Outcomes of multiple myeloma patients with del 17p undergoing autologous stem cell transplantation
The optimal treatment sequence for high risk (HR) myeloma has not been defined and many experts recommend various intensifications for this subpopulation, including quadruplets, consolidation, tandem autologous stem cell transplantation (ASCT), allogeneic transplantation and dual maintenance.
Recently, the long-term outcomes of the EMN02 trial were published.1 This is a large phase three RCT in which all patients received VCd induction and randomized to intensification with VMP (bortezomib, melphalan, prednisone) or ASCT (tandem or single according to siteʼs policy). The study was not powered to assess the issue of tandem vs single ASCT. The HR definition included del 17p, t (4;14) and t (14;16). In the 17p deletion subgroup, PFS was better for patients that underwent tandem ASCT (HR 0.24, P = .006). The STaMINA trial, in which 55% of patients received VRd induction, did not support tandem ASCT for HR MM patients in the intention-to-treat analysis.2
We evaluated newly diagnosed MM (NDMM) patients with del 17p, comparing them to the EMN02 study population and draw inferences about the use of tandem ASCT for this HR population.
We identified NDMM patients who underwent ASCT and harbored del 17p at Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minnesota. The study was approved by the Mayo Clinic Institutional Review Board (IRB). Patients were defined as 17p deleted FISH if they met the following criteria: If 50 plasma cells in the bone marrow sample and 10 with the deletion were identified (20%) or if sample had between 20-50 plasma cells and 20% with the deletion were identified. Bone marrow MRD assessment was carried out using eight-color next generation flow cytometry (sensitivity ≥1 × 105). We excluded patients that relapsed prior to ASCT, underwent ASCT more than 12 months from the diagnosis and patients that underwent tandem ASCT. The OS was defined as time from day zero of the transplant to death. The PFS was defined as time from day zero of the transplant to progression or death. Consolidation treatment was defined as treatment given after transplant for up to six 28-day cycles and maintenance was defined as all treatment given after ASCT for more than 6 months. Combined maintenance was defined as maintenance regimens that included two novel agents. Double-hit (DH) and triple-hit (TH) was defined as one additional HR genetic abnormality (t (4;14), t (14;16), t (14;20)). Statistical analysis was carried out using JMP 14 (SAS Institute, Cary, NC) statistical software.
We identified 170 patients with MM and del 17p, diagnosed between January 2012 and December 2019, that underwent ASCT. Fifty-four patients were excluded due to ASCT more than 12 months from diagnosis (24), relapse prior to ASCT (19), tandem ASCT (8) and BEAM induction.3 Overall, 116 patients were included in the analysis.
The median age at diagnosis was 62 (range 34-76) years. Forty-five (39%) patients were over 65 years. Nine patients (8%) had TH and 34 (29%) had DH. Median follow-up of survivors was 33 months (IQR 21-54). Consolidation and maintenance therapy were given to 36 (31%) and 91 (78%) patients, respectively.
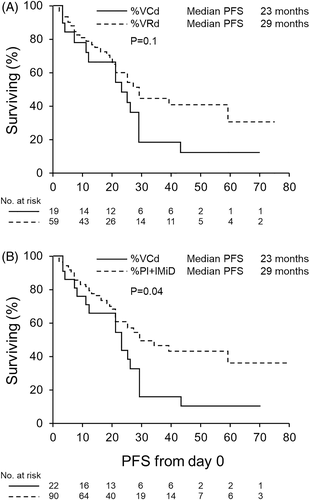
Induction included: VRd (54%), VCd (21%), KRd/KPD (10%), DaraKRd/DaraIRd (5%) doublet Rd/Vd (3%) or others (7%). There was no difference in terms of OS (P = .72), PFS (P = .1) or depth of response prior to ASCT between patients that received VRd and VCd induction (Figure 1A). The PFS was longer for patients that received PI + IMiD vs VCd induction (HR 0.53 P = .04, 95% CI = 0.3-0.98) (Figure 1B), without an OS difference (P = .61).
Post-ASCT, eighteen patients (16%) achieved MRDneg stringent CR, and eight patients (7%) attained MRDpos stringent CR, No PFS (P = .62) or OS (P = .85) difference was evident between the subset that achieved MRDneg vs MRDpos MRD CR.
Consolidation therapy was given to 36 patients (31%). The following regimens were used: KRd/KPd (14 patients), VRd (11 patients), VCd (six patients) and DKd/DVd (two patients). Maintenance therapy was given to 91 patients (78%). There was no difference in PFS (P = .36) or OS (P = .34) among patients that received IMiD based maintenance (23 patients), PI based maintenance (52 patients) and PI+IMiD maintenance (13 patients). However, PFS was longer in patients receiving two-drug maintenance (HR = 0.41, P = .037, 95% CI 0.14-0.95) without an OS benefit (P = .12).
The median OS and PFS of the entire cohort were not reached (95% CI 47 months -NR) and 29 months (95% CI 23-39), respectively. At 33 months 72% of patients are alive.
