Ligand-Directed Strategy for Zeolite-Type Metal–Organic Frameworks: Zinc(II) Imidazolates with Unusual Zeolitic Topologies†
Xiao-Chun Huang Dr.
State Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Materials and Technologies, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou 510275, China, Fax: (+86) 20-8411-2245
Department of Chemistry, Shantou University, Shantou, Guangdong 515063, China
Search for more papers by this authorYan-Yong Lin
State Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Materials and Technologies, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou 510275, China, Fax: (+86) 20-8411-2245
Search for more papers by this authorJie-Peng Zhang Dr.
State Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Materials and Technologies, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou 510275, China, Fax: (+86) 20-8411-2245
Search for more papers by this authorXiao-Ming Chen Prof. Dr.
State Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Materials and Technologies, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou 510275, China, Fax: (+86) 20-8411-2245
Search for more papers by this authorXiao-Chun Huang Dr.
State Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Materials and Technologies, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou 510275, China, Fax: (+86) 20-8411-2245
Department of Chemistry, Shantou University, Shantou, Guangdong 515063, China
Search for more papers by this authorYan-Yong Lin
State Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Materials and Technologies, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou 510275, China, Fax: (+86) 20-8411-2245
Search for more papers by this authorJie-Peng Zhang Dr.
State Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Materials and Technologies, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou 510275, China, Fax: (+86) 20-8411-2245
Search for more papers by this authorXiao-Ming Chen Prof. Dr.
State Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Materials and Technologies, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou 510275, China, Fax: (+86) 20-8411-2245
Search for more papers by this authorThis work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 20531070) and the Guangdong Provincial Science and Technology Bureau (No. 04205405).
Graphical Abstract
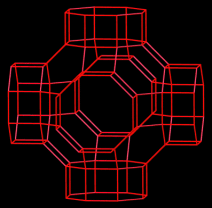
Thermally robust porous metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) with zeolitic topologies were constructed by means of a ligand-directed strategy involving molecular tailoring of simple bridging imidazolates with coordinatively unimportant substituents. This led to the isolation of three new MOFs having unusually high symmetries, intriguing topologies such as the supercage shown in the picture, and high thermal stability.
Supporting Information
Supporting information for this article is available on the WWW under http://www.wiley-vch.de/contents/jc_2002/2006/z503778_s.pdf or from the author.
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1
- 1aC. Baerlocher, W. M. Meier, D. H. Olson, Atlas of Zeolite Framework Types, 5th ed., Elsevier, Amsterdam, 2001;
10.1016/B978-044450701-3/50359-1 Google Scholar
- 1bD. W. Breck, Zeolite Molecular Sieves, Wiley, New York, 1974;
- 1cX. Bu, P. Feng, G. D. Stucky, Science 1997, 278, 2080.
- 2S. Kitagawa, R. Kitaura, S. Noro, Angew. Chem. 2004, 116, 2388; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2004, 43, 2334.
- 3aO. M. Yaghi, M. O'Keeffe, N. W. Ockwig, H. K. Chae, M. Eddaoudi, J. Kim, Nature 2003, 423, 705;
- 3bS. S.-Y. Chui, S. M.-F. Lo, J. P. H. Charmant, A. G. Orpen, I. D. Williams, Science 1999, 283, 1148.
- 4
- 4aG. Férey, C. Serre, C. Mellot-Draznieks, F. Millange, S. Surblé, J. Dutour, I. Margiolaki, Angew. Chem. 2004, 116, 6456;
10.1002/ange.200460592 Google ScholarAngew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2004, 43, 6296;
- 4bG. Férey, C. Mellot-Draznieks, C. Serre, F. Millange, Acc. Chem. Res. 2005, 38, 217;
- 4cG. Férey, C. Mellot-Draznieks, C. Serre, F. Millange, J. Dutour, S. Surblé, I. Margiolaki, Science 2005, 309, 2040.
- 5Q. Fang, G. Zhu, M. Xue, J. Sun, Y. Wei, S. Qiu, R. Xu, Angew. Chem. 2005, 117, 3913; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 3845.
