A Titanium-Doped SiOx Passivation Layer for Greatly Enhanced Performance of a Hematite-Based Photoelectrochemical System
Dr. Hyo-Jin Ahn
Center for Multidimensional Carbon Materials, Institute for Basic Science IBS, Ulsan, 44919 Republic of Korea
School of Energy & Chemical Engineering, Low Dimensional Carbon Materials Center, UNIST, Ulsan, 44919 Republic of Korea
Search for more papers by this authorKi-Yong Yoon
Center for Multidimensional Carbon Materials, Institute for Basic Science IBS, Ulsan, 44919 Republic of Korea
School of Energy & Chemical Engineering, Low Dimensional Carbon Materials Center, UNIST, Ulsan, 44919 Republic of Korea
Search for more papers by this authorMyung-Jun Kwak
Center for Multidimensional Carbon Materials, Institute for Basic Science IBS, Ulsan, 44919 Republic of Korea
School of Energy & Chemical Engineering, Low Dimensional Carbon Materials Center, UNIST, Ulsan, 44919 Republic of Korea
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Ji-Hyun Jang
Center for Multidimensional Carbon Materials, Institute for Basic Science IBS, Ulsan, 44919 Republic of Korea
School of Energy & Chemical Engineering, Low Dimensional Carbon Materials Center, UNIST, Ulsan, 44919 Republic of Korea
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Hyo-Jin Ahn
Center for Multidimensional Carbon Materials, Institute for Basic Science IBS, Ulsan, 44919 Republic of Korea
School of Energy & Chemical Engineering, Low Dimensional Carbon Materials Center, UNIST, Ulsan, 44919 Republic of Korea
Search for more papers by this authorKi-Yong Yoon
Center for Multidimensional Carbon Materials, Institute for Basic Science IBS, Ulsan, 44919 Republic of Korea
School of Energy & Chemical Engineering, Low Dimensional Carbon Materials Center, UNIST, Ulsan, 44919 Republic of Korea
Search for more papers by this authorMyung-Jun Kwak
Center for Multidimensional Carbon Materials, Institute for Basic Science IBS, Ulsan, 44919 Republic of Korea
School of Energy & Chemical Engineering, Low Dimensional Carbon Materials Center, UNIST, Ulsan, 44919 Republic of Korea
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Ji-Hyun Jang
Center for Multidimensional Carbon Materials, Institute for Basic Science IBS, Ulsan, 44919 Republic of Korea
School of Energy & Chemical Engineering, Low Dimensional Carbon Materials Center, UNIST, Ulsan, 44919 Republic of Korea
Search for more papers by this authorGraphical Abstract
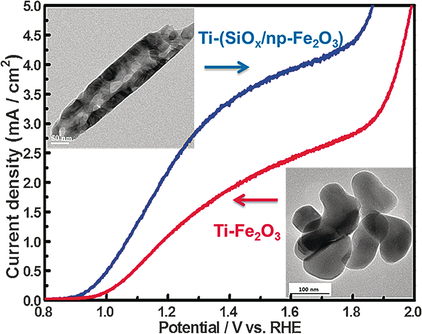
A nanoporous hematite with a Ti-doped SiOx layer (Ti-(SiOx/np-Fe2O3)) has a photocurrent density of 2.44 mA cm−2 at 1.23 VRHE and 3.70 mA cm−2 at 1.50 VRHE. This is due to a synergistic effect of decreased charge recombination, the increased number of active sites, and the reduced hole-diffusion pathway from the hematite to the electrolyte.
Abstract
This study introduces an in situ fabrication of nanoporous hematite with a Ti-doped SiOx passivation layer for a high-performance water-splitting system. The nanoporous hematite with a Ti-doped SiOx layer (Ti-(SiOx/np-Fe2O3)) has a photocurrent density of 2.44 mA cm−2 at 1.23 VRHE and 3.70 mA cm−2 at 1.50 VRHE. When a cobalt phosphate co-catalyst was applied to Ti-(SiOx/np-Fe2O3), the photocurrent density reached 3.19 mA cm−2 at 1.23 VRHE with stability, which shows great potential of the use of the Ti-doped SiOx layer with a synergistic effect of decreased charge recombination, the increased number of active sites, and the reduced hole-diffusion pathway from the hematite to the electrolyte.
Supporting Information
As a service to our authors and readers, this journal provides supporting information supplied by the authors. Such materials are peer reviewed and may be re-organized for online delivery, but are not copy-edited or typeset. Technical support issues arising from supporting information (other than missing files) should be addressed to the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| anie201603666-sup-0001-misc_information.pdf4.9 MB | Supplementary |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1S. Chu, A. Majumdar, Nature 2012, 488, 294–303.
- 2
- 2aJ. Y. Kim, G. Magesh, D. H. Youn, J.-W. Jang, J. Kubota, K. Domen, J. S. Lee, Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 2681;
- 2bA. Fujishima, K. Honda, Nature 1972, 238, 37–38.
- 3
- 3aN. Liu, C. Schneider, D. Freitag, M. Hartmann, U. Venkatesan, J. Müller, E. Spiecker, P. Schmuki, Nano Lett. 2014, 14, 3309–3313;
- 3bH. Chen, Z. Wei, K. Yan, Y. Bai, Z. Zhu, T. Zhang, S. Yang, Small 2014, 10, 4760–4769;
- 3cK.-Y. Yoon, H.-J. Ahn, M.-J. Kwak, P. Thiyagarajan, J.-H. Jang, Adv. Opt. Mater. 2015, 3, 907–912;
- 3dK. Sivula, F. Le Formal, M. Grätzel, ChemSusChem 2011, 4, 432–449;
- 3eY. Li, T. Takata, D. Cha, K. Takanabe, T. Minegishi, J. Kubota, K. Domen, Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 152–152;
- 3fH.-J. Ahn, M.-J. Kim, K. Kim, M.-J. Kwak, J.-H. Jang, Small 2014, 10, 2325–2330.
