A CuO Nanowire-Based Alternating Current Oxide Powder Electroluminescent Device with High Stability
Siwei Ma
Department of Material Science and Engineering, McMaster University, 1280 Main Street West, Hamilton, Ontario, L8S 4L8 Canada
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Zhilin Peng
Department of Engineering Physics, McMaster University, 1280 Main Street West, Hamilton, Ontario, L8S 4L8 Canada
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. Adrian H. Kitai
Department of Material Science and Engineering, McMaster University, 1280 Main Street West, Hamilton, Ontario, L8S 4L8 Canada
Department of Engineering Physics, McMaster University, 1280 Main Street West, Hamilton, Ontario, L8S 4L8 Canada
Search for more papers by this authorSiwei Ma
Department of Material Science and Engineering, McMaster University, 1280 Main Street West, Hamilton, Ontario, L8S 4L8 Canada
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Zhilin Peng
Department of Engineering Physics, McMaster University, 1280 Main Street West, Hamilton, Ontario, L8S 4L8 Canada
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. Adrian H. Kitai
Department of Material Science and Engineering, McMaster University, 1280 Main Street West, Hamilton, Ontario, L8S 4L8 Canada
Department of Engineering Physics, McMaster University, 1280 Main Street West, Hamilton, Ontario, L8S 4L8 Canada
Search for more papers by this authorGraphical Abstract
Abstract
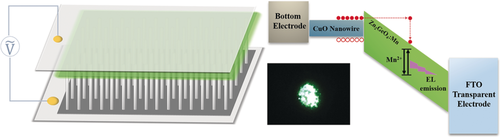
An AC-driven powder electroluminescent (EL) device has been achieved by constructing a CuO nanowire–Zn2GeO4:Mn phosphor heterogeneous junction. The CuO nanowires enhance the local electric field, resulting in electroluminescence of an oxide-based phosphor in EL devices owing to field injection at the nanowire tips. The CuO nanowire array was synthesized by an in situ thermal oxidation method at 400 °C in air and employed as an electric field enhancement layer in the EL device. The heterogeneous structures were created through drop coating of a phosphor suspension on the CuO nanowire array. The initial EL device tests show good luminescent performance with very promising brightness maintenance for over 360 h, with a loss of luminescent intensity of under 1 % at over 10 cd m−2 luminance. The fabrication method offers the prospect of simple, low-cost, large-scale EL devices with the potential to solve the limited operational lifetime of sulfide-based AC powder EL devices.
Supporting Information
As a service to our authors and readers, this journal provides supporting information supplied by the authors. Such materials are peer reviewed and may be re-organized for online delivery, but are not copy-edited or typeset. Technical support issues arising from supporting information (other than missing files) should be addressed to the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| anie201805519-sup-0001-misc_information.pdf1,004.5 KB | Supplementary |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1S. H. Cho, S. S. Jo, I. Hwang, J. Sung, J. Seo, S. H. Jung, I. Bae, J. R. Choi, H. Cho, T. Lee, J. K. Lee, T. W. Lee, C. Park, ACS Nano 2013, 7, 10809–10817.
- 2C. H. Yang, B. Chen, J. Zhou, Y. M. Chen, Z. Suo, Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 4480–4484.
- 3F. H. Wang, K. F. Chen, Y. H. Chien, C. C. Chang, M. Y. Chuang, J. Lumin. 2013, 141, 106–110.
- 4L. Wen, N. Liu, S. Wang, H. Zhang, W. Zhao, Z. Yang, Y. Wang, J. Su, L. Li, F. Long, Z. Zou, Y. Gao, Opt. Express 2016, 24, 23419–23428.
- 5J. Wang, C. Yan, G. Cai, M. Cui, A. L. S. Eh, P. S. Lee, Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 4490–4496.
- 6C. Schrage, S. Kaskel, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2009, 1, 1640–1644.
- 7Z. Wang, Y. Chen, P. Li, X. Hao, J. Liu, R. Huang, Y. Li, ACS Nano 2011, 5, 7149–7154.
- 8G. Liang, H. Hu, L. Liao, Y. He, C. Ye, Adv. Electron. Mater. 2017, 3, 1600535.
- 9J. Wang, C. Yan, K. J. Chee, P. S. Lee, Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 2876–2882.
- 10H. Takashima, K. Shimada, N. Miura, T. Katsumata, Y. Inaguma, K. Ueda, M. Itoh, Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 3699–3702.
- 11S. Ma, A. H. Kitai, J. Mater. Sci. 2017, 52, 9324–9334.
- 12M. Warkentin, F. Bridges, S. A. Carter, M. Anderson, Phys. Rev. B 2007, 75, 075301.
- 13A. G. Fischer, J. Electrochem. Soc. 1963, 110, 733–748.
- 14N. E. Grzeskowiak, J. F. Winkel, J. Electrochem. Soc. 2007, 154, J 289–J294.
- 15S. Medling, F. Bridges, S. A. Carter, J. Lumin. 2013, 134, 251–254.
- 16F. Chen, A. H. Kitai, Y. Xiang, J. Electrochem. Soc. 2009, 156, H 585–H587.
