Graphene: A Cathode Material of Choice for Aluminum-Ion Batteries
Corresponding Author
Dr. Shyamal K. Das
Department of Physics, Tezpur University, Assam-, 784028 India
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Dr. Shyamal K. Das
Department of Physics, Tezpur University, Assam-, 784028 India
Search for more papers by this authorGraphical Abstract
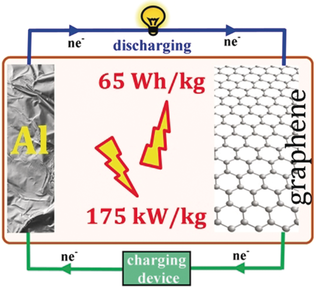
Superpower: The electrochemical coupling of an aluminum anode with a graphene cathode holds extraordinary promise in delivering the much sought after utility demands of ultrahigh power density, ultralong durability, enhanced safety, and flexibility. This Minireview deals with the accomplishments and challenges of Al–graphene batteries.
Abstract
The pairing of an aluminum anode with a cathode of high energy and power density determines the future of aluminum-ion battery technology. The question is—“Is there any suitable cathode material which is capable of storing sufficiently large amount of trivalent aluminum-ions at relatively higher operating potential?”. Graphene emerges to be a fitting answer. Graphene emerged in the research arena of aluminum-ion battery merely three years ago. However, research progress in this front has since been tremendous. Outperforming all other known cathode materials, several remarkable breakthroughs have been made with graphene, in offering extraordinary energy density, power density, cycle life, thermal stability, safety and flexibility. The future of the Al–graphene couple is indeed bright. This Minireview highlights the electrochemical performances, advantages and challenges of using graphene as the cathode in aluminum-ion batteries in conjugation with chloroaluminate based electrolytes. Additionally, the complex mechanism of charge storage in graphene is also elaborated.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- 1http://www.un.org/sustainabledevelopment/sustainable-development-goals/.
- 2https://energy.gov/science-innovation/clean-energy.
- 3https://ec.europa.eu/energy/en/topics/renewable-energy.
- 4http://www.ireda.in/.
- 5B. Dunn, H. Kamath, J. M. Tarascon, Science 2011, 334, 928–935.
- 6https://d-lab.mit.edu/news/improving-livelihoods-morocco-solar-light-field-evaluation.
- 7http://www.myclimate.org/carbon-offset-projects/projekt/ethiopia-solar-7124/.
- 8S. K. Das, S. Mahapatra, H. Lahan, J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 6347–6367.
- 9G. L. Holleck, J. Electrochem. Soc. 1972, 119, 1158–1161.
- 10N. Jayaprakash, S. K. Das, L. A. Archer, Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 12610–12612.
- 11M. C. Lin, M. Gong, B. Lu, Y. Wu, D. Y. Wang, M. Guan, M. Angell, C. Chen, J. Yang, B. J. Hwang, H. Dai, Nature 2015, 520, 324–328.
- 12W. Wang, B. Jiang, W. Xiong, H. Sun, Z. Lin, L. Hu, J. Tu, J. Hou, H. Zhu, S. Jiao, Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 3383–3388.
- 13S. Wang, Z. Yu, J. Tu, J. Wang, D. Tian, Y. Liu, S. Jiao, Adv. Energy Mater. 2016, 6, 1600137.
- 14N. S. Hudak, J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 5203–5215.
- 15L. D. Reed, S. N. Ortiz, M. Xiong, E. J. Menke, Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 14397–14400.
- 16N. P. Stadie, S. Wang, K. V. Kravchyk, M. V. Kovalenko, ACS Nano 2017, 11, 1911–1919.
- 17L. Geng, J. P. Scheifers, C. Fu, J. Zhang, B. P. T. Fokwa, J. Guo, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 21251–21257.
- 18K. S. Novoselov, A. K. Geim, S. V. Morozov, D. Jiang, Y. Zhang, S. V. Dubonos, I. V. Grigorieva, A. A. Firsov, Science 2004, 306, 666–669.
- 19K. S. Novoselov, D. Jiang, F. Schedin, T. J. Booth, V. V. Khotkevich, S. V. Morozov, A. K. Geim, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 10451–10453.
