Activation of Prodrugs by NIR-Triggered Release of Exogenous Enzymes for Locoregional Chemo-photothermal Therapy
Li Cheng
State Key Laboratory of Chemical Resource Engineering, Beijing University of Chemical Technology, Beijing, 100029 P. R. China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorFengrong Zhang
State Key Laboratory of Chemical Resource Engineering, Beijing University of Chemical Technology, Beijing, 100029 P. R. China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorShunhao Wang
State Key Laboratory of Chemical Resource Engineering, Beijing University of Chemical Technology, Beijing, 100029 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorXueting Pan
State Key Laboratory of Chemical Resource Engineering, Beijing University of Chemical Technology, Beijing, 100029 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorSichong Han
State Key Laboratory of Chemical Resource Engineering, Beijing University of Chemical Technology, Beijing, 100029 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorShuang Liu
State Key Laboratory of Chemical Resource Engineering, Beijing University of Chemical Technology, Beijing, 100029 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorJunjie Ma
State Key Laboratory of Chemical Resource Engineering, Beijing University of Chemical Technology, Beijing, 100029 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorHongyu Wang
State Key Laboratory of Chemical Resource Engineering, Beijing University of Chemical Technology, Beijing, 100029 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Heyun Shen
State Key Laboratory of Chemical Resource Engineering, Beijing University of Chemical Technology, Beijing, 100029 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Huiyu Liu
State Key Laboratory of Chemical Resource Engineering, Beijing University of Chemical Technology, Beijing, 100029 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Qipeng Yuan
State Key Laboratory of Chemical Resource Engineering, Beijing University of Chemical Technology, Beijing, 100029 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorLi Cheng
State Key Laboratory of Chemical Resource Engineering, Beijing University of Chemical Technology, Beijing, 100029 P. R. China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorFengrong Zhang
State Key Laboratory of Chemical Resource Engineering, Beijing University of Chemical Technology, Beijing, 100029 P. R. China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorShunhao Wang
State Key Laboratory of Chemical Resource Engineering, Beijing University of Chemical Technology, Beijing, 100029 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorXueting Pan
State Key Laboratory of Chemical Resource Engineering, Beijing University of Chemical Technology, Beijing, 100029 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorSichong Han
State Key Laboratory of Chemical Resource Engineering, Beijing University of Chemical Technology, Beijing, 100029 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorShuang Liu
State Key Laboratory of Chemical Resource Engineering, Beijing University of Chemical Technology, Beijing, 100029 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorJunjie Ma
State Key Laboratory of Chemical Resource Engineering, Beijing University of Chemical Technology, Beijing, 100029 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorHongyu Wang
State Key Laboratory of Chemical Resource Engineering, Beijing University of Chemical Technology, Beijing, 100029 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Heyun Shen
State Key Laboratory of Chemical Resource Engineering, Beijing University of Chemical Technology, Beijing, 100029 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Huiyu Liu
State Key Laboratory of Chemical Resource Engineering, Beijing University of Chemical Technology, Beijing, 100029 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Qipeng Yuan
State Key Laboratory of Chemical Resource Engineering, Beijing University of Chemical Technology, Beijing, 100029 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorGraphical Abstract
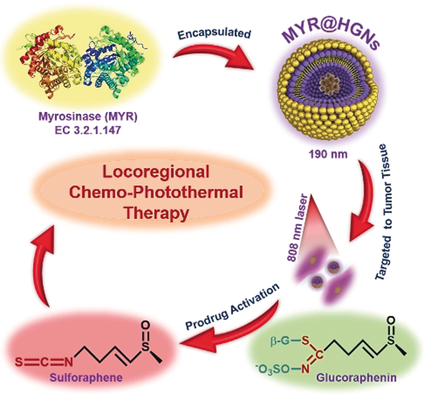
Exogenous myrosinase was encapsulated inside photoresponsive honeycomb-gold nanoparticles to mask enzyme activity and target tumor tissues. Near-infrared light was used to trigger the release of myrosinase, which catalyzed the conversion of nontoxic glucoraphenin to therapeutic sulforaphene at the tumor sites to achieve locoregional chemo-photothermal therapy.
