Lead-Free Halide Perovskite Nanocrystals: Crystal Structures, Synthesis, Stabilities, and Optical Properties
Qianqian Fan
College of Bioresources Chemical and Materials Engineering, Shaanxi University of Science & Technology, Xi'an, 710021 P. R. China
School of Materials Science and Engineering, Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta, GA, 30332 USA
These authors contributed equally.
Search for more papers by this authorGill V. Biesold-McGee
School of Materials Science and Engineering, Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta, GA, 30332 USA
These authors contributed equally.
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Jianzhong Ma
College of Bioresources Chemical and Materials Engineering, Shaanxi University of Science & Technology, Xi'an, 710021 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Qunna Xu
College of Bioresources Chemical and Materials Engineering, Shaanxi University of Science & Technology, Xi'an, 710021 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorShuang Pan
School of Materials Science and Engineering, Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta, GA, 30332 USA
State Key Laboratory of Molecular Engineering of Polymers, Department of Macromolecular Science, Fudan University, Shanghai, 200438 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Juan Peng
State Key Laboratory of Molecular Engineering of Polymers, Department of Macromolecular Science, Fudan University, Shanghai, 200438 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. Zhiqun Lin
School of Materials Science and Engineering, Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta, GA, 30332 USA
Search for more papers by this authorQianqian Fan
College of Bioresources Chemical and Materials Engineering, Shaanxi University of Science & Technology, Xi'an, 710021 P. R. China
School of Materials Science and Engineering, Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta, GA, 30332 USA
These authors contributed equally.
Search for more papers by this authorGill V. Biesold-McGee
School of Materials Science and Engineering, Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta, GA, 30332 USA
These authors contributed equally.
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Jianzhong Ma
College of Bioresources Chemical and Materials Engineering, Shaanxi University of Science & Technology, Xi'an, 710021 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Qunna Xu
College of Bioresources Chemical and Materials Engineering, Shaanxi University of Science & Technology, Xi'an, 710021 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorShuang Pan
School of Materials Science and Engineering, Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta, GA, 30332 USA
State Key Laboratory of Molecular Engineering of Polymers, Department of Macromolecular Science, Fudan University, Shanghai, 200438 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Juan Peng
State Key Laboratory of Molecular Engineering of Polymers, Department of Macromolecular Science, Fudan University, Shanghai, 200438 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. Zhiqun Lin
School of Materials Science and Engineering, Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta, GA, 30332 USA
Search for more papers by this authorGraphical Abstract
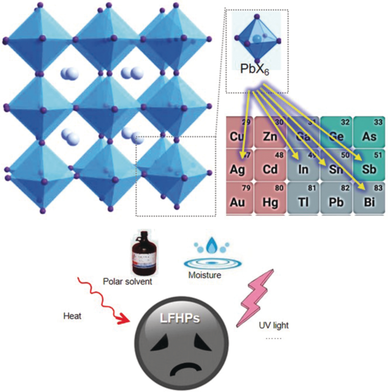
Taking the lead: This Review summarizes recent advances in widely studied lead-free halide perovskite nanocrystals, centering on understanding their crystal structures, synthesis methods, environmental stability, and optical properties. The challenges in this rapidly evolving field and opportunities to further improve the quality and stability of these nanocrystals are also provided.
Abstract
In recent years, there have been rapid advances in the synthesis of lead halide perovskite nanocrystals (NCs) for use in solar cells, light emitting diodes, lasers, and photodetectors. These compounds have a set of intriguing optical, excitonic, and charge transport properties, including outstanding photoluminescence quantum yield (PLQY) and tunable optical band gap. However, the necessary inclusion of lead, a toxic element, raises a critical concern for future commercial development. To address the toxicity issue, intense recent research effort has been devoted to developing lead-free halide perovskite (LFHP) NCs. In this Review, we present a comprehensive overview of currently explored LFHP NCs with an emphasis on their crystal structures, synthesis, optical properties, and environmental stabilities (e.g., UV, heat, and moisture resistance). In addition, strategies for enhancing optical properties and stabilities of LFHP NCs as well as the state-of-the-art applications are discussed. With the perspective of their properties and current challenges, we provide an outlook for future directions in this rapidly evolving field to achieve high-quality LFHP NCs for a broader range of fundamental research and practical applications.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- 1C. K. Møller, Nature 1958, 182, 1436.