- 20F. Bonaccorso, Z. Sun, T. Hasan, A. C. Ferrari, Nat. Photonics 2010, 4, 611–622.
- 21W. Han, R. K. Kawakami, M. Gmitra, J. Fabian, Nat. Nanotechnol. 2014, 9, 794–807.
- 22N. M. Gabor, J. C. W. Song, Q. Ma, N. L. Nair, T. Taychatanapat, K. Watanabe, T. Taniguchi, L. S. Levitov, P. J. Herrero, Science 2011, 334, 648–652.
- 23M. Liu, X. Yin, E. U. Avila, B. Geng, T. Zentgraf, L. Ju, F. Wang, X. Zhang, Nature 2011, 474, 64–67.
- 24K. S. Kim, Y. Zhao, H. Jang, S. Y. Lee, J. M. Kim, K. S. Kim, J. H. Ahn, P. Kim, J. Y. Choi, B. H. Hong, Nature 2009, 457, 706–710.
- 25Y. B. Zhang, Y. W. Tan, H. L. Stormer, P. Kim, Nature 2005, 438, 201–204.
- 26R. Nair, P. Blake, A. Grigorenko, K. Novoselov, T. Booth, T. Stauber, N. Peres, A. Geim, Science 2008, 320, 1308–1310.
- 27A. A. Balandin, S. Ghosh, W. Z. Bao, I. Calizo, D. Teweldebrhan, F. Miao, C. N. Lau, Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 902–907.
- 28C. Lee, X. Wei, J. W. Kysar, J. Hone, Science 2008, 321, 385–388.
- 29A. Zurutuza, C. Marinelli, Nat. Nanotechnol. 2014, 9, 730–734.
- 30https://www.graphene-info.com/graphene-products.
- 31http://graphene-flagship.eu.
- 32R. Raccichini, A. Varzi, S. Passerini, B. Scrosati, Nat. Mater. 2015, 14, 271–279.
- 33Y. Dong, Z. S. Wu, W. Ren, H. M. Cheng, X. Bao, Sci. Bull. 2017, 62, 724–740.
- 34F. Bonaccorso, L. Colombo, G. Yu, M. Stoller, V. Tozzini, A. C. Ferrari, R. S. Ruoff, V. Pellegrini, Science 2015, 347, 1246501–1246509.
- 35W. Lv, Z. Li, Y. Deng, Q. H. Yang, F. Kang, Energy Storage Mater. 2016, 2, 107–138.
- 36H. Chen, H. Xu, S. Wang, T. Huang, J. Xi, S. Cai, F. Guo, Z. Xu, W. Gao, C. Gao, Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, eaao 7233.
- 37X. Yu, B. Wang, D. Gong, Z. Xu, B. Lu, Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1604118–1604126.
- 38P. R. Gifford, J. B. Palmisano, J. Electrochem. Soc. 1988, 135, 650–654.
- 39K. S. Mohandas, N. Sanil, M. Noel, P. Rodriguez, Carbon 2003, 41, 927–932.
- 40H. Sun, W. Wang, Z. Yu, Y. Yuan, S. Wang, S. Jiao, Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 11892–11895.
- 41S. Jiao, H. Lei, J. Tu, J. Zhu, J. Wang, X. Mao, Carbon 2016, 109, 276–281.
- 42Y. Wu, M. Gong, M. C. Lin, C. Yuan, M. Angell, L. Huang, D. Y. Wang, X. Zhang, J. Yang, B. J. Hwang, H. Dai, Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 9218–9222.
- 43L. Y. Zhang, L. Chen, H. Luo, X. F. Zhou, Z. P. Liu, Adv. Energy Mater. 2017, 7, 1700034–1700041.
- 44D. Y. Wang, C. Y. Wei, M. C. Lin, C. Pan, H. L. Chou, H. A. Chen, M. Gong, Y. Wu, C. Yuan, M. Angell, Y. J. Hsieh, Y. H. Chen, C. Y. Wen, C. W. Chen, B. J. Hwang, C. C. Chen, H. Dai, Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14283.