Abstract
Enzymes have been used to direct the conversion of prodrugs in cancer therapy. However, non-specific distribution of endogenous enzymes seriously hinders their bioapplications. Herein, we developed a near-infrared-triggered locoregional chemo-photothermal therapy based on the exogenous enzyme delivery and remolded tumor mivroenvironment. The catalytic efficiency of enzymes was enhanced by the hyperthermia, and the therapeutic efficacy of photothermal therapy (PTT) was improved owing to the inhibition of heat shock protein 90 by chemotherapeutics. The locoregional chemo-phototherapy achieved a one-time successful cure in 4T1 tumor-bearing mice model. Thus, a mutually reinforcing feedback loop between PTT and chemotherapy can be initiated by the irradiation, which holds a promising future in cancer therapy.
Supporting Information
As a service to our authors and readers, this journal provides supporting information supplied by the authors. Such materials are peer reviewed and may be re-organized for online delivery, but are not copy-edited or typeset. Technical support issues arising from supporting information (other than missing files) should be addressed to the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| anie201902476-sup-0001-misc_information.pdf1.7 MB | Supplementary |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1
- 1aN. Wang, Z. Wang, Z. Xu, X. Chen, G. Zhu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 3426–3430; Angew. Chem. 2018, 130, 3484–3488;
- 1bX. Li, Y. Hou, X. Meng, C. Ge, H. Ma, J. Li, J. Fang, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 6141–6145; Angew. Chem. 2018, 130, 6249–6253;
- 1cS. Bakthavatsalam, M. L. Sleeper, A. Dharani, D. J. George, T. Zhang, K. J. Franz, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 12780–12784; Angew. Chem. 2018, 130, 12962–12966.
- 2C. Ansari, G. A. Tikhomirov, S. H. Hong, R. A. Falconer, P. M. Loadman, J. H. Gill, R. Castaneda, F. K. Hazard, L. Tong, O. D. Lenkov, D. W. Felsher, J. Rao, H. E. Daldrup-Link, Small 2014, 10, 566–575.
- 3X. Jia, Y. Zhang, Y. Zou, Y. Wang, D. Niu, Q. He, Z. Huang, W. Zhu, H. Tian, J. Shi, Y. Li, Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1704490.
- 4P.-A. Burnouf, Y.-L. Leu, Y.-C. Su, K. Wu, W.-C. Lin, S. R. Roffler, Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1843.
- 5
- 5aM. Huo, L. Wang, Y. Chen, J. Shi, Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 357;
- 5bR. Walther, J. Rautio, A. N. Zelikin, Adv. Drug Delivery Rev. 2017, 118, 65–78.
- 6
- 6aC. Li, P. T. Winnard, T. Takagi, D. Artemov, Z. M. Bhujwalla, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 15072–15073;
- 6bJ. Hou, Y. Pan, D. Zhu, Y. Fan, G. Feng, Y. Wei, H. Wang, K. Qin, T. Zhao, Q. Yang, Y. Zhu, Y. Liu, J. Chen, D. Kong, P. G. Wang, Q. Zhao, Nat. Chem. Biol. 2019, 15, 151.
- 7
- 7aR. S. Salvat, D. Verma, A. S. Parker, J. R. Kirsch, S. A. Brooks, C. Bailey-Kellogg, K. E. Griswold, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E 5085–E5093;
- 7bP. Holliger, P. J. Hudson, Nat. Biotechnol. 2005, 23, 1126.
- 8X. Lian, Y. Huang, Y. Zhu, Y. Fang, R. Zhao, E. Joseph, J. Li, J.-P. Pellois, H.-C. Zhou, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 5725–5730; Angew. Chem. 2018, 130, 5827–5832.
- 9
- 9aS. Kartha, L. Yan, C. L. Weisshaar, M. E. Ita, V. V. Shuvaev, V. R. Muzykantov, A. Tsourkas, B. A. Winkelstein, Z. Cheng, Adv. Healthcare Mater. 2017, 6, 1700500;
- 9bY. Anraku, A. Kishimura, M. Kamiya, S. Tanaka, T. Nomoto, K. Toh, Y. Matsumoto, S. Fukushima, D. Sueyoshi, M. R. Kano, Y. Urano, N. Nishiyama, K. Kataoka, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 560–565; Angew. Chem. 2016, 128, 570–575.
