Conversion of Magnetic Impulses into Cellular Responses by Self-Assembled Nanoparticle–Vesicle Hydrogels†
Felicity de Cogan
School of Chemistry and Manchester Interdisciplinary Biocentre, The University of Manchester, 131 Princess St, Manchester M1 7DN (UK) http://www.webblab.org
School of Materials, Materials Science Centre, The University of Manchester, Manchester, M13 9PL (UK)
Search for more papers by this authorAndrew Booth
School of Chemistry and Manchester Interdisciplinary Biocentre, The University of Manchester, 131 Princess St, Manchester M1 7DN (UK) http://www.webblab.org
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Dr. Julie E. Gough
School of Materials, Materials Science Centre, The University of Manchester, Manchester, M13 9PL (UK)
Julie E. Gough, School of Materials, Materials Science Centre, The University of Manchester, Manchester, M13 9PL (UK)
Simon J. Webb, School of Chemistry and Manchester Interdisciplinary Biocentre, The University of Manchester, 131 Princess St, Manchester M1 7DN (UK) http://www.webblab.org
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Dr. Simon J. Webb
School of Chemistry and Manchester Interdisciplinary Biocentre, The University of Manchester, 131 Princess St, Manchester M1 7DN (UK) http://www.webblab.org
Julie E. Gough, School of Materials, Materials Science Centre, The University of Manchester, Manchester, M13 9PL (UK)
Simon J. Webb, School of Chemistry and Manchester Interdisciplinary Biocentre, The University of Manchester, 131 Princess St, Manchester M1 7DN (UK) http://www.webblab.org
Search for more papers by this authorFelicity de Cogan
School of Chemistry and Manchester Interdisciplinary Biocentre, The University of Manchester, 131 Princess St, Manchester M1 7DN (UK) http://www.webblab.org
School of Materials, Materials Science Centre, The University of Manchester, Manchester, M13 9PL (UK)
Search for more papers by this authorAndrew Booth
School of Chemistry and Manchester Interdisciplinary Biocentre, The University of Manchester, 131 Princess St, Manchester M1 7DN (UK) http://www.webblab.org
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Dr. Julie E. Gough
School of Materials, Materials Science Centre, The University of Manchester, Manchester, M13 9PL (UK)
Julie E. Gough, School of Materials, Materials Science Centre, The University of Manchester, Manchester, M13 9PL (UK)
Simon J. Webb, School of Chemistry and Manchester Interdisciplinary Biocentre, The University of Manchester, 131 Princess St, Manchester M1 7DN (UK) http://www.webblab.org
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Dr. Simon J. Webb
School of Chemistry and Manchester Interdisciplinary Biocentre, The University of Manchester, 131 Princess St, Manchester M1 7DN (UK) http://www.webblab.org
Julie E. Gough, School of Materials, Materials Science Centre, The University of Manchester, Manchester, M13 9PL (UK)
Simon J. Webb, School of Chemistry and Manchester Interdisciplinary Biocentre, The University of Manchester, 131 Princess St, Manchester M1 7DN (UK) http://www.webblab.org
Search for more papers by this authorThis work was supported by the award of a BBSRC Doctoral Training Grant to F.C. We thank Dr. R. Collins and Dr. A. Harvey for TEM, and Dr. L. Carney for cell culture.
Graphical Abstract
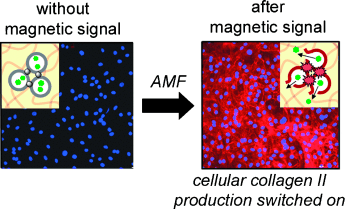
Crosslinking vesicles with magnetic nanoparticles produced MNPVs, self-assembled “nanopills” that can be “unlocked” by an alternating magnetic field (AMF), releasing chemical messengers stored within the vesicles. When MNPVs are co-immobilized with cells in a hydrogel matrix, exposure to an AMF magnetic signal releases the chemical messengers, which then induce a cellular response.
Supporting Information
Detailed facts of importance to specialist readers are published as ”Supporting Information”. Such documents are peer-reviewed, but not copy-edited or typeset. They are made available as submitted by the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| anie_201103469_sm_miscellaneous_information.pdf544 KB | miscellaneous_information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1V. P. Torchilin, Nat. Rev. Drug Discovery 2005, 4, 145–160.
- 2F. M. Menger, M. I. Angelova, Acc. Chem. Res. 1998, 31, 789–797.
- 3
- 3aN. Sakai, J. Mareda, S. Matile, Acc. Chem. Res. 2005, 38, 79–87;
- 3bP. Barton, C. A. Hunter, T. J. Potter, S. J. Webb, N. H. Williams, Angew. Chem. 2002, 114, 4034–4037;
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2002, 41, 3878–3881;
10.1002/1521-3773(20021018)41:20<3878::AID-ANIE3878>3.0.CO;2-F CAS PubMed Web of Science® Google Scholar
- 3cC. C. Hayden, J. S. Hwang, E. A. Abate, M. S. Kent, D. Y. Sasaki, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 8728–8729.
- 4M. Biondi, F. Ungaro, F. Quaglia, P. A. Netti, Adv. Drug Delivery Rev. 2008, 60, 229–242.
- 5
- 5aJ. Gao, H. Gu, B. Xu, Acc. Chem. Res. 2009, 42, 1097–1107;
- 5bJ. Riegler, J. A. Wells, P. G. Kyrtatos, A. N. Price, Q. A. Pankhurst, M. F. Lythgoe, Biomaterials 2010, 31, 5366–5371.
- 6J. Dobson, Nat. Nanotechnol. 2008, 3, 139–143.