- 45S. C. Jung, Y. J. Kang, D. J. Yoo, J. W. Choi, Y. K. Han, J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 13384–13389.
- 46H. Chen, F. Guo, Y. Liu, T. Huang, B. Zheng, N. Ananth, Z. Xu, W. Gao, C. Gao, Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1605958–1605965.
- 47A. S. Childress, P. Parajuli, J. Zhu, R. Podila, A. M. Rao, Nano Energy 2017, 39, 69–76.
- 48H. Chen, C. Chen, Y. Liu, X. Zhao, N. Ananth, B. Zheng, L. Peng, T. Huang, W. Gao, C. Gao, Adv. Energy Mater. 2017, 7, 1700051–1700060.
- 49X. L. Zhao, W. Q. Yao, W. W. Gao, H. Chen, C. Gao, Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1701482–1701490.
- 50X. Huang, Y. Liu, H. Zhang, J. Zhang, O. Noonan, C. Yu, J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 19416–19421.
- 51G. Y. Yang, L. Chen, P. Jiang, Z. Y. Guo, W. Wang, Z. P. Liu, RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 47655–47660.
- 52M. Angell, C. J. Pan, Y. Rong, C. Yuan, M. C. Lin, B. J. Hwang, H. Dai, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 834–839.
- 53H. Jiao, C. Wang, J. Tu, D. Tian, S. Jiao, Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 2331–2334.
- 54C. J. Dymek, J. L. Williams, D. J. Groeger, J. J. Auborn, J. Electrochem. Soc. 1984, 131, 2887–2892.
- 55H. Wang, S. Gu, Y. Bai, S. Chen, N. Zhu, C. Wu, F. Wu, J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 22677–22686.
- 56T. Jiang, M. J. C. Brym, G. Dubé, A. Lasia, G. M. Brisard, Surf. Coatings Technol. 2006, 201, 1–9.
- 57G. A. Elia, I. Hasa, G. Greco, T. Diemant, K. Marquardt, K. Hoeppner, R. J. Behm, A. Hoell, S. Passerini, R. Hahn, J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 9682–9690.
- 58C. Sole, N. E. Drewett, L. J. Hardwick, Faraday Discuss. 2014, 172, 223–237.
- 59G. Schmuelling, T. Placke, R. Kloepsch, O. Fromm, H. W. Meyer, S. Passerini, M. Winter, J. Power Sources 2013, 239, 563–571.
- 60H. Kim, J. Hong, G. Yoon, H. Kim, K. Y. Park, M. S. Park, W. S. Yoon, K. Kang, Energy Environ. Sci. 2015, 8, 2963–2969.
- 61Y. Gao, C. Zhu, Z. Z. Chen, G. Lu, J. Phys. Chem. C 2017, 121, 7131–7138.
- 62K. V. Kravchyk, S. Wang, L. Piveteau, M. V. Kovalenko, Chem. Mater. 2017, 29, 4484–4492.
- 63M. S. Dresselhaus, G. Dresselhaus, Adv. Phys. 2002, 51, 1–186.
- 64L. Geng, G. Lv, X. Xing, J. Guo, Chem. Mater. 2015, 27, 4926–4929.
- 65S. Wang, S. Jiao, J. Wang, H. S. Chen, D. Tian, H. Lei, D. N. Fang, ACS Nano 2017, 11, 469–477.
- 66J. Jiang, H. Li, J. Huang, K. Li, J. Zeng, Y. Yang, J. Li, Y. Wang, J. Wang, J. Zhao, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 28486–28494.
- 67A. V. Mohammadi, A. Hadjikhani, S. Shahbazmohamadi, M. Beidaghi, ACS Nano 2017, 11, 11135–11144.
- 68L. D. Reed, E. Menke, J. Electrochem. Soc. 2013, 160, A 915–A917.
- 69M. Chen, R. C. Haddon, R. Yana, E. Bekyarova, Mater. Horiz. 2017, 4, 1054–1063.
- 70H. Chen, H. Xu, B. Zheng, S. Wang, T. Huang, F. Guo, W. Gao, C. Gao, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 22628–22634.
- 71P. Simon, Y. Gogotsi, B. Dunn, Science 2014, 343, 1210–1213.