- 2A. Poglitsch, D. Weber, J. Chem. Phys. 1987, 87, 6373.
- 3D. Weber, Z. Naturforsch. B 1978, 33, 1443.
- 4N. Onoda-Yamamuro, T. Matsuo, H. Suga, J. Phys. Chem. Solids 1992, 53, 935.
- 5G. C. Papavassiliou, I. B. Koutselas, Synth. Met. 1995, 71, 1713.
- 6W. J. Yin, T. Shi, Y. Yan, Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 4653.
- 7M. A. Green, A. Ho-Baillie, H. J. Snaith, Nat. Photonics 2014, 8, 506.
- 8A. Miyata, A. Mitioglu, P. Plochocka, O. Portugall, J. T.-W. Wang, S. D. Stranks, H. J. Snaith, R. J. Nicholas, Nat. Phys. 2015, 11, 582.
- 9D. Shi, V. Adinolfi, R. Comin, M. Yuan, E. Alarousu, A. Buin, Y. Chen, S. Hoogland, A. Rothenberger, K. Katsiev, Y. Losovyj, X. Zhang, P. A. Dowben, O. F. Mohammed, E. H. Sargent, O. M. Bakr, Science 2015, 347, 519.
- 10J. M. Ball, M. M. Lee, A. Hey, H. J. Snaith, Energy Environ. Sci. 2013, 6, 1739.
- 11D. Liu, T. L. Kelly, Nat. Photonics 2014, 8, 133.
- 12W. Nie, H. Tsai, R. Asadpour, J.-C. Blancon, A. J. Neukirch, G. Gupta, J. J. Crochet, M. Chhowalla, S. Tretiak, M. A. Alam, H.-L. Wang, A. D. Mohite, Science 2015, 347, 522.
- 13A. Kojima, K. Teshima, Y. Shirai, T. Miyasaka, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 6050.
- 14H.-S. Kim, C.-R. Lee, J.-H. Im, K.-B. Lee, T. Moehl, A. Marchioro, S.-J. Moon, R. Humphry-Baker, J.-H. Yum, J. E. Moser, M. Grätzel, N.-G. Park, Sci. Rep. 2012, 2, 591.
- 15M. M. Lee, J. Teuscher, T. Miyasaka, T. N. Murakami, H. J. Snaith, Science 2012, 338, 643.
- 16M. Liu, M. B. Johnston, H. J. Snaith, Nature 2013, 501, 395.
- 17G. Hodes, Science 2013, 342, 317.
- 18M. Saliba, T. Matsui, K. Domanski, J.-Y. Seo, A. Ummadisingu, S. M. Zakeeruddin, J.-P. Correa-Baena, W. R. Tress, A. Abate, A. Hagfeldt, M. Grätzel, Science 2016, 354, 206.
- 19N. J. Jeon, H. Na, E. H. Jung, T.-Y. Yang, Y. G. Lee, G. Kim, H.-W. Shin, S. I. Seok, J. Lee, J. Seo, Nat. Energy 2018, 3, 682.
- 20M. He, B. Li, X. Cui, B. Jiang, Y. He, Y. Chen, D. O'Neil, P. Szymanski, M. A. EI-Sayed, J. Huang, Z. Lin, Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 16045.
- 21M. Ye, C. He, X. Hong, X. Liu, J. Iocozzia, X. Cui, X. Meng, M. Rager, Z. Lin, X. Liu, J. Phys. D 2017, 50, 373002.
- 22M. He, X. Pang, X. Liu, B. Jiang, Y. He, H. Snaith, Z. Lin, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 4280; Angew. Chem. 2016, 128, 4352.
- 23M. He, D. Zheng, M. Wang, C. Lin, Z. Lin, J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 5994.
