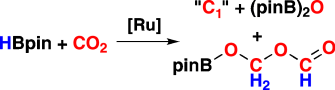Borane-Mediated Carbon Dioxide Reduction at Ruthenium: Formation of C1 and C2 Compounds†
Dr. Sébastien Bontemps
CNRS, LCC (Laboratoire de Chimie de Coordination), 205 route de Narbonne, 31077 Toulouse (France) http://www.lcc-toulouse.fr/lcc/spip.php?article433
Université de Toulouse, UPS, INPT, 31077 Toulouse (France)
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Laure Vendier
CNRS, LCC (Laboratoire de Chimie de Coordination), 205 route de Narbonne, 31077 Toulouse (France) http://www.lcc-toulouse.fr/lcc/spip.php?article433
Université de Toulouse, UPS, INPT, 31077 Toulouse (France)
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Dr. Sylviane Sabo-Etienne
CNRS, LCC (Laboratoire de Chimie de Coordination), 205 route de Narbonne, 31077 Toulouse (France) http://www.lcc-toulouse.fr/lcc/spip.php?article433
Université de Toulouse, UPS, INPT, 31077 Toulouse (France)
CNRS, LCC (Laboratoire de Chimie de Coordination), 205 route de Narbonne, 31077 Toulouse (France) http://www.lcc-toulouse.fr/lcc/spip.php?article433Search for more papers by this authorDr. Sébastien Bontemps
CNRS, LCC (Laboratoire de Chimie de Coordination), 205 route de Narbonne, 31077 Toulouse (France) http://www.lcc-toulouse.fr/lcc/spip.php?article433
Université de Toulouse, UPS, INPT, 31077 Toulouse (France)
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Laure Vendier
CNRS, LCC (Laboratoire de Chimie de Coordination), 205 route de Narbonne, 31077 Toulouse (France) http://www.lcc-toulouse.fr/lcc/spip.php?article433
Université de Toulouse, UPS, INPT, 31077 Toulouse (France)
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Dr. Sylviane Sabo-Etienne
CNRS, LCC (Laboratoire de Chimie de Coordination), 205 route de Narbonne, 31077 Toulouse (France) http://www.lcc-toulouse.fr/lcc/spip.php?article433
Université de Toulouse, UPS, INPT, 31077 Toulouse (France)
CNRS, LCC (Laboratoire de Chimie de Coordination), 205 route de Narbonne, 31077 Toulouse (France) http://www.lcc-toulouse.fr/lcc/spip.php?article433Search for more papers by this authorWe thank the ANR (Programme blanc “HyBoCat” ANR-09-BLAN-0184), the CNRS for support, and Johnson Matthey plc for the generous gift of hydrated ruthenium trichloride.
Graphical Abstract
One and two: The C2 compound pinBOCH2OCHO (see scheme; HBpin=pinacolborane) and several C1 compounds have been obtained from the borane-mediated reduction of CO2 under mild conditions with the catalyst precursor [RuH2(H2)2(PCy3)2]. Mechanistic investigation highlights the role of a series of new carbonyl ruthenium complexes that were characterized by multinuclear NMR spectroscopy, IR spectroscopy, and X-ray diffraction studies.
Supporting Information
Detailed facts of importance to specialist readers are published as ”Supporting Information”. Such documents are peer-reviewed, but not copy-edited or typeset. They are made available as submitted by the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| anie_201107352_sm_miscellaneous_information.pdf365 KB | miscellaneous_information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1
- 1aS. N. Riduan, Y. Zhang, Dalton Trans. 2010, 39, 3347;
- 1bC. Federsel, R. Jackstell, M. Beller, Angew. Chem. 2010, 122, 6392;
10.1002/ange.201000533 Google ScholarAngew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 6254;
- 1cG. Centi, S. Perathoner, Catal. Today 2009, 148, 191;
- 1dT. Sakakura, J.-C. Choi, H. Yasuda, Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 2365;
- 1eM. Aresta, A. Dibenedetto, Dalton Trans. 2007, 2975;
- 1fP. G. Jessop, F. Joo, C.-C. Tai, Coord. Chem. Rev. 2004, 248, 2425;
- 1gT. J. Marks et al., Chem. Rev. 2001, 101, 953, see the Supporting Information.
