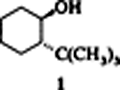
trans-2-tert-Butylcyclohexanol, a Simple Selectively Optimized Cyclohexanol Auxiliary†
This work was supported by the Deutsche Forschungsanstalt für Luft und Raumfahrt e.V, Hauptabteilung Energietechnik, Köln, der Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft, and the Fonds der Chemischen Industrie. We are grateful to Hüls AG (Marl) for supplying technical 2-tert-butylcyclohexanol. We also thank D. Gillmann for the synthetic work and S. Diebel for performing the GC analyses.
Graphical Abstract
An economical auxiliary comparable to 8-phenylmenthol, trans-2-tert-butylcyclohexanol (1) was derived as a “structurally minimized” cyclohexanol with an optimized induction potential by application of the isoinversion principle and the structure–selectivity relationship of the cyclohexanol auxiliaries. A simple preparation of both enantiomers of 1 is possible on a large scale by the enzymatic saponification of a technical-grade product.