- 24X. Meng, X. Cui, M. Rager, S. Zhang, Z. Wang, J. Yu, Y. Harn, Z. Kang, B. K. Wagner, Y. Liu, C. Yu, J. Qiu, Z. Lin, Nano Energy 2018, 52, 123.
- 25Https://www.nrel.gov/pv/cell-efficiency.html.
- 26D. P. McMeekin, G. Sadoughi, W. Rehman, G. E. Eperon, M. Saliba, M. T. Hörantner, A. Haghighirad, N. Sakai, L. Korte, B. Rech, M. B. Johnston, L. M. Herz, H. J. Snaith, Science 2016, 351, 151.
- 27L. Wu, H. Hu, Y. Xu, S. Jiang, M. Chen, Q. Zhong, D. Yang, Q. Liu, Y. Zhao, B. Sun, Q. Zhang, Y. Yin, Nano Lett. 2017, 17, 5799.
- 28Y. Tong, E. Bladt, M. F. Aygüler, A. Manzi, K. Z. Milowska, V. A. Hintermayr, P. Docampo, S. Bals, A. S. Urban, L. Polavarapu, J. Feldmann, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 13887; Angew. Chem. 2016, 128, 14091.
- 29Y. Hassan, O. J. Ashton, J. H. Park, G. Li, N. Sakai, B. Wenger, A.-A. Haghighirad, N. K. Noel, M. H. Song, B. R. Lee, R. H. Friend, H. J. Snaith, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 1269.
- 30F. Zhang, H. Zhong, C. Chen, X. Wu, X. Hu, H. Huang, J. Han, B. Zou, Y. Dong, ACS Nano 2015, 9, 4533.
- 31L. Protesescu, S. Yakunin, M. I. Bodnarchuk, F. Krieg, R. Caputo, C. H. Hendon, R. X. Yang, A. Walsh, M. V. Kovalenko, Nano Lett. 2015, 15, 3692.
- 32Q. A. Akkerman, V. D′Innocenzo, S. Accornero, A. Scarpellini, A. Petrozza, M. Prato, L. Manna, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 10276.
- 33M. C. Brennan, J. Zinna, M. Kuno, ACS Energy Lett. 2017, 2, 1487.
- 34D. N. Dirin, L. Protesescu, D. Trummer, I. V. Kochetygov, S. Yakunin, F. Krumeich, N. P. Stadie, M. V. Kovalenko, Nano Lett. 2016, 16, 5866.
- 35H. Huang, M. I. Bodnarchuk, S. V. Kershaw, M. V. Kovalenko, A. L. Rogach, ACS Energy Lett. 2017, 2, 2071.
- 36M. Pandey, K. W. Jacobsen, K. S. Thygesen, J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2016, 7, 4346.
- 37A. Swarnkar, A. R. Marshall, E. M. Sanehira, B. D. Chernomordik, D. T. Moore, J. A. Christians, T. Chakrabart, J. M. Luther, Science 2016, 354, 92.
- 38G. Li, F. W. R. Rivarola, N. J. L. K. Davis, S. Bai, T. C. Jellicoe, F. D. L. Peña, S. Hou, C. Ducati, F. Gao, R. H. Friend, N. C. Greenham, Z.-K. Tan, Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 3528.
- 39X. Zhang, H. Lin, H. Huang, C. Reckmeier, Y. Zhang, W. C. H. Choy, A. L. Rogach, Nano Lett. 2016, 16, 1415.
- 40J.-H. Im, C.-R. Lee, J.-W. Lee, S.-W. Park, N.-G. Park, Nanoscale 2011, 3, 4088.
- 41P. Ramasamy, D.-H. Lim, B. Kim, S.-H. Lee, M.-S. Leeb, J.-S. Lee, Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 2067.
- 42F. Giustino, H. J. Snaith, ACS Energy Lett. 2016, 1, 1233.
- 43S. F. Hoefler, G. Trimmel, T. Rath, Monatsh. Chem. 2017, 148, 795.
- 44S. Chatterjee, A. J. Pal, J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 3793.