- 2
- 2aR. Tanaka, M. Yamashita, K. Nozaki, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 14168;
- 2bC. Federsel, A. Boddien, R. Jackstell, R. Jennerjahn, P. J. Dyson, R. Scopelliti, G. Laurenczy, M. Beller, Angew. Chem. 2010, 122, 9971;
10.1002/ange.201004263 Google ScholarAngew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 9777;
- 2cR. Langer, Y. Diskin-Posner, G. Leitus, L. J. W. Shimon, Y. Ben-David, D. Milstein, Angew. Chem. 2011, 123, 10122; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 9948;
- 2dA. Boddien, D. Mellmann, F. Gärtner, R. Jackstell, H. Junge, P. J. Dyson, G. Laurenczy, R. Ludwig, M. Beller, Science 2011, 333, 1733.
- 3
- 3aI. I. F. Boogaerts, S. P. Nolan, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 8858;
- 3bI. I. F. Boogaerts, G. C. Fortman, M. R. L. Furst, C. S. J. Cazin, S. P. Nolan, Angew. Chem. 2010, 122, 8856;
10.1002/ange.201004153 Google ScholarAngew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 8674;
- 3cL. Zhang, J. Cheng, T. Ohishi, Z. Hou, Angew. Chem. 2010, 122, 8852; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 8670.
- 4
- 4aM. A. Rankin, C. C. Cummins, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 10021;
- 4bO. Tardif, D. Hashizume, Z. Hou, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 8080;
- 4cN. E. Schlörer, E. J. Cabrita, S. Berger, Angew. Chem. 2002, 114, 114;
10.1002/1521-3757(20020104)114:1<114::AID-ANGE114>3.0.CO;2-D Google ScholarAngew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2002, 41, 107;10.1002/1521-3773(20020104)41:1<107::AID-ANIE107>3.0.CO;2-N CAS PubMed Web of Science® Google Scholar
- 4dM. T. Whited, R. H. Grubbs, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 5874;
- 4eN. J. Brookes, A. Ariafard, R. Stranger, B. F. Yates, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 5800;
- 4fX. Zhao, D. W. Stephan, Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 1833;
- 4gG. Ménard, D. W. Stephan, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 1796;
- 4hA. E. Ashley, A. L. Thompson, D. O’Hare, Angew. Chem. 2009, 121, 10023;
10.1002/ange.200905466 Google ScholarAngew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 9839.
- 5
- 5aD. S. Laitar, P. Mueller, J. P. Sadighi, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 17196;
- 5bH. Zhao, Z. Lin, T. B. Marder, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 15637.
- 6
- 6aT. Matsuo, H. Kawaguchi, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 12362;
- 6bS. Chakraborty, J. Zhang, J. A. Krause, H. Guan, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 8872;
- 6cF. Huang, C. Zhang, J. Jiang, Z.-X. Wang, H. Guan, Inorg. Chem. 2011, 50, 3816.
- 7
- 7aS. N. Riduan, Y. Zhang, J. Y. Ying, Angew. Chem. 2009, 121, 3372;
10.1002/ange.200806058 Google ScholarAngew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 3322;
- 7bL. Gu, Y. Zhang, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 132, 914;
- 7cA. Berkefeld, W. E. Piers, M. Parvez, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 10660.
- 8
- 8aP. G. Jessop, T. Ikarlya, R. Noyori, Nature 1994, 368, 231;
- 8bS.-I. Murahashi, Editor, Ruthenium in Organic Synthesis, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2004;
10.1002/3527603832 Google Scholar
- 8cY. Y. Ohnishi, T. Matsunaga, Y. Nakao, H. Sato, S. Sakaki, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 4021.
- 9G. Alcaraz, M. Grellier, S. Sabo-Etienne, Acc. Chem. Res. 2009, 42, 1640.
