Photochemical Conjugation and One-Pot Radiolabelling of Antibodies for Immuno-PET
Graphical Abstract
Abstract
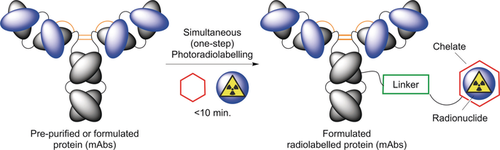
Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs), immunoglobulin fragments, and other proteins are important scaffolds in the development of radiopharmaceuticals for diagnostic immuno-positron emission tomography (immuno-PET) and targeted radioimmunotherapy (RIT). Conventional methods for radiolabelling proteins with metal ions such as 68Ga, 64Cu, 89Zr, and 90Y require multi-step procedures involving pre-purification, functionalisation with a chelate, and subsequent radiolabelling. Standard coupling chemistries are time-consuming, difficult to automate, and involve synthesis, isolation, and storage of an intermediate, new molecular entity (the conjugated mAb) whose biochemical properties can differ from those of the parent protein. To circumvent these issues, we developed a photoradiochemical approach that uses fast, chemoselective, light-induced protein modification under mild conditions with novel metal-ion-binding chelates derivatised with aryl azide (ArN3) groups. Experiments show that one-pot photochemical conjugation and radiolabelling of formulated mAbs can be achieved in <20 min.