- 10
- 10aB.-Y. Hung, Y. Kuthati, R. K. Kankala, S. Kankala, J.-P. Deng, C.-L. Liu, C.-H. Lee, Nanomaterials 2015, 5, 2169–2191;
- 10bW. Wang, N. S. R. Satyavolu, Z. Wu, J.-R. Zhang, J.-J. Zhu, Y. Lu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 6798–6802; Angew. Chem. 2017, 129, 6902–6906.
- 11
- 11aX.-Q. Wang, F. Gao, X.-Z. Zhang, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 9029–9033; Angew. Chem. 2017, 129, 9157–9161;
- 11bJ. Song, P. Huang, X. Chen, Nat. Protoc. 2016, 11, 2287–2299;
- 11cC. Liu, S. Zhang, J. Li, J. Wei, K. Müllen, M. Yin, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 1638–1642; Angew. Chem. 2019, 131, 1652–1656.
- 12
- 12aW. Tao, X. Ji, X. Xu, M. A. Islam, Z. Li, S. Chen, P. E. Saw, H. Zhang, Z. Bharwani, Z. Guo, J. Shi, O. C. Farokhzad, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 11896–11900; Angew. Chem. 2017, 129, 12058–12062;
- 12bY. Chen, L. Cheng, Z. Dong, Y. Chao, H. Lei, H. Zhao, J. Wang, Z. Liu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 12991–12996; Angew. Chem. 2017, 129, 13171–13176;
- 12cY. Cheng, Y. Chang, Y. Feng, H. Jian, Z. Tang, H. Zhang, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 246–251; Angew. Chem. 2018, 130, 252–257.
- 13
- 13aB. Brachi, C. G. Meyer, R. Villoutreix, A. Platt, T. C. Morton, F. Roux, J. Bergelson, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 4032–4037;
- 13bC. Bao, M. C. Kim, J. Chen, J. Song, H. W. Ko, H. J. Lee, J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 5515–5524.
- 14F. Zhang, X. Han, Y. Hu, S. Wang, S. Liu, X. Pan, H. Wang, J. Ma, W. Wang, S. Li, Q. Wu, H. Shen, X. Yu, Q. Yuan, H. Liu, Adv. Sci. 2019, 6, 1801507.
- 15
- 15aL. Calzolai, F. Franchini, D. Gilliland, F. Rossi, Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 3101–3105;
- 15bL. Wang, X. Jiang, M. Zhang, M. Yang, Y.-N. Liu, Chem. Asian J. 2017, 12, 2374–2378.
- 16L. Li, C. Chen, H. Liu, C. Fu, L. Tan, S. Wang, S. Fu, X. Liu, X. Meng, H. Liu, Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 4252–4261.
- 17J. Ma, P. Li, W. Wang, S. Wang, X. Pan, F. Zhang, S. Li, S. Liu, H. Wang, G. Gao, B. Xu, Q. Yuan, H. Shen, H. Liu, ACS Nano 2018, 12, 9022–9032.
- 18J. Zeng, D. Goldfeld, Y. Xia, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 4169–4173; Angew. Chem. 2013, 125, 4263–4267.
- 19D. Kim, B. You, E.-K. Jo, S.-K. Han, M. I. Simon, S. J. Lee, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 14851–14856.
- 20
- 20aT. K. Hayes, N. F. Neel, C. Hu, P. Gautam, M. Chenard, B. Long, M. Aziz, M. Kassner, K. L. Bryant, M. Pierobon, R. Marayati, S. Kher, S. D. George, M. Xu, A. Wang-Gillam, A. A. Samatar, A. Matira, K. Wennerberg, E. F. Petricoin III, H. H. Yin, B. Nelkin, A. D. Cox, J. J. Yeh, C. J. Der, Cancer Cell 2016, 29, 75–89;
- 20bA. Brunet, A. Bonni, M. J. Zigmond, M. Z. Lin, P. Juo, L. S. Hu, M. J. Anderson, K. C. Arden, J. Blenis, M. E. Greenberg, Cell 1999, 96, 857–868.
- 21H. Luo, Q. Wang, Y. Deng, T. Yang, H. Ke, H. Yang, H. He, Z. Guo, D. Yu, H. Wu, H. Chen, Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27, 1702834.