- 45S. Yang, W. Fu, Z. Zhang, H. Chen, C.-Z. Li, J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 11462.
- 46C. Zhang, L. Gao, S. Hayase, T. Ma, Chem. Lett. 2017, 46, 1276.
- 47M. Lyu, J. H. Yun, P. Chen, M. Hao, L. Wang, Adv. Energy Mater. 2017, 7, 1602512.
- 48H. Hu, B. Dong, W. Zhang, J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 11436.
- 49J. Sun, J. Yang, J. I. Lee, J. H. Cho, M. S. Kang, J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2018, 9, 1573.
- 50S. Ghosh, B. Pradhan, ChemNanoMat 2019, 5, 300.
10.1002/cnma.201800645 Google Scholar
- 51S. Khalfin, Y. Bekenstein, Nanoscale 2019, https://doi.org/10.1039/C9NR01031A.
- 52W. Ke, C. C. Stoumpos, M. Zhu, L. Mao, I. Spanopoulos, J. Liu, O. Y. Kontsevoi, M. Chen, D. Sarma, Y. Zhang, M. R. Wasielewski, M. G. Kanatzidis, Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1701293.
- 53M. V. Kovalenko, L. Protesescu, M. I. Bodnarchuk, Science 2017, 358, 745.
- 54T. C. Jellicoe, J. M. Richter, H. F. J. Glass, M. Tabachnyk, R. Brady, S. E. Dutton, A. Rao, R. H. Friend, D. Credgington, N. C. Greenham, M. L. Böhm, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 2941.
- 55D. E. Scaife, P. F. Weller, W. G. Fisher, J. Solid State Chem. 1974, 9, 308.
- 56L.-J. Chen, C.-R. Lee, Y.-J. Chuang, Z.-H. Wu, C. Chen, J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2016, 7, 5028.
- 57J. Xi, Z. Wu, B. Jiao, H. Dong, C. Ran, C. Piao, T. Lei, T.-B. Song, W. Ke, T. Yokoyama, X. Hou, M. G. Kanatzidis, Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1606964.
- 58F. Hao, C. C. Stoumpos, D. H. Cao, R. P. H. Chang, M. G. Kanatzidis, Nat. Photonics 2014, 8, 489.
- 59Z. Tan, J. Li, C. Zhang, Z. Li, Q. Hu, Z. Xiao, T. Kamiya, H. Hosono, G. Niu, E. Lifshitz, Y. Cheng, J. Tang, Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1801131.
- 60X. Wu, W. Song, Q. Li, X. Zhao, D. He, Z. Quan, Chem. Asian J. 2018, 13, 1654.
- 61D.-K. Seo, N. Gupta, M.-H. Whangbo, Inorg. Chem. 1998, 37, 407.
- 62T. Krishnamoorthy, H. Ding, C. Yan, W. L. Leong, T. Baikie, Z. Zhang, M. Sherburne, S. Li, M. Asta, N. Mathews, S. G. Mhaisalkar, J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 23829.
- 63B. Saparov, F. Hong, J.-P. Sun, H.-S. Duan, W. Meng, S. Cameron, I. G. Hill, Y. Yan, D. B. Mitzi, Chem. Mater. 2015, 27, 5622.
- 64J. Pal, S. Manna, A. Mondal, S. Das, K. V. Adarsh, A. Nag, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 14187; Angew. Chem. 2017, 129, 14375.
- 65F. Jiang, D. Yang, Y. Jiang, T. Liu, X. Zhao, Y. Ming, B. Luo, F. Qin, J. Fan, H. Han, L. Zhang, Y. Zhou, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 1019.
- 66T. Singh, A. Kulkarni, M. Ikegami, T. Miyasaka, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 14542.
- 67C. Zuo, L. Ding, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 6528; Angew. Chem. 2017, 129, 6628.
- 68A. J. Lehner, D. H. Fabini, H. A. Evans, C.-A. Hébert, S. R. Smock, J. Hu, H. Wang, J. W. Zwanziger, M. L. Chabinyc, R. Seshadri, Chem. Mater. 2015, 27, 7137.