- 6E. B. Rusanov, V. V. Ponomarova, V. V. Komarchuk, H. Stoeckli-Evans, E. Fernandez-Ibañez, F. Stoeckli, J. Sieler, K. V. Domasevitch, Angew. Chem. 2003, 115, 2603; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2003, 42, 2499.
- 7
- 7aY.-Q. Tian, C.-X. Cai, J. Ji, X.-Z. You, S.-M. Peng, G.-H. Lee, Angew. Chem. 2002, 114, 1442;
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2002, 41, 1384;
10.1002/1521-3773(20020415)41:8<1384::AID-ANIE1384>3.0.CO;2-6 CAS PubMed Web of Science® Google Scholar
- 7bY.-Q. Tian, C.-X. Cai, X.-M. Ren, C.-Y. Duan, Y. Xu, S. Gao, X.-Z. You, Chem. Eur. J. 2003, 9, 5673;
- 7cY.-Q. Tian, Z.-X. Chen, L.-H. Weng, H.-B. Guo, S. Gao, D.-Y. Zhao, Inorg. Chem. 2004, 43, 4631.
- 8For recent examples, see
- 8aX.-M. Chen, G.-F. Liu, Chem. Eur. J. 2002, 8, 4811;
10.1002/1521-3765(20021018)8:20<4811::AID-CHEM4811>3.0.CO;2-R CAS PubMed Web of Science® Google Scholar
- 8bY.-T. Wang, M.-L. Tong, H.-H. Fan, H.-Z. Wang, X.-M. Chen, Dalton Trans. 2005, 424;
- 8cX.-L. Wang, C. Qin, E.-B. Wang, Y.-G. Li, Z.-M. Su, L. Xu, L. Carlucci, Angew. Chem. 2005, 117, 5974; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 5824.
- 9
- 9aR. Lehnert, F. Z. Seel, Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem. 1980, 464, 187;
- 9bM. Sturm, F. Bromdl, D. Engel, W. Hoppe, Acta Crystallogr. Sect. B 1975, 31, 2369;
- 9cN. Masciocchi, S. Bruni, E. Cariati, F. Cariati, S. Galli, A. Sironi, Inorg. Chem. 2001, 40, 5897.
- 10
- 10aX.-C. Huang, J.-P. Zhang, X.-M. Chen, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 13218;
- 10bX.-C. Huang, J.-P. Zhang, Y.-Y. Lin, X.-M. Chen, Chem. Commun. 2005, 2232.
- 11Y.-Q. Tian, H.-J. Xu, L.-H. Weng, Z.-X. Chen, D.-Y. Zhao, X.-Z. You, Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2004, 1813.
- 12J.-P. Zhang, Y.-Y. Lin, X.-C. Huang, X.-M. Chen, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 5495.
- 13X.-C. Huang, J.-P. Zhang, X.-M. Chen, Chin. Sci. Bull. 2003, 48, 1531.
- 14The size was determined by considering van der Waals radii for constituent atoms (C 1.7, H 1.2, N 1.55, Zn 2.25 Å). Hereafter, all pore sizes reported in this paper are defined in this way. A. Bondi, J. Phys. Chem. 1964, 68, 441.
- 15
- 15aT. Devic, C. Serre, N. Audebrand, J. Marrot, G. Férey, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 12788;
- 15bT. K. Maji, K. Uemura, H.-C. Chang, R. Matsuda, S. Kitagawa, Angew. Chem. 2004, 116, 3331; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2004, 43, 3269.
- 16For 1, the effective window size of 3.3 Å is slightly larger than the van der Waals diameter of a nitrogen atom (3.1 Å), whereas for 2 the effective windows size is 2.2 Å.
- 17Shelxtl 6.10, Bruker Analytical Instrumentation, Madison, Wisconsin, USA, 2000.
- 18A. L. Spek, Acta Crystallogr. Sect. A 1990, 46, C 34.
Citing Literature
February 27, 2006
Pages 1557-1559