- 4O. Zandi, B. M. Klahr, T. W. Hamann, Energy Environ. Sci. 2013, 6, 634–642.
- 5
- 5aF. J. Morin, Phys. Rev. 1951, 83, 1005–1010;
- 5bJ. A. Glasscock, P. R. F. Barnes, I. C. Plumb, N. Savvides, J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 16477–16488;
- 5cM. Barroso, S. R. Pendlebury, A. J. Cowan, J. R. Durrant, Chem. Sci. 2013, 4, 2724–2734.
- 6
- 6aK.-Y. Yoon, J.-S. Lee, K. Kim, C. H. Bak, S.-I. Kim, J.-B. Kim, J.-H. Jang, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 22634–22639;
- 6bH.-J. Ahn, M.-J. Kwak, J.-S. Lee, K.-Y. Yoon, J.-H. Jang, J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 19999–20003.
- 7L. Xi, S. Y. Chiam, W. F. Mak, P. D. Tran, J. Barber, S. C. J. Loo, L. H. Wong, Chem. Sci. 2013, 4, 164–169.
- 8T. Hisatomi, F. Le Formal, M. Cornuz, J. Brillet, N. Tetreault, K. Sivula, M. Grätzel, Energy Environ. Sci. 2011, 4, 2512–2515.
- 9F. Le Formal, N. Tetreault, M. Cornuz, T. Moehl, M. Gratzel, K. Sivula, Chem. Sci. 2011, 2, 737–743.
- 10
- 10aY. Hou, F. Zuo, A. Dagg, P. Feng, Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 6464–6473;
- 10bH.-J. Ahn, K.-Y. Yoon, M.-J. Kwak, J.-S. Lee, P. Thiyagarajan, J.-H. Jang, J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 21444–21450;
- 10cY.-C. Wang, C.-Y. Chang, T.-F. Yeh, Y.-L. Lee, H. Teng, J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 20570–20577.
- 11
- 11aR. H. Goncalves, E. R. Leite, Energy Environ. Sci. 2014, 7, 2250–2254;
- 11bT. P. Almeida, M. W. Fay, T. W. Hansen, Y. Zhu, P. D. Brown, CrystEngComm 2014, 16, 1540–1546;
- 11cI. C. Masthoff, A. Gutsche, H. Nirschl, G. Garnweitner, CrystEngComm 2015, 17, 2464–2470.
- 12
- 12aA. Kim, S. Lim, D.-H. Peck, S.-K. Kim, B. Lee, D. Jung, Nanomaterials 2012, 2, 206;
- 12bP. Zhu, M. Teranishi, J. Xiang, Y. Masuda, W.-S. Seo, K. Koumoto, Thin Solid Films 2005, 473, 351–356.
- 13Y. Ling, G. Wang, J. Reddy, C. Wang, J. Z. Zhang, Y. Li, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 4074–4079; Angew. Chem. 2012, 124, 4150–4155.
- 14X. Gou, G. Wang, X. Kong, D. Wexler, J. Horvat, J. Yang, J. Park, Chem. Eur. J. 2008, 14, 5996–6002.
- 15P. Zhang, L. Gao, X. Song, J. Sun, Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 562–568.
- 16J. R. Shallenberger, J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 1996, 14, 693–698.
- 17
- 17aD. Noguchi, T. Sakai, T. Nagatomo, J. Ceram. Soc. Jpn. 2005, 113, 630–633;
- 17bL. Bousse, S. Mostarshed, B. Van Der Shoot, N. F. de Rooij, P. Gimmel, W. Göpel, J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1991, 147, 22–32.
- 18J. Y. Kim, J.-W. Jang, D. H. Youn, G. Magesh, J. S. Lee, Adv. Energy Mater. 2014, 4, 1400476.
- 19P. Zhang, A. Kleiman-Shwarsctein, Y.-S. Hu, J. Lefton, S. Sharma, A. J. Forman, E. McFarland, Energy Environ. Sci. 2011, 4, 1020–1028.
- 20
- 20aC. Schindler, S. C. P. Thermadam, R. Waser, M. N. Kozicki, IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2007, 54, 2762–2768;
- 20bH. Na, J. Oh, K. Lee, J. Kim, S. Lee, D. H. Lim, M.-H. Cho, H. Sohn, Microelectron. Eng. 2013, 110, 6–11.
- 21J. Brillet, M. Grätzel, K. Sivula, Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 4155–4160.
- 22D. K. Zhong, M. Cornuz, K. Sivula, M. Gratzel, D. R. Gamelin, Energy Environ. Sci. 2011, 4, 1759–1764.
- 23J. Li, Y. Qiu, Z. Wei, Q. Lin, Q. Zhang, K. Yan, H. Chen, S. Xiao, Z. Fan, S. Yang, Energy Environ. Sci. 2014, 7, 3651–3658.
- 24Y. Qiu, S.-F. Leung, Q. Zhang, B. Hua, Q. Lin, Z. Wei, K.-H. Tsui, Y. Zhang, S. Yang, Z. Fan, Nano Lett. 2014, 14, 2123–2129.