Acetylcholinesterase-Catalyzed Hydrolysis Allows Ultrasensitive Detection of Pathogens with the Naked Eye†
Dingbin Liu
Laboratory of Molecular Imaging and Nanomedicine (LOMIN), National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering (NIBIB), National Institutes of Health (NIH), Bethesda, MD 20892 (USA)
Search for more papers by this authorZhantong Wang
National Institute of Diagnostics and Vaccine Development in Infectious Disease, School of Public Health, Xiamen University, Xiamen 361102 (China)
Center for Molecular Imaging and Translational Medicine, School of Public Health, Xiamen University, Xiamen 361005 (China)
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Albert Jin
Laboratory of Cellular Imaging and Macromolecular Biophysics, National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD 20982 (USA)
Search for more papers by this authorXinglu Huang
Laboratory of Molecular Imaging and Nanomedicine (LOMIN), National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering (NIBIB), National Institutes of Health (NIH), Bethesda, MD 20892 (USA)
Search for more papers by this authorXiaolian Sun
Laboratory of Molecular Imaging and Nanomedicine (LOMIN), National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering (NIBIB), National Institutes of Health (NIH), Bethesda, MD 20892 (USA)
Search for more papers by this authorFu Wang
Laboratory of Molecular Imaging and Nanomedicine (LOMIN), National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering (NIBIB), National Institutes of Health (NIH), Bethesda, MD 20892 (USA)
Search for more papers by this authorQiang Yan
National Institute of Diagnostics and Vaccine Development in Infectious Disease, School of Public Health, Xiamen University, Xiamen 361102 (China)
Search for more papers by this authorShengxiang Ge
National Institute of Diagnostics and Vaccine Development in Infectious Disease, School of Public Health, Xiamen University, Xiamen 361102 (China)
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Ningshao Xia
National Institute of Diagnostics and Vaccine Development in Infectious Disease, School of Public Health, Xiamen University, Xiamen 361102 (China)
Search for more papers by this authorGang Niu
Laboratory of Molecular Imaging and Nanomedicine (LOMIN), National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering (NIBIB), National Institutes of Health (NIH), Bethesda, MD 20892 (USA)
Search for more papers by this authorGang Liu
Center for Molecular Imaging and Translational Medicine, School of Public Health, Xiamen University, Xiamen 361005 (China)
Search for more papers by this authorDr. A. R. Hight Walker
Optical Technology Division, Physics Laboratory, National Institute of Standards and Technology, Gaithersburg, MD 20899 (USA)
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Dr. Xiaoyuan Chen
Laboratory of Molecular Imaging and Nanomedicine (LOMIN), National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering (NIBIB), National Institutes of Health (NIH), Bethesda, MD 20892 (USA)
Laboratory of Molecular Imaging and Nanomedicine (LOMIN), National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering (NIBIB), National Institutes of Health (NIH), Bethesda, MD 20892 (USA)Search for more papers by this authorDingbin Liu
Laboratory of Molecular Imaging and Nanomedicine (LOMIN), National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering (NIBIB), National Institutes of Health (NIH), Bethesda, MD 20892 (USA)
Search for more papers by this authorZhantong Wang
National Institute of Diagnostics and Vaccine Development in Infectious Disease, School of Public Health, Xiamen University, Xiamen 361102 (China)
Center for Molecular Imaging and Translational Medicine, School of Public Health, Xiamen University, Xiamen 361005 (China)
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Albert Jin
Laboratory of Cellular Imaging and Macromolecular Biophysics, National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD 20982 (USA)
Search for more papers by this authorXinglu Huang
Laboratory of Molecular Imaging and Nanomedicine (LOMIN), National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering (NIBIB), National Institutes of Health (NIH), Bethesda, MD 20892 (USA)
Search for more papers by this authorXiaolian Sun