There was a difference between OS of the patients that had DH or TH and patients that had del 17p as the sole HR abnormality (HR-2.3, P = .01, 95% CI 1.16-4.68) and a trend towards inferior PFS in patients that had DH or TH (HR = 1.7, P = .054, 95% CI 0.99-2.92). Comparable PFS (P = .83) and OS (P = .94) were observed in patients older than 65 years and patients ≤65 years.
The current study shows that there was no difference in the OS or PFS between patients that received VRd vs VCd induction. Patients that received PI+ IMiD induction had a better PFS than patients that received VCd induction. There was no OS or PFS difference between IMiD-based and PI-based maintenance, but PFS was longer with dual vs single agent maintenance.
Mixed results were reported in phase three studies aiming to intensify treatment with tandem ASCT. In the EMNO2 trial1 tandem significantly improved PFS and OS compared to single ASCT in the entire cohort, but not in the HR subgroup. In patients with 17p deletion, tandem significantly improved PFS with a trend towards improved OS. Interestingly, in 17p deleted patients who received a tandem ASCT, the PFS and OS were similar to standard risk patients, which suggest that tandem ASCT may overcome the adverse prognosis of del 17p.
The STaMINA trial is the only prospective trial that evaluated outcomes of tandem transplants in patients treated in the US.2 One should note that the definition of HR also included beta 2 microglobulin ≥5.5 mg/L, del 13p and aneuploidy, which cannot be compared to the EMN02 trial.1 At the 6 years follow up for STaMINA presented at ASCO 2020,3 in the per protocol analysis, PFS in HR patients was significantly superior in the tandem arm. One of the limitations of this trial is that 30% of the patients that were randomized to tandem transplant did not actually undergo the second transplant and one may assume that these were patients that had a complicated course of the first transplant or refused a second transplant. In our study we have shown patients over the age of 65 do as well as younger patients so tandem transplants may also be feasible in older individuals.
In the IFM trial,4 NDMM patients received VAD induction followed by a randomization to single ASCT vs tandem ASCT, followed by interferon maintenance. Tandem ASCT was shown to improve OS, especially in those that failed to achieve VGPR after the first transplant. No data regarding the HR population was provided. The HOVON-65/GMMG-H4 compared bortezomib to VAD induction and used thalidomide maintenance.5 Single transplants were done in the HOVON cohort and tandem ASCT were done in the GMMG cohort and the latter had a longer PFS.
The risk of second primary malignancies (SPM) in the EMN02 and STaMINA trials was 5.8% and 10%, respectively, but no data are provided about the difference in the risk of SPM between single and tandem ASCT. The SPM risks in those two studies are similar to the risk of SPM reported with lenalidomide maintenance after a single ASCT (6.6%)6 so it cannot be inferred that a second transplant increases the risk of SPM.
In our cohort, patientʼs survival was comparable to patients in the EMN02 study that received a single ASCT (median PFS of approximately 30 months). There was no difference between PFS in VRd induction vs VCd induction in our cohort, however this may be explained by a small sample size. One may argue that the EMN02 trialʼs results are applicable to the US population and suggest that tandem transplantation can also be considered in patients with 17p deletion that receive VRd induction. Of note, patients that received PI+ IMiD as induction had a better PFS than patients that received VCd induction, which can be attributed to carfilzomib, since only one patient received pomalidomide induction.
There are several limitations to our study. This is a retrospective study, with heterogenous induction/consolidation/maintenance regimens. The number of patients treated with VCd was small and may have underpowered the statistical significance of the comparison between VCd and VRd. Few patients achieved MRDneg CR, so we cannot draw conclusions about the impact of achieving MRD negativity in 17p deleted patients. We do not have reliable data regarding SPM in our cohort since we are a referral center and many patients are followed long term elsewhere.
In conclusion, the outcomes of our patients were similar to that of the single arm ASCT in the EMN02 trial, and no difference in outcomes were found between patients that received VRd and VCd induction, suggesting that tandem transplants should be considered for 17p deleted MM patients.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
M.A.G. served as a consultant for Millennium Pharmaceuticals and received honoraria from Celgene, Millennium Pharmaceuticals, Onyx Pharmaceuticals, Novartis, GlaxoSmithKline, Prothena, Ionis Pharmaceuticals, and Amgen. P.K. received research funding from Takeda Pharmaceuticals, Celgene, and Amgen. A.D. received research funding from Celgene, Millennium Pharmaceuticals, Pfizer, and Janssen and received a travel grant from Pfizer. M.L. received research funding from Celgene. S.K. served as a consultant for Celgene, Millennium Pharmaceuticals, Onyx Pharmaceuticals, Janssen, and Bristol-Myers Squibb and received research funding from Celgene, Millennium Pharmaceuticals, Novartis, Onyx Pharmaceuticals, AbbVie, Janssen, and Bristol-Myers Squibb. The remaining authors declare no conflict of interest.
Open Research
DATA AVAILABILITY STATEMENT
The data that support the findings of this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to privacy or ethical restrictions.




