Using Ambient Ion Beams to Write Nanostructured Patterns for Surface Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy†
Corresponding Author
Dr. Anyin Li
Department of Chemistry and Center for Advanced Analytical Instrumentation Development, Purdue University, 560 Oval Drive, West Lafayette, IN 47907 (USA)
Anyin Li, Department of Chemistry and Center for Advanced Analytical Instrumentation Development, Purdue University, 560 Oval Drive, West Lafayette, IN 47907 (USA)
Thalappil Pradeep, DST Unit of Nanoscience (DST UNS) and Thematic Unit of Excellence (TUE), Department of Chemistry, Indian Institute of Technology Madras (IITM), Chennai, 600 036 (India)
R. Graham Cooks, Department of Chemistry and Center for Advanced Analytical Instrumentation Development, Purdue University, 560 Oval Drive, West Lafayette, IN 47907 (USA)
Search for more papers by this authorZane Baird
Department of Chemistry and Center for Advanced Analytical Instrumentation Development, Purdue University, 560 Oval Drive, West Lafayette, IN 47907 (USA)
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Soumabha Bag
Department of Chemistry and Center for Advanced Analytical Instrumentation Development, Purdue University, 560 Oval Drive, West Lafayette, IN 47907 (USA)
Search for more papers by this authorDepanjan Sarkar
DST Unit of Nanoscience (DST UNS) and Thematic Unit of Excellence (TUE), Department of Chemistry, Indian Institute of Technology Madras (IITM), Chennai, 600 036 (India)
Search for more papers by this authorAnupama Prabhath
DST Unit of Nanoscience (DST UNS) and Thematic Unit of Excellence (TUE), Department of Chemistry, Indian Institute of Technology Madras (IITM), Chennai, 600 036 (India)
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Thalappil Pradeep
DST Unit of Nanoscience (DST UNS) and Thematic Unit of Excellence (TUE), Department of Chemistry, Indian Institute of Technology Madras (IITM), Chennai, 600 036 (India)
Anyin Li, Department of Chemistry and Center for Advanced Analytical Instrumentation Development, Purdue University, 560 Oval Drive, West Lafayette, IN 47907 (USA)
Thalappil Pradeep, DST Unit of Nanoscience (DST UNS) and Thematic Unit of Excellence (TUE), Department of Chemistry, Indian Institute of Technology Madras (IITM), Chennai, 600 036 (India)
R. Graham Cooks, Department of Chemistry and Center for Advanced Analytical Instrumentation Development, Purdue University, 560 Oval Drive, West Lafayette, IN 47907 (USA)
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. R. Graham Cooks
Department of Chemistry and Center for Advanced Analytical Instrumentation Development, Purdue University, 560 Oval Drive, West Lafayette, IN 47907 (USA)
Anyin Li, Department of Chemistry and Center for Advanced Analytical Instrumentation Development, Purdue University, 560 Oval Drive, West Lafayette, IN 47907 (USA)
Thalappil Pradeep, DST Unit of Nanoscience (DST UNS) and Thematic Unit of Excellence (TUE), Department of Chemistry, Indian Institute of Technology Madras (IITM), Chennai, 600 036 (India)
R. Graham Cooks, Department of Chemistry and Center for Advanced Analytical Instrumentation Development, Purdue University, 560 Oval Drive, West Lafayette, IN 47907 (USA)
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Dr. Anyin Li
Department of Chemistry and Center for Advanced Analytical Instrumentation Development, Purdue University, 560 Oval Drive, West Lafayette, IN 47907 (USA)
Anyin Li, Department of Chemistry and Center for Advanced Analytical Instrumentation Development, Purdue University, 560 Oval Drive, West Lafayette, IN 47907 (USA)
Thalappil Pradeep, DST Unit of Nanoscience (DST UNS) and Thematic Unit of Excellence (TUE), Department of Chemistry, Indian Institute of Technology Madras (IITM), Chennai, 600 036 (India)
R. Graham Cooks, Department of Chemistry and Center for Advanced Analytical Instrumentation Development, Purdue University, 560 Oval Drive, West Lafayette, IN 47907 (USA)
Search for more papers by this authorZane Baird
Department of Chemistry and Center for Advanced Analytical Instrumentation Development, Purdue University, 560 Oval Drive, West Lafayette, IN 47907 (USA)
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Soumabha Bag
Department of Chemistry and Center for Advanced Analytical Instrumentation Development, Purdue University, 560 Oval Drive, West Lafayette, IN 47907 (USA)
Search for more papers by this authorDepanjan Sarkar
DST Unit of Nanoscience (DST UNS) and Thematic Unit of Excellence (TUE), Department of Chemistry, Indian Institute of Technology Madras (IITM), Chennai, 600 036 (India)
Search for more papers by this authorAnupama Prabhath
DST Unit of Nanoscience (DST UNS) and Thematic Unit of Excellence (TUE), Department of Chemistry, Indian Institute of Technology Madras (IITM), Chennai, 600 036 (India)