- 69J. Pal, A. Bhunia, S. Chakraborty, S. Manna, S. Das, A. Dewan, S. Datta, A. Nag, J. Phys. Chem. C 2018, 122, 10643.
- 70S. Sun, S. Tominaka, J.-H. Lee, F. Xie, P. D. Bristowe, A. K. Cheetham, APL Mater. 2016, 4, 031101.
- 71B.-W. Park, B. Philippe, X. Zhang, H. Rensmo, G. Boschloo, E. M. J. Johansson, Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 6806.
- 72R. D. Nelson, K. Santra, Y. Wang, A. Hadi, J. W. Petrichbc, M. G. Panthani, Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 3640.
- 73M. Leng, Y. Yang, Z. Chen, W. Gao, J. Zhang, G. Niu, D. Li, H. Song, J. Zhang, S. Jin, J. Tang, Nano Lett. 2018, 18, 6076.
- 74M. Leng, Y. Yang, K. Zeng, Z. Chen, Z. Tan, S. Li, J. Li, B. Xu, D. Li, M. P. Hautzinger, Y. Fu, T. Zhai, L. Xu, G. Niu, S. Jin, J. Tang, Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1704446.
- 75M.-Q. Li, Y.-Q. Hu, L.-Y. Bi, H.-L. Zhang, Y. Wang, Y.-Z. Zheng, Chem. Mater. 2017, 29, 5463.
- 76J. Zhang, Y. Yang, H. Deng, U. Farooq, X. Yang, J. Khan, J. Tang, H. Song, ACS Nano 2017, 11, 9294.
- 77B. Yang, J. Chen, S. Yang, F. Hong, L. Sun, P. Han, T. Pullerits, W. Deng, K. Han, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 5359; Angew. Chem. 2018, 130, 5457.
- 78A. H. Slavney, T. Hu, A. M. Lindenberg, H. I. Karunadasa, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 2138.
- 79F. Wei, Z. Deng, S. Sun, F. Zhang, D. M. Evans, G. Kieslich, S. Tominaka, M. A. Carpenter, J. Zhang, P. D. Bristowe, A. K. Cheetham, Chem. Mater. 2017, 29, 1089.
- 80B. Yang, F. Hong, J. Chen, Y. Tang, L. Yang, Y. Sang, X. Xia, J. Guo, H. He, S. Yang, W. Deng, K. Han, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 2278; Angew. Chem. 2019, 131, 2300.
- 81F. Locardi, M. Cirignano, D. Baranov, Z. Dang, M. Prato, F. Drago, M. Ferretti, V. Pinchetti, M. Fanciulli, S. Brovelli, L. De Trizio, L. Manna, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 12989.
- 82J. De Roo, M. Ibáñez, P. Geiregat, G. Nedelcu, W. Walravens, J. Maes, J. C. Martins, I. V. Driessche, M. V. Kovalenko, Z. Hens, ACS Nano 2016, 10, 2071.
- 83M. Kwoka, L. Ottaviano, M. Passacantando, S. Santucci, G. Czempik, J. Szuber, Thin Solid Films 2005, 490, 36.
- 84H. Xu, H. Yuan, J. Duan, Y. Zhao, Z. Jiao, Q. Tang, Electrochim. Acta 2018, 282, 807.
- 85L. N. Quan, M. Yuan, R. Comin, O. Voznyy, E. M. Beauregard, S. Hoogland, A. Buin, A. R. Kirmani, K. Zhao, A. Amassian, D. H. Kim, E. H. Sargent, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 2649.
- 86H. Tsai, W. Nie, J.-C. Blancon, C. C. Stoumpos, R. Asadpour, B. Harutyunyan, A. J. Neukirch, R. Verduzco, J. J. Crochet, S. Tretiak, L. Pedesseau, J. Even, M. A. Alam, G. Gupta, J. Lou, P. M. Ajayan, M. J. Bedzyk, M. G. Kanatzidis, A. D. Mohite, Nature 2016, 536, 312.