Laboratory of Molecular Imaging and Nanomedicine (LOMIN), National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering (NIBIB), National Institutes of Health (NIH), Bethesda, MD 20892 (USA)
Search for more papers by this authorFu Wang
Laboratory of Molecular Imaging and Nanomedicine (LOMIN), National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering (NIBIB), National Institutes of Health (NIH), Bethesda, MD 20892 (USA)
Search for more papers by this authorQiang Yan
National Institute of Diagnostics and Vaccine Development in Infectious Disease, School of Public Health, Xiamen University, Xiamen 361102 (China)
Search for more papers by this authorShengxiang Ge
National Institute of Diagnostics and Vaccine Development in Infectious Disease, School of Public Health, Xiamen University, Xiamen 361102 (China)
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Ningshao Xia
National Institute of Diagnostics and Vaccine Development in Infectious Disease, School of Public Health, Xiamen University, Xiamen 361102 (China)
Search for more papers by this authorGang Niu
Laboratory of Molecular Imaging and Nanomedicine (LOMIN), National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering (NIBIB), National Institutes of Health (NIH), Bethesda, MD 20892 (USA)
Search for more papers by this authorGang Liu
Center for Molecular Imaging and Translational Medicine, School of Public Health, Xiamen University, Xiamen 361005 (China)
Search for more papers by this authorDr. A. R. Hight Walker
Optical Technology Division, Physics Laboratory, National Institute of Standards and Technology, Gaithersburg, MD 20899 (USA)
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Dr. Xiaoyuan Chen
Laboratory of Molecular Imaging and Nanomedicine (LOMIN), National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering (NIBIB), National Institutes of Health (NIH), Bethesda, MD 20892 (USA)
Laboratory of Molecular Imaging and Nanomedicine (LOMIN), National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering (NIBIB), National Institutes of Health (NIH), Bethesda, MD 20892 (USA)Search for more papers by this authorThis work was supported in part the Major State Basic Research Development Program of China (973 Program; 2013CB733802 and 2014CB744503), the National Science Foundation of China (NSFC; 81101101, 51273165, 81201086, 81201190, and 81371596), a Key Project of the Chinese Ministry of Education (212149), the Intramural Research Program (IRP) of the National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering (NIBIB), and the National Institutes of Health (NIH). D.L. was supported by a postdoctoral fellowship from NIH-NIBIB/NIST NRC.
Graphical Abstract
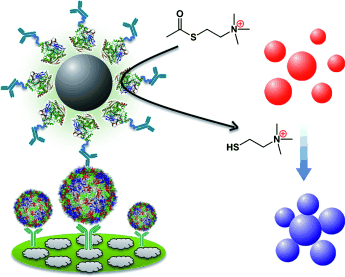
Gut zu sehen: Ein Diagnosesystem zum schnellen Pathogennachweis auf der Grundlage der Acetylcholinesterase- katalysierten Hydrolyse bringt es dank Signalverstärkungsstrategien auf eine vergleichbare Empfindlichkeit wie PCR-Methoden. Das Ergebnis des Assays zeigt sich in einer Farbänderung der Lösung und ist leicht mit dem bloßen Auge erkennbar.
Supporting Information
As a service to our authors and readers, this journal provides supporting information supplied by the authors. Such materials are peer reviewed and may be re-organized for online delivery, but are not copy-edited or typeset. Technical support issues arising from supporting information (other than missing files) should be addressed to the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| ange_201307952_sm_miscellaneous_information.pdf787.8 KB | miscellaneous_information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1
- 1aJ. F. Rusling, Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 5304–5310;
- 1bN. L. Rosi, C. A. Mirkin, Chem. Rev. 2005, 105, 1547–1562;
- 1cY. Xiang, Y. Lu, Nat. Chem. 2011, 3, 697–703;
- 1dS. Song, Z. Liang, J. Zhang, L. Wang, G. Li, C. Fan, Angew. Chem. 2009, 121, 8826–8830; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 8670–8674.
- 2K. Hsieh, A. S. Patterson, B. S. Ferguson, K. W. Plaxco, H. T. Soh, Angew. Chem. 2012, 124, 4980–4984;
10.1002/ange.201109115 Google ScholarAngew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 4896–4900.
- 3
- 3aB. Lam, J. Das, R. D. Holmes, L. Live, A. Sage, E. H. Sargent, S. O. Kelley, Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2001;
- 3bX. Guo, A. Kulkarni, A. Doepke, H. B. Halsall, S. Iyer, W. R. Heineman, Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 241–246.