- 7
- 7aQ. A. Pankhurst, N. K. T. Thanh, S. K. Jones, J. Dobson, J. Phys. D 2009, 42, 224001;
- 7bJ.-P. Fortin, C. Wilhelm, J. Servais, C. Ménager, J.-C. Bacri, F. Gazeau, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 2628–2635;
- 7cF. Sonvico, S. Mornet, S. Vasseur, C. Dubernet, D. Jaillard, J. Degrouard, J. Hoebeke, E. Duguet, P. Colombo, P. Couvreur, Bioconjugate Chem. 2005, 16, 1181–1188;
- 7dA. Ito, Y. Kuga, H. Honda, H. Kikkawa, A. Horiuchi, Y. Watanabe, T. Kobayashi, Cancer Lett. 2004, 212, 167–175.
- 8
- 8aK. P. Liem, R. J. Mart, S. J. Webb, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 12080–12081;
- 8bR. J. Mart, K. P. Liem, S. J. Webb, Pharm. Res. 2009, 26, 1701–1710.
- 9R. J. Mart, K. P. Liem, S. J. Webb, Chem. Commun. 2009, 2287–2289.
- 10
- 10aJ. H. Collier, Soft Matter 2008, 4, 2310–2315;
- 10bS. I. Stupp, Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 4783–4786;
- 10cR. J. Mart, R. D. Osborne, M. M. Stevens, R. V. Ulijn, Soft Matter 2006, 2, 822–835;
- 10dA. R. Hirst, B. Escuder, J. F. Miravet, D. K. Smith, Angew. Chem. 2008, 120, 8122–8139;
10.1002/ange.200800022 Google ScholarAngew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 8002–8018.
- 11
- 11aD. G. Anderson, J. A. Burdick, R. Langer, Science 2004, 305, 1923–1924;
- 11bM. P. Lutolf, F. E. Weber, H. G. Schmoekel, J. C. Schense, T. Kohler, R. Müller, J. A. Hubbell, Nat. Biotechnol. 2003, 21, 513–518;
- 11cM. W. Tibbitt, K. S. Anseth, Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2009, 103, 655–663.
- 12
- 12aG. Beaune, M. Levy, S. Neveu, F. Gazeau, C. Wilhelm, C. Ménager, Soft Matter 2011, 7, 6248–6254;
- 12bS. Nappini, F. B. Bombelli, M. Bonini, B. Nordèn, P. Baglioni, Soft Matter 2010, 6, 154–162.
- 13Hyperthermia assays suggest release occurs through MNP heating by Néel or Brown relaxation, but membrane disruption due to MNP oscillations could also be possible.
- 14S. Chiruvolu, S. Walker, J. Israelachvili, F.-J. Schmitt, D. Leckband, J. A. Zasadzinski, Science 1994, 264, 1753–1756.
- 15H. Gu, Z. Yang, J. Gao, C. K. Chang, B. Xu, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 34–35.
- 16S. Laurent, D. Forge, M. Port, A. Roch, C. Robic, L. Vander Elst, R. N. Muller, Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 2064–2110.
- 17J. Hjort Ipsen, G. Karlström, O. G. Mouritsen, H. Wennerström, M. J. Zuckermann, Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 1987, 905, 162–172.
- 18Several other assembly outcomes may also occur, including crosslinking of biotin residues across the surface of MNPs or vesicles, which could lower release efficiency.
- 19
- 19aG. Klöck, A. Pfeffermann, C. Ryser, P. Grohn, B. Kuttler, H. J. Hahn, U. Zimmermann, Biomaterials 1997, 18, 707–713;
- 19bF. Leng, J. E. Gough, S. J. Webb, Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. 2010, 1272, 1272-PP07-02.
- 20F. de Cogan, J. E. Gough, S. J. Webb, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2011, 22, 1045–1051.
- 21T. A. E. Ahmed, M. T. Hincke, Tissue Eng. Part B 2010, 16, 305–329.
- 22S. Loty, J.-M. Sautier, C. Loty, H. Boulekbache, T. Kokubo, N. Forest, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1998, 42, 213–222.
10.1002/(SICI)1097-4636(199811)42:2<213::AID-JBM6>3.0.CO;2-S CAS PubMed Web of Science® Google Scholar
- 23H. Lodish, A. Berk, C. A. Kaiser, M. Krieger, M. P. Scott, A. Bretscher, H. Ploegh, P. T. Matsudaira, in Molecular Cell Biology, 6th ed., W. H. Freeman, New York, 2008, p. 826.
- 24
- 24aP. S. Leboy, L. Vaias, B. Uschmann, E. Golub, S. L. Adams, M. Pacifici, J. Biol. Chem. 1989, 264, 17281–17286;
- 24bJ. C. Daniel, B. U. Pauli, K. E. Kuettner, J. Cell Biol. 1984, 99, 1960–1969.
- 25B. Kazakevičienė, G. Valinčius, M. Kažemėkaitė, V. Razumas, Electroanalysis 2008, 20, 2235–2240.
- 26The first two pKa values of monoalkylphosphoric acids are ca. 1 and 6. See: W. D. Kumler, J. J. Eiler, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1943, 65, 2355–2361.
- 27Chondrocytes have been reported as producing 5 mg mL−1 collagen in an alginate hydrogel. See: G. M. Williams, T. J. Klein, R. L. Sah, Acta Biomater. 2005, 1, 625–633.
- 28J. Kisiday, M. Jin, B. Kurz, H. Hung, C. Semino, S. Zhang, A. J. Grodzinsky, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 9996–10001.
- 29X. Zhao, J. Kim, C. A. Cezar, N. Huebsch, K. Lee, K. Bouhadir, D. J. Mooney, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 67–72.