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Thalappil Pradeep
DST Unit of Nanoscience (DST UNS) and Thematic Unit of Excellence (TUE), Department of Chemistry, Indian Institute of Technology Madras (IITM), Chennai, 600 036 (India)
Anyin Li, Department of Chemistry and Center for Advanced Analytical Instrumentation Development, Purdue University, 560 Oval Drive, West Lafayette, IN 47907 (USA)
Thalappil Pradeep, DST Unit of Nanoscience (DST UNS) and Thematic Unit of Excellence (TUE), Department of Chemistry, Indian Institute of Technology Madras (IITM), Chennai, 600 036 (India)
R. Graham Cooks, Department of Chemistry and Center for Advanced Analytical Instrumentation Development, Purdue University, 560 Oval Drive, West Lafayette, IN 47907 (USA)
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. R. Graham Cooks
Department of Chemistry and Center for Advanced Analytical Instrumentation Development, Purdue University, 560 Oval Drive, West Lafayette, IN 47907 (USA)
Anyin Li, Department of Chemistry and Center for Advanced Analytical Instrumentation Development, Purdue University, 560 Oval Drive, West Lafayette, IN 47907 (USA)
Thalappil Pradeep, DST Unit of Nanoscience (DST UNS) and Thematic Unit of Excellence (TUE), Department of Chemistry, Indian Institute of Technology Madras (IITM), Chennai, 600 036 (India)
R. Graham Cooks, Department of Chemistry and Center for Advanced Analytical Instrumentation Development, Purdue University, 560 Oval Drive, West Lafayette, IN 47907 (USA)
Search for more papers by this authorWe acknowledge financial support from the Separations and Analysis Program, Office of Basic Energy Sciences, US Department of Energy, DE-FG02-06ER15807 and funding from NASA-PIDDP (grant number NNX12AB16G). Equipment support from the Nano Mission, Government of India is acknowledged. Part of the research was performed while A.L. was visiting IITM.
Graphical Abstract
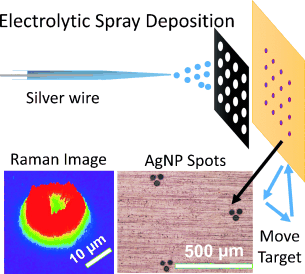
Electrolytic spray deposition was employed for the formation of nanoparticle spots on various substrates in air. These materials are rugged, versatile substrates for surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy, in which they lead to good enhancements. Lithographic applications of this method of ion deposition were also investigated.
Abstract
Electrolytic spray deposition was used to pattern surfaces with 2D metallic nanostructures. Spots that contain silver nanoparticles (AgNP) were created by landing solvated silver ions at desired locations using electrically floated masks to focus the metal ions to an area as little as 20 μm in diameter. The AgNPs formed are unprotected and their aggregates can be used for surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS). The morphology and SERS activity of the NP structures were controlled by the surface coverage of landed silver ions. The NP structures created could be used as substrates onto which SERS samples were deposited or prepared directly on top of predeposited samples of interest. The evenly distributed hot spots in the micron-sized aggregates had an average SERS enhancement factor of 108. The surfaces showed SERS activity when using lasers of different wavelengths (532, 633, and 785 nm) and were stable in air.
Supporting Information
As a service to our authors and readers, this journal provides supporting information supplied by the authors. Such materials are peer reviewed and may be re-organized for online delivery, but are not copy-edited or typeset. Technical support issues arising from supporting information (other than missing files) should be addressed to the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| anie_201406660_sm_miscellaneous_information.pdf1.8 MB | miscellaneous_information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1
- 1aS. Eustis, M. A. El-Sayed, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2006, 35, 209–217;
- 1bN. L. Rosi, C. A. Mirkin, Chem. Rev. 2005, 105, 1547–1562;
- 1cP. K. Jain, X. H. Huang, I. H. El-Sayed, M. A. El-Sayed, Acc. Chem. Res. 2008, 41, 1578–1586.
- 2
- 2aJ. D. Biggs, Y. Zhang, D. Healion, S. Mukamel, J. Chem. Phys. 2012, 136, 174117;
- 2bK. Kneipp, H. Kneipp, I. I, R. R. Dasari, M. S. Feld, Chem. Rev. 1999, 99, 2957–2976.
- 3
- 3aD. L. Jeanmaire, R. P. Van Duyne, J. Electroanal. Chem. Interfacial Electrochem. 1977, 84, 1–20;
- 3bH. Wang, Z. D. Schultz, Analyst 2013, 138, 3150–3157;
- 3cR. M. Stockle, Y. D. Suh, V. Deckert, R. Zenobi, Chem. Phys. Lett. 2000, 318, 131–136.
- 4
- 4aE. Hao, G. C. Schatz, J. Chem. Phys. 2004, 120, 357–366;
- 4bD. A. Genov, A. K. Sarychev, V. M. Shalaev, A. Wei, Nano Lett. 2004, 4, 153–158;
- 4cP. Negri, R. J. Flaherty, O. O. Dada, Z. D. Schultz, Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 2707–2710.