- 17K. Hirabayashi, H. Kozawaguchi, B. Tsujiyama, J. Electrochem. Soc. 1983, 130, 2259–2263.
- 18A. A. Bol, J. Ferwerda, J. A. Bergwerff, A. Meijerink, J. Electrochem. Soc. 2002, 99, 325–334.
- 19J. Stanley, Y. Jiang, F. Bridges, S. A. Carter, L. Ruhlen, J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2010, 22, 055301.
- 20N. E. Brese, C. L. Rohrer, G. S. Rohrer, Solid State Ionics 1999, 123, 19–24.
- 21G. Anoop, K. M. Krishna, M. K. Jayaraj, J. Electrochem. Soc. 2008, 155, J 7–J10.
- 22T. Minami, Y. Kuroi, T. Miyata, H. Yamada, S. Takata, J. Lumin. 1997, 72, 997–998.
- 23I. K. Jeong, H. L. Park, S. Mho, Solid State Commun. 1998, 108, 823–826.
- 24K. M. Krishna, G. Anoop, M. K. Jayaraj, J. Electrochem. Soc. 2007, 154, J 310–J313.
- 25K. H. Hsu, M. R. Yang, K. S. Chen, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 1998, 9, 283–288.
- 26L. C. Williams, D. Norton, J. Budai, P. H. Holloway, J. Electrochem. Soc. 2004, 151, H 188–H191.
- 27J. S. Lewis, P. H. Holloway, J. Electrochem. Soc. 2000, 147, 3148–3150.
- 28J. P. Bender, J. F. Wager, J. Kissick, B. L. Clark, D. A. Keszler, J. Lumin. 2002, 99, 311–324.
- 29T. Xiao, A. H. Kitai, G. Liu, Nakua, A. J. Barbier, Appl. Phys. Lett. 1998, 72, 3356–3358.
- 30X. Ouyang, A. H. Kitai, T. Xiao, J. Appl. Phys. 1996, 79, 3229–3234.
- 31X. Jiang, T. Herricks, Y. Xia, Nano Lett. 2002, 2, 1333–1338.
- 32M. L. Zhong, D. C. Zeng, Z. W. Liu, H. Y. Yu, X. C. Zhong, W. Q. Qiu, Acta Mater. 2010, 58, 5926–5932.
- 33J. Zhang, B. Wang, J. Zhou, R. Xia, Y. Chu, J. Huang, Materials 2017, 10, 72.
- 34R. Mohammadpour, H. Ahmadvand, I. A. Zad, Sens. Actuators A 2014, 216, 202–206.
- 35L. Liao, Z. Zhang, B. Yan, Z. Zheng, Q. L. Bao, T. Wu, C. M. Li, Z. X. Shen, J. X. Zhang, H. Gong, J. C. Li, T. Yu, Nanotechnology 2009, 20, 085203.
- 36P. Raksa, A. Gardchareon, T. Chairuangsri, P. Mangkorntong, N. Mangkorntong, S. Choopun, Ceram. Int. 2009, 35, 649–652.
- 37M. Farbod, N. M. Ghaffari, I. Kazeminezhad, Mater. Lett. 2012, 81, 258–260.
- 38H. T. Hsueh, T. J. Hsueh, S. J. Chang, F. Y. Hung, T. Y. Tsai, W. Y. Weng, C. L. Hsu, B. T. Dai, Sens. Actuators B 2011, 156, 906–911.
- 39J. Chen, K. Wang, L. Hartman, W. Zhou, J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 16017–16021.
- 40A. Kargar, Y. Jing, S. J. Kim, C. T. Riley, X. Pan, D. Wang, ACS Nano 2013, 7, 11112–11120.
- 41J. B. Reitz, E. I. Solomon, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1998, 120, 11467–11478.
- 42F. Lanza, R. Feduzi, J. Fuger, J. Mater. Res. 1990, 5, 1739–1744.
- 43P. Podhájecký, Z. Zábranský, P. Novák, Z. Dobiášová, R. Černý, V. Valvoda, Electrochim. Acta 1990, 35, 245–249.
- 44H. T. Hsueh, T. J. Hsueh, S. J. Chang, T. Y. Tsai, F. Y. Hung, S. P. Chang, W. Y. Weng, B. T. Dai, IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 2011, 10, 1161–1165.
- 45Q. Zhang, K. Zhang, D. Xu, G. Yang, H. Huang, F. Nie, C. Liu, S. Yang, Prog. Mater. Sci. 2014, 60, 208–337.
- 46P. Wang, X. Zhao, B. Li, Opt. Express 2011, 19, 11271–11279.
- 47J. B. Liang, N. Kishi, T. Soga, T. Jimbo, Appl. Surf. Sci. 2010, 257, 62–65.
- 48A. Li, H. Song, W. Wan, J. Zhou, X. Chen, Electrochim. Acta 2014, 132, 42–48.
- 49R. Mema, L. Yuan, Q. Du, Y. Wang, G. Zhou, Chem. Phys. Lett. 2011, 512, 87–91.
- 50B. Wagstaff, A. Kitai, J. Lumin. 2015, 167, 310–315.
- 51Y. Takahashi, M. Ando, R. Ihara, T. Fujiwara, Opt. Mater. Express 2011, 1, 372–378.