- 87M. C. Weidman, M. Seitz, S. D. Stranks, W. A. Tisdale, ACS Nano 2016, 10, 7830.
- 88M. C. Weidman, A. J. Goodman, W. A. Tisdale, Chem. Mater. 2017, 29, 5019.
- 89A. B. Wong, Y. Bekenstein, J. Kang, C. S. Kley, D. Kim, N. A. Gibson, D. Zhang, Y. Yu, S. R. Leone, L.-W. Wang, A. P. Alivisatos, P. Yang, Nano lett. 2018, 18, 2060.
- 90A. G. Kontos, A. Kaltzoglou, E. Siranidi, D. Palles, G. K. Angeli, M. K. Arfanis, V. Psychari, Y. S. Raptis, E. I. Kamitsos, P. N. Trikalitis, C. C. Stoumpos, M. G. Kanatzidis, P. Falaras, Inorg. Chem. 2017, 56, 84.
- 91S. Gupta, T. Bendikov, G. Hodes, D. Cahen, ACS Energy Lett. 2016, 1, 1028.
- 92M.-Y. Chen, J.-T. Lin, C.-S. Hsu, C.-K. Chang, C.-W. Chiu, H. M. Chen, P.-T. Chou, Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1706592.
- 93A. Wang, Y. Guo, F. Muhammad, Z. Deng, Chem. Mater. 2017, 29, 6493.
- 94G. Xing, M. H. Kumar, W. K. Chong, X. Liu, Y. Cai, H. Ding, M. Asta, M. Grätzel, S. Mhaisalkar, N. Mathews, T. C. Sum, Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 8191.
- 95T. M. Koh, T. Krishnamoorthy, N. Yantara, C. Shi, W. L. Leong, P. P. Boix, A. C. Grimsdale, S. G. Mhaisalkar, N. Mathews, J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 14996.
- 96A. Wang, X. Yan, M. Zhang, S. Sun, M. Yang, W. Shen, X. Pan, P. Wang, Z. Deng, Chem. Mater. 2016, 28, 8132.
- 97D. S. Dolzhnikov, C. Wang, Y. Xu, M. G. Kanatzidis, E. A. Weiss, Chem. Mater. 2017, 29, 7901.
- 98D. V. Talapin, J.-S. Lee, M. V. Kovalenko, E. V. Shevchenko, Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 389.
- 99A. T. Fafarman, W.-K. Koh, B. T. Diroll, D. K. Kim, D.-K. Ko, S. J. Oh, X. Ye, V. Doan-Nguyen, M. R. Crump, D. C. Reifsnyder, C. B. Murray, C. R. Kagan, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 15753.
- 100D. M. Balazs, D. N. Dirin, H.-H. Fang, L. Protesescu, G. H. T. Brink, B. J. Kooi, M. V. Kovalenko, M. A. Loi, ACS Nano 2015, 9, 11951.
- 101H. Katagiri, K. Saitoh, T. Washio, H. Shinohara, T. Kurumadani, S. Miyajima, Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2001, 65, 141.
- 102S. Ghosh, S. Paul, S. K. De, Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 2018, 35, 1800199.
- 103R. Begum, M. R. Parida, A. L. Abdelhady, B. Murali, N. M. Alyami, G. H. Ahmed, M. N. Hedhili, O. M. Bakr, O. F. Mohammed, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 731.
- 104W. van der Stam, J. J. Geuchies, T. Altantzis, K. H. W. V. D. Bos, J. D. Meeldijk, S. V. Aert, S. Bals, D. Vanmaekelbergh, C. D. M. Donega, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 4087.
- 105H. Liu, Z. Wu, J. Shao, D. Yao, H. Gao, Y. Liu, W. Yu, H. Zhang, B. Yang, ACS Nano 2017, 11, 2239.
- 106M. Leng, Z. Chen, Y. Yang, Z. Li, K. Zeng, K. Li, G. Niu, Y. He, Q. Zhou, J. Tang, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 15012; Angew. Chem. 2016, 128, 15236.
