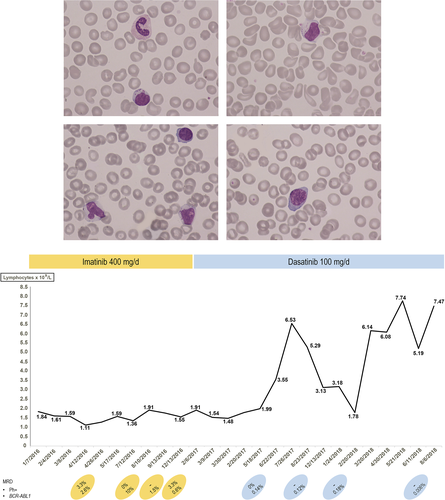
Large granular lymphocytosis induced by dasatinib
A diagnosis of chronic myeloid leukemia, BCR-ABL1-positive, was made in a 66-year-old woman in 2016. She was treated with imatinib, 400 mg/daily, with initial response but 12 months later the cytogenetic response had been lost. Therapy was therefore changed to dasatinib, 100 mg/daily. Six months after the change of therapy her lymphocyte count, which had been normal, had increased to 6.54 × 109/L and by 18 months had risen further with peak counts of 7.5-7.7 × 109/L (bottom, Graph).
The patient's blood film showed that the lymphocytosis was largely due to an increase of large granular lymphocytes. These were mainly cytologically normal, often with large, prominent granules (top left, top right Images), but a minority showed dysplastic features, such as nuclear lobulation (bottom left Image). A minor population showed features resembling those seen in viral infections (bottom right Image). A bone marrow aspirate showed 28% lymphocytes, mainly small lymphocytes, which had less obvious cytoplasmic granules.
Peripheral blood immunophenotyping showed 24% of leucocytes to have the immunophenotype of natural killer (NK) cells: CD3−/CD16+/CD56+; most expressed CD2 but 9% of this population did not. Molecular evaluation showed an IS BCR-ABL1 of 0.06%, the lowest value obtained since the beginning of dasatinib therapy.
Large granular lymphocytosis is a well recognized feature of dasatinib therapy. It may occur in as many as a third to a half of patients on this drug.1, 2 Both T cells and NK cells can be increased. Rearrangement of T-cell receptor genes can indicate monoclonality or oligoclonality of both T cells and NK cells, with a small clone being present at diagnosis and expanding during dasatinib therapy.1 This phenomenon may be associated with higher response rates, longer response durations, and increased overall survival.1, 2
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors declare no conflict of interest with the content of the paper.
Open Research
DATA AVAILABILITY STATEMENT
Data sharing not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated or analysed during the current study