. J. Price Mortimer, P. A. Keller, M. J. Gresser, J. Garner, M. Breuning, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 5384;
- 7cT. W. Wallace, Org. Biomol. Chem. 2006, 4, 3197;
- 7dJ. Wencel-Delord, A. Panossian, F. R. Leroux, F. Colobert, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 3418;
- 7eG. Ma, M. P. Sibi, Chem. Eur. J. 2015, 21, 11644;
- 7fB. Zilate, A. Castrogiovanni, C. Sparr, ACS Catal. 2018, 8, 2981;
- 7gY.-B. Wang, B. Tan, Acc. Chem. Res. 2018, 51, 534;
- 7hS. Zhang, G. Liao, B.-F. Shi, Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2019, https://doi.org/10.6023/cjoc201904030.
- 8For reviews on asymmetric C−H functionalization, see:
- 8aR. Giri, B.-F. Shi, K. M. Engle, N. Maugel, J.-Q. Yu, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 3242;
- 8bJ. Wencel-Delord, F. Colobert, Chem. Eur. J. 2013, 19, 14010;
- 8cC. Zheng, S.-L. You, RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 6173;
- 8dC. G. Newton, S.-G. Wang, C. C. Oliveira, N. Cramer, Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 8908;
- 8eD.-W. Gao, Q. Gu, C. Zheng, S.-L. You, Acc. Chem. Res. 2017, 50, 351;
- 8fT. G. Saint-Denis, R.-Y. Zhu, G. Chen, Q.-F. Wu, J.-Q. Yu, Science 2018, 359, 759;
- 8gQ. Zhang, B.-F. Shi, Chin. J. Chem. 2019, 37, 647.
- 9For selected examples of atroposelective C−H activation, see:
- 9aF. Kakiuchi, P. L. Gendre, A. Yamada, H. Ohtaki, S. Murai, Tetrahedron: Asymmetry 2000, 11, 2647;
- 9bJ. L. Gustafson, D. Lim, S. J. Miller, Science 2010, 328, 1251;
- 9cJ. Zheng, S.-L. You, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 13244;
- 9dD.-W. Gao, Q. Gu, S.-L. You, ACS Catal. 2014, 4, 2741;
- 9eC. K. Hazra, Q. Dherbassy, J. Wencel-Delord, F. Colobert, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 13871;
- 9fQ. Dherbassy, J.-P. Djukic, J. Wencel-Delord, F. Colobert, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 4668;
- 9gC. G. Newton, E. Braconi, J. Kuziola, M. D. Wodrich, N. Cramer, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 11040;
- 9hY.-S. Jang, Ł. Woźniak, J. Pedroni, N. Cramer, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 12901;
- 9iZ.-J. Jia, C. Merten, R. Gontla, C. G. Daniliuc, A. P. Antonchick, H. Waldmann, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 2429;
- 9jS.-X. Li, Y.-N. Ma, S.-D. Yang, Org. Lett. 2017, 19, 1842;
- 9kC. He, M. Hou, Z. Zhu, Z. Gu, ACS Catal. 2017, 7, 5316;
- 9lJ. Luo, T. Zhang, L. Wang, G. Liao, Q.-J. Yao, Y.-J. Wu, B.-B. Zhan, Y. Lan, X.-F. Lin, B.-F. Shi, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 6708.
- 10
- 10aM. S. F. Yang, K. Rauch, M. S. K. Kettelhoit, L. Ackermann, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 11285;
- 10bD. A. X.-Y. Chen, S. Ozturk, E. J. Sorensen, Org. Lett. 2017, 19, 6280;
- 10cFor a review, see: D. A. Alonso, C. Najera, I. M. Pastro, M. Yus, Chem. Eur. J. 2010, 16, 5274.
- 11P.-X. Ling, K. Chen, B.-F. Shi, Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 2166.
- 12
- 12aX.-H. Liu, H. Park, J.-H. Hu, Y. Hu, Q.-L. Zhang, B.-L. Wang, B. Sun, K.-S. Yeung, F.-L. Zhang, J.-Q. Yu, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 888;
- 12bD. Mu, G. He, G. Chen, Chem. Asian J. 2018, 13, 2423;
- 12cD.-Y. Wang, S.-H. Guo, G.-F. Pan, X.-Q. Zhu, Y.-R. Gao, Y.-Q. Wang, Org. Lett. 2018, 20, 1794;
- 12dM. Y. Zhang, R. A. Barrow, J. Org. Chem. 2018, 83, 6776.
- 13In the total synthesis of Boletopsin 11, Pd-catalyzed C−H arylation of benzaldehyde resulted in very low yield of interannular arylation product (3 %), see ref. [12d].
- 14
- 14aF.-L. Zhang, K. Hong, T.-J. Li, H. Park, J.-Q. Yu, Science 2016, 351, 252;
- 14bH. Park, P. Verma, K. Hong, J.-Q. Yu, Nat. Chem. 2018, 10, 755;
- 14cQ.-J. Yao, S. Zhang, B.-B. Zhan, B.-F. Shi, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 6617;
- 14dG. Liao, Q.-J. Yao, Z.-Z. Zhang, Y.-J. Wu, D.-Y. Huang, B.-F. Shi, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 3661;
- 14eG. Liao, B. Li, H.-M. Chen, Q.-J. Yao, Y.-N. Xia, J. Luo, B.-F. Shi, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 17151;
- 14fS. Zhang, Q.-J. Yao, G. Liao, X. Li, H. Li, H.-M. Chen, X. Hong, B.-F. Shi, ACS Catal. 2019, 9, 1956;
- 14gJ. Xu, Y. Liu, J. Zhang, X. Xu, Z. Jin, Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 689;
- 14hG. Li, J. Jiang, H. Xie, J. Wang, Chem. Eur. J. 2019, 25, 4688.
- 15Z. Qi, X. Li, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 8995.
- 16
- 16aF. Wang, S. Yu, X. Li, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 6462;
- 16bY. Unoh, T. Satoh, K. Hirano, M. Miura, ACS Catal. 2015, 5, 6634;
- 16cL. Kong, S. Yu, G. Tang, H. Wang, X. Zhou, X. Li, Org. Lett. 2016, 18, 3802;
- 16dK. Muralirajan, S. Prakash, C.-H. Cheng, Adv. Synth. Catal. 2017, 359, 513.
- 17Biaryl aldehydes 1 were prepared by Suzuki coupling of commercially available aryl bromides with arylboronic acids, see reference [14c–e] for details.
- 18Suitable crystals were selected for measurement on an Oxford diffraction Gemini A Ultra diffractometer with CuKa radiation (l=1.54178 c). CCDC 1882817 (3 e) and 1882815 (3 k) contain the supplementary crystallographic data for this paper. These data can be obtained free of charge from The Cambridge Crystallographic Data Centre.
- 19M. W. Giuliano, S. J. Miller, Top. Curr. Chem. 2016, 372, 157.