- 4
- 4aL. Chen, X. Zhang, G. Zhou, X. Xiang, X. Ji, Z. Zheng, Z. He, H. Wang, Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 3200–3207;
- 4bK. Zagorovsky, W. C. W. Chan, Angew. Chem. 2013, 125, 3250–3253;
10.1002/ange.201208715 Google ScholarAngew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 3168–3171;
- 4cJ. H. Jung, D. S. Cheon, F. Liu, K. B. Lee, T. S. Seo, Angew. Chem. 2010, 122, 5844–5847; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 5708–5711;
- 4dH. J. Chung, C. M. Castro, H. Im, H. Lee, R. Weissleder, Nat. Nanotechnol. 2013, 8, 369–375.
- 5E. L. Tan, L. L. Yong, S. H. Quak, W. C. Yeo, V. T. Chow, C. L. Poh, J. Clin. Virol. 2008, 42, 203–206.
- 6
- 6aR. Elghanian, J. J. Storhoff, R. C. Mucic, R. L. Letsinger, C. A. Mirkin, Science 1997, 277, 1078–1081;
- 6bR. de La Rica, M. M. Stevens, Nat. Nanotechnol. 2012, 7, 821–824;
- 6cA. Laromaine, L. L. Koh, M. Murugesan, R. V. Ulijn, M. M. Stevens, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 4156–4157;
- 6dJ. W. Liu, Y. Lu, Angew. Chem. 2006, 118, 96–100; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 90–94;
- 6eD. Li, A. Wieckowska, I. Willner, Angew. Chem. 2008, 120, 3991–3995; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 3927–3931;
- 6fD. Liu, W. Chen, K. Sun, K. Deng, W. Zhang, Z. Wang, X. Jiang, Angew. Chem. 2011, 123, 4189–4193; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 4103–4107;
- 6gY. Jiang, H. Zhao, Y. Lin, N. Zhu, Y. Ma, L. Mao, Angew. Chem. 2010, 122, 4910–4914; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 4800–4804.
- 7D. Liu, W. Qu, W. Chen, W. Zhang, Z. Wang, X. Jiang, Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 9606–9610.
- 8
- 8aS. Krishnan, V. Mani, D. P. Wasalathanthri, C. V. Kumar, J. F. Rusling, Angew. Chem. 2011, 123, 1207–1210; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 1175–1178;
- 8bV. Mani, D. P. Wasalathanthri, A. A. Joshi, C. V. Kumar, J. F. Rusling, Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 10485–10491.
- 9J. M. Baskin, J. A. Prescher, S. T. Laughlin, N. J. Agard, P. V. Chang, I. A. Miller, A. Lo, J. A. Codelli, C. R. Bertozzi, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 16793–16797.
- 10M. Wang, X. Gu, G. Zhang, D. Zhang, D. Zhu, Langmuir 2009, 25, 2504–2507.
- 11G. L. Ellman, K. D. Courtney, V. Andres, R. M. Featherstone, Biochem. Pharmacol. 1961, 7, 88–95.
- 12X. Liu, M. Atwater, J. Wang, Q. Huo, Colloids Surf. B 2007, 58, 3–7.
- 13F. C. Zhu, Z. L. Liang, X. L. Li, H. M. Ge, F. Y. Meng, Q. Y. Mao, Y. T. Zhang, Y. M. Hu, Z. Y. Zhang, J. X. Li, F. Gao, Q. H. Chen, Q. Y. Zhu, K. Chu, X. Wu, X. Yao, H. J. Guo, X. Q. Chen, P. Liu, Y. Y. Dong, F. X. Li, X. L. Shen, J. Z. Wang, Lancet 2013, 381, 1037–1045.
- 14S. Wu, N. Duan, X. Ma, Y. Xia, Y. Yu, Z. Wang, H. Wang, Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 4866–4868.
Citing Literature
This is the
German version
of Angewandte Chemie.
Note for articles published since 1962:
Do not cite this version alone.
Take me to the International Edition version with citable page numbers, DOI, and citation export.
We apologize for the inconvenience.