- 10
- 10aR. Reguillo, M. Grellier, N. Vautravers, L. Vendier, S. Sabo-Etienne, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 7854;
- 10bG. Alcaraz, L. Vendier, E. Clot, S. Sabo-Etienne, Angew. Chem. 2010, 122, 930;
10.1002/ange.200905970 Google ScholarAngew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 918;
- 10cS. Lachaize, L. Vendier, S. Sabo-Etienne, Dalton Trans. 2010, 39, 8492;
- 10dA. Toner, J. Matthes, S. Gruendemann, H.-H. Limbach, B. Chaudret, E. Clot, S. Sabo-Etienne, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 6945;
- 10eR. N. Perutz, S. Sabo-Etienne, Angew. Chem. 2007, 119, 2630;
10.1002/ange.200603224 Google ScholarAngew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 2578.
- 11M. L. Christ, S. Sabo-Etienne, G. Chung, B. Chaudret, Inorg. Chem. 1994, 33, 5316.
- 12For experimental details, see the Supporting Information.
- 13ROESY experiments indicate the spatial connectivity of the methyl groups of the pinacol backbone with the 13CH2 and 13CH3 of 10, 11, or 8. For the formoxy compound 9, the carbon resonance and the large 1JHC coupling constant (δH=8.21 ppm; δC=159.7 ppm, 1JHC=227.3 Hz) compare well to the related values reported for the analogous CatBOCHO compound (δC 162.1, 1JHC=214.0 Hz; Cat=catechol).[6b] The methylene 1H and 13C signals of compound 10 in the NMR spectra (δH=5.49 ppm, 1JHC=167.2 Hz and δC=85.4 ppm) compare well to those reported for the related silicon product CH2(OSiEt3)2 (δH=5.01 ppm, 1JHC=161.4 Hz and δC=84.2 ppm).[7c]
- 14M. L. Christ, S. Sabo-Etienne, B. Chaudret, Organometallics 1994, 13, 3800.
- 15S. Burling, G. Kociok-Köhn, M. F. Mahon, M. K. Whittlesey, J. M. J. Williams, Organometallics 2005, 24, 5868.
- 16
- 16aM. K. Whittlesey, R. N. Perutz, M. H. Moore, Organometallics 1996, 15, 5166;
- 16bR. F. R. Jazzar, P. H. Bhatia, M. F. Mahon, M. K. Whittlesey, Organometallics 2003, 22, 670.
- 17
- 17aV. Montiel-Palma, M. Lumbierres, B. Donnadieu, S. Sabo-Etienne, B. Chaudret, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 5624;
- 17bS. Lachaize, K. Essalah, V. Montiel-Palma, L. Vendier, B. Chaudret, J.-C. Barthelat, S. Sabo-Etienne, Organometallics 2005, 24, 2935.
- 18For a borohydride(carbonyl)ruthenium complex, see: H. Werner, M. A. Esteruelas, U. Meyer, B. Wrackmeyer, Chem. Ber. 1987, 120, 11.
- 19
- 19aJ. P. Lee, K. A. Pittard, N. J. DeYonker, T. R. Cundari, T. B. Gunnoe, J. L. Petersen, Organometallics 2006, 25, 1500;
- 19bW. Baratta, A. Del Zotto, G. Esposito, A. Sechi, M. Toniutti, E. Zangrando, P. Rigo, Organometallics 2004, 23, 6264;
- 19cB. N. Chaudret, D. J. Cole-Hamilton, R. S. Nohr, G. Wilkinson, J. Chem. Soc. Dalton Trans. 1977, 1546.
- 20C. Das Neves Gomes, O. Jacquet, C. Villiers, P. Thuéry, M. Ephritikhine, T. Cantat, Angew. Chem. 2012, 124, 191;
10.1002/ange.201105516 Google ScholarAngew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 187.
- 21
- 21aFor electrocatalytic conversion of CO2 into oxalate see: R. Angamuthu, P. Byers, M. Lutz, A. L. Spek, E. Bouwman, Science 2010, 327, 313;
- 21bit has been mentioned that methane and ethane were produced from the reaction of a nickel hydride(methyl)complex with CO2, but without any information on the origin of the gases: D. J. Darensbourg, M. Y. Darensbourg, L. Y. Goh, M. Ludvig, P. Wiegreffe, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1987, 109, 7539.