- 5
- 5aT. T. Nge, M. Nogi, K. Suganuma, J. Mater. Chem. C 2013, 1, 5235–5243;
- 5bJ. F. Li, Y. F. Huang, Y. Ding, Z. L. Yang, S. B. Li, X. S. Zhou, F. R. Fan, W. Zhang, Z. Y. Zhou, D. Y. Wu, B. Ren, Z. L. Wang, Z. Q. Tian, Nature 2010, 464, 392–395;
- 5cJ. Wang, L. Yang, B. Liu, H. Jiang, R. Liu, J. Yang, G. Han, Q. Mei, Z. Zhang, Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 3338–3345.
- 6
- 6aY. N. Xia, J. A. Rogers, K. E. Paul, G. M. Whitesides, Chem. Rev. 1999, 99, 1823–1848;
- 6bD. R. Baer, M. H. Engelhard, G. E. Johnson, J. Laskin, J. F. Lai, K. Mueller, P. Munusamy, S. Thevuthasan, H. F. Wang, N. Washton, A. Elder, B. L. Baisch, A. Karakoti, S. V. N. T. Kuchibhatla, D. Moon, J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 2013, 31, 050820;
- 6cK. D. Osberg, M. Rycenga, G. R. Bourret, K. A. Brown, C. A. Mirkin, Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 6065–6070;
- 6dJ. Cyriac, M. Wleklinski, G. T. Li, L. Gao, R. G. Cooks, Analyst 2012, 137, 1363–1369.
- 7N. G. Greeneltch, M. G. Blaber, A. I. Henry, G. C. Schatz, R. P. Van Duyne, Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 2297–2303.
- 8
- 8aS. Rauschenbach, F. L. Stadler, E. Lunedei, N. Malinowski, S. Koltsov, G. Costantini, K. Kern, Small 2006, 2, 540–547;
- 8bG. E. Johnson, T. Priest, J. Laskin, J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 24977–24986;
- 8cY. Lei, F. Mehmood, S. Lee, J. Greeley, B. Lee, S. Seifert, R. E. Winans, J. W. Elam, R. J. Meyer, P. C. Redfern, D. Teschner, R. Schlogl, M. J. Pellin, L. A. Curtiss, S. Vajda, Science 2010, 328, 224–228;
- 8dJ. Cyriac, T. Pradeep, H. Kang, R. Souda, R. G. Cooks, Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 5356–5411;
- 8eX. Li, K. A. Wepasnick, X. Tang, Y. Wang, K. H. Bowen, D. H. Fairbrother, G. Gantefoer, J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B 2012, 30, 031806.
- 9A. Li, Q. Luo, S.-J. Park, R. G. Cooks, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 3147–3150; Angew. Chem. 2014, 126, 3211–3214.
- 10S. M. Asiala, Z. D. Schultz, Analyst 2011, 136, 4472–4479.
- 11T. R. Jensen, M. D. Malinsky, C. L. Haynes, R. P. Van Duyne, J. Phys. Chem. B 2000, 104, 10549–10556.
- 12O. Hadjar, G. Johnson, J. Laskin, G. Kibelka, S. Shill, K. Kuhn, C. Cameron, S. Kassan, J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2011, 22, 612–623.
- 13Y. Fang, N. H. Seong, D. D. Dlott, Science 2008, 321, 388–392.
- 14I. Chakraborty, S. Bag, U. Landman, T. Pradeep, J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2013, 4, 2769–2773.
- 15
- 15aJ. W. Kim, Y. Yamagata, B. J. Kim, T. Higuchi, J. Micromech. Microeng. 2009, 19, 025021;
- 15bJ. Ju, Y. Yamagata, T. Higuchi, Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 4343–4347.
- 16J. C. Hulteen, R. P. Vanduyne, J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 1995, 13, 1553–1558.
- 17
- 17aA. K. Badu-Tawiah, A. Li, F. P. M. Jjunju, R. G. Cooks, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 9417–9421; Angew. Chem. 2012, 124, 9551–9555;
- 17bA. K. Badu-Tawiah, C. P. Wu, R. G. Cooks, Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 2648–2654;
- 17cZ. Baird, W. P. Peng, R. G. Cooks, Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 2012, 330, 277–284.
- 18K. M. Evans-Nguyen, S. C. Tao, H. Zhu, R. J. Cotter, Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 1448–1458.
- 19K. V. G. K. Murty, M. Venkataramanan, T. Pradeep, Langmuir 1998, 14, 5446–5456.
- 20
- 20aX. M. Lu, H. Y. Tuan, J. Y. Chen, Z. Y. Li, B. A. Korgel, Y. N. Xia, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 1733–1742;
- 20bM. C. Liu, Y. Q. Zheng, L. Zhang, L. J. Guo, Y. N. Xia, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 11752–11755.
Citing Literature
Special Issue:Nanotechnology & Nanomaterials, Nanotoxicology & Nanomedicine
November 10, 2014
Pages 12528-12531