Coordinative Behaviour of Tridentate NS2-Donor Ligands with Cadmium: Synthesis and Crystal Structures of New Complexes
Abstract
enThe reaction of cadmium salts with various amounts of the tridentate NS2-chelating ligands 1-(2-mercapto-acetophenone)-4-triphenylmethylthiosemicarbazone (H2L1) and 1-(5-mercapto-3-methyl-1-phenylpyrazole-4-carboxaldehyde)-4-triphenyl-methylthiosemicarbazone (H2L2) in the presence of bases like N-methylimidazole (N–MeIm), pyridine (py) or triethylamine (Et3N) provided a series of novel mono-, di-, tri- and heptanuclear cadmium complexes. They are of the general formulas [CdL1(N–MeIm)]2 (1), [CdL1(py)]2 (2), [CdL2(N–MeIm)]2 (3), [CdL2(py)3] · 0.25 C6H14 · 0.5 py (4), [Et3NH]2[Cd3L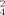 ] · 7 MeOH (5), [Et3NH]2[Cd3L
] · 7 MeOH (5), [Et3NH]2[Cd3L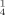 ] (6) and [Et3NH]2[Cd7L
] (6) and [Et3NH]2[Cd7L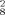 ] · 14 MeOH (7). The compounds were characterized by elemental analysis, IR- and 1H-NMR-spectroscopy. Single-crystal X-ray structure analyses are reported for the complexes 2, 4, 5 and 7. While 2 has a dimeric structure where each cadmium ion is pentacoordinated in a N2S3-environment, 4 consists of a monomeric cadmium center with distorted octahedral N4S2-coordination. The complexes 5 and 7 exhibit new structural types for tri- and heptanuclear cadmium compounds. It is shown that sulfur bridging might proceed via arylthiolates, iminothiolates or even both functions of the ligand. Aggregation is influenced by various factors like solvents, counterions and ligand properties.
] · 14 MeOH (7). The compounds were characterized by elemental analysis, IR- and 1H-NMR-spectroscopy. Single-crystal X-ray structure analyses are reported for the complexes 2, 4, 5 and 7. While 2 has a dimeric structure where each cadmium ion is pentacoordinated in a N2S3-environment, 4 consists of a monomeric cadmium center with distorted octahedral N4S2-coordination. The complexes 5 and 7 exhibit new structural types for tri- and heptanuclear cadmium compounds. It is shown that sulfur bridging might proceed via arylthiolates, iminothiolates or even both functions of the ligand. Aggregation is influenced by various factors like solvents, counterions and ligand properties.
Abstract
deKoordinationsverhalten tridentater NS2-Donor-Liganden mit Cadmium: Synthese und Kristallstrukturen neuer Komplexverbindungen
Die Reaktion von Cadmiumsalzen mit unterschiedlichen Mengen der dreifach chelatisierenden Liganden 1-(2-Mercapto-acetophenon)-4-triphenylmethylthiosemicarbazon (H2L1) und 1-(5-Mercapto-3-methyl-1phenylpyrazole-4-carboxaldehyde)-4-triphenylmethylthiosemicarbazone (H2L2) in Gegenwart verschiedener Basen wie N-Methylimidazol (N–MeIm), Pyridin (py) oder Triethylamin (Et3N) ergab eine Reihe neuer mono-, di-, tri- und heptanuklearer Cadmiumkomplexe mit folgenden Strukturformeln: [CdL1(N–MeIm)]2 (1), [CdL1(py)]2 (2), [CdL2(N–MeIm)]2 (3), [CdL2(py)3] · 0.25 C6H14 · 0.5 py (4), [Et3NH]2[Cd3L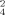 ] · 7 MeOH (5), [Et3NH]2[Cd3L
] · 7 MeOH (5), [Et3NH]2[Cd3L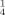 ] (6) und [Et3NH]2[Cd7L
] (6) und [Et3NH]2[Cd7L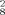 ] · 14 MeOH (7). Die Verbindungen wurden durch Elementaranalysen, IR- und 1H-NMR-Spektroskopie charakterisiert. Röntgenstrukturanalysen wurden für die Komplexe 2, 4, 5 und 7 durchgeführt. Während 2 eine dimere Struktur hat, in der jedes Cadmiumatom in einer N2S3-Umgebung fünffach koordiniert ist, ist 4 ein Monomer mit einer verzerrt oktaedrischen N4S2-Koordination. 5 und 7 stellen neue Strukturtypen für tri- und heptanukleare Cadmiumkomplexe dar. Die Verbrückung durch die Schwefelatome geschieht einerseits nur über die Aryl- oder Iminothiolate und andererseits über beide Funktionen des Liganden. Der Umfang der Aggregation wird dabei durch verschiedene Faktoren wie Lösungsmittel, Gegenionen und Ligandeigenschaften beeinflußt.
] · 14 MeOH (7). Die Verbindungen wurden durch Elementaranalysen, IR- und 1H-NMR-Spektroskopie charakterisiert. Röntgenstrukturanalysen wurden für die Komplexe 2, 4, 5 und 7 durchgeführt. Während 2 eine dimere Struktur hat, in der jedes Cadmiumatom in einer N2S3-Umgebung fünffach koordiniert ist, ist 4 ein Monomer mit einer verzerrt oktaedrischen N4S2-Koordination. 5 und 7 stellen neue Strukturtypen für tri- und heptanukleare Cadmiumkomplexe dar. Die Verbrückung durch die Schwefelatome geschieht einerseits nur über die Aryl- oder Iminothiolate und andererseits über beide Funktionen des Liganden. Der Umfang der Aggregation wird dabei durch verschiedene Faktoren wie Lösungsmittel, Gegenionen und Ligandeigenschaften beeinflußt.