- 107B. Yang, J. Chen, F. Hong, X. Mao, K. Zheng, S. Yang, Y. Li, T. Pullerits, W. Deng, K. Han, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 12471; Angew. Chem. 2017, 129, 12645.
- 108Y. Lou, M. Fang, J. Chen, Y. Zhao, Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 3779.
- 109M. Gao, C. Zhang, L. Lian, J. Guo, Y. Xia, F. Pan, X. Su, J. Zhang, H. Li, D. Zhang, J. Mater. Chem. C 2019, 7, 3688.
- 110J.-L. Xie, Z.-Q. Huang, B. Wang, W.-J. Chen, W.-X. Lu, X. Liu, J.-L. Song, Nanoscale 2019, 11, 6719.
- 111C. Carrillo-Carrión, S. Cárdenas, B. M. Simonet, M. Valcárcel, Chem. Commun. 2009, 5214.
- 112B. Pradhan, G. S. Kumar, S. Sain, A. Dalui, U. K. Ghorai, S. K. Pradhan, S. Acharya, Chem. Mater. 2018, 30, 2135.
- 113L. Zhou, Y.-F. Xu, B.-X. Chen, D.-B. Kuang, C.-Y. Su, Small 2018, 14, 1703762.
- 114S. E. Creutz, E. N. Crites, M. C. D. Siena, D. R. Gamelin, Nano Lett. 2018, 18, 1118.
- 115B. Yang, X. Mao, F. Hong, W. Meng, Y. Tang, X. Xia, S. Yang, W. Deng, K. Han, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 17001.
- 116M. R. Filip, X. Liu, A. Miglio, G. Hautier, F. Giustino, J. Phys. Chem. C 2018, 122, 158.
- 117R. T. Shannon, Acta Crystallogr. Sect. A 1976, 32, 751.
10.1107/S0567739476001551 Google Scholar
- 118L. Zhou, J.-F. Liao, Z.-Gu. Huang, X.-D. Wang, Y.-F. Xu, H.-Y. Chen, D.-B. Kuang, C.-Y. Su, ACS Energy Lett. 2018, 3, 2613.
- 119P. Yang, G. Liu, B. Liu, X. Liu, Y. Lou, J. Chen, Y. Zhao, Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 11638.
- 120J. Shamsi, A. S. Urban, M. Imran, L. D. Trizio, L. Manna, Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 3296.
- 121Q. Chen, N. D. Marco, Y. (M.) Yang, T.-B. Song, C.-C. Chen, H. Zhao, Z. Hong, H. Zhou, Y. Yang, Nano Today 2015, 10, 355.
- 122N. K. Noel, S. D. Stranks, A. Abate, C. Wehrenfennig, S. Guarnera, A.-A. Haghighirad, A. Sadhanala, G. E. Eperon, S. K. Pathak, M. B. Johnston, A. Petrozza, L. M. Herz, H. J. Snaith, Energy Environ. Sci. 2014, 7, 3061.
- 123Y. Zhang, J. Yin, M. R. Parida, G. H. Ahmed, J. Pan, O. M. Bakr, J.-L. Bredas, O. F. Mohammed, J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2017, 8, 3173.
- 124K. Xu, A. Meijerink, Chem. Mater. 2018, 30, 5346.
- 125S. Hou, Y. Guo, Y. Tang, Q. Quan, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 18417.
- 126Y. Chang, Y. Yoon, G. Li, E. Xu, S. Yu, C. Lu, Z. Wang, Y. He, C. Lin, B. K. Wagner, V. V. Tsukruk, Z. Kang, N. Thadhani, Y. Jiang, Z. Lin, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 37267.
- 127Q. Fan, J. Ma, Q. Xu, J. Wang, Y. Ma, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2018, 57, 6171.
- 128Y. Zhang, M. Wang, Y. Zheng, H. Tan, B. Y. Hsu, Z. Yang, S. Y. Wong, A. Y. Chang, M. Choolani, X. Li, J. Wang, Chem. Mater. 2013, 25, 2976.
- 129S. Huang, Z. Li, L. Kong, N. Zhu, A. Shan, L. Li, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 5749.