Abstract
[75-36-5] C2H3ClO (MW 78.50)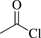
InChI = 1S/C2H3ClO/c1-2(3)4/h1H3
InChIKey = WETWJCDKMRHUPV-UHFFFAOYSA-N
(useful for electrophilic acetylation of arenes,2 alkenes,2a,3 alkynes,4 saturated alkanes,3a,5 organometallics, and enolates (on C or O);6 for cleavage of ethers;7 for esterification of sterically unhindered8 or acid-sensitive9 alcohols; for generation of solutions of anhydrous hydrogen chloride in methanol;10 as a dehydrating agent; as a solvent for organometallic reactions;11 for deoxygenation of sulfoxides;12 as a scavenger for chlorine13 and bromine;14 as a source of ketene; and for nucleophilic acetylation15)
Physical Data: bp 51.8 °C;1a mp −112.9 °C;1a d 1.1051 g cm−3;1a refractive index 1.38976.1b IR (neat) ν 1806.7 cm−1;16 1H NMR (CDCl3) δ 2.66 ppm; 13C NMR (CDCl3) δ 33.69 ppm (q) and 170.26 ppm (s); the bond angles (determined by electron diffraction17) are 127.5° (OCC), 120.3° (OCCl), and 112.2° (ClCC).
Analysis of Reagent Purity: a GC assay for potency has been described;18 to check qualitatively for the presence of HCl, a common impurity, add a few drops of a solution of crystal violet in chloroform;19 a green or yellow color indicates that HCl is present, while a purple color that persists for at least 10 min indicates that HCl is absent.1b
Preparative Methods: treatment of Acetic Acid or sodium acetate with the standard inorganic chlorodehydrating agents (PCl3,1b,23 SO2Cl2,1a,24 or SOCl21b,25) generates material that may contain phosphorus- or sulfur-containing impurities.1b,23a,26 Inorganic-free material can be prepared by treatment of HOAc with Cl2CHCOCl (Δ; 70%),27 PhCOCl (Δ; 88%),28 PhCCl3 (cat. H2SO4, 90 °C; 92.5%),29 or phosgene30 (optionally catalyzed by DMF,30e magnesium or other metal salts,30a,b,d or activated carbon30b,c), or by addition of hydrogen chloride to acetic anhydride (85–90 °C; ‘practically quantitative’).1a,31
Purification: HCl-free material can be prepared either by distillation from dimethylaniline11c,20 or by standard degassing procedures.20c,21
Handling, Storage, and Precautions: acetyl chloride should be handled only in a well-ventilated fume hood since it is volatile and toxic via inhalation.22 It should be stored in a sealed container under an inert atmosphere. Spills should be cleaned up by covering with aq sodium bicarbonate.1a
Bibliography
- 1(a) Moretti, T. A. Kirk-Othmer Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology, 3rd ed.; Wiley: New York, 1978; 1, p 162. (b) Wagner, F. S. Jr. Kirk-Othmer Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology, 4th ed.; Wiley: New York, 1991; 1, p 155.
- 2(a) Baddeley, G. Q. Rev., Chem. Soc. 1954, 8, 355. (b) Gore, P. H. Friedel–Crafts and Related Reactions; Wiley: New York, 1964; 3, p 1. (c) House, H. O. Modern Synthetic Reactions, 2nd ed; Benjamin: Menlo Park, 1972; p 797. (d) Olah, G. A. Friedel–Crafts Chemistry; Wiley: New York, 1973; pp 91, 191. (e) Heaney, H. COC 1979, 1, 241. (f) Olah, G. A.; Meidar, D. Kirk-Othmer Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology, 3rd ed.; Wiley: New York, 1980; 11, p 269. (g) Olah, G. A.; Prakash, G. K. S.; Sommer, J. Superacids; Wiley: New York, 1985; p 293.
- 3(a) Nenitzescu, C. D.; Balaban, A. T. Friedel–Crafts and Related Reactions; Wiley: New York, 1964; 3, p 1033. (b) Groves, J. K. Chem. Soc. Rev. 1972, 1, 73. (c) Olah, G. A. Friedel–Crafts Chemistry; Wiley: New York, 1973; pp 129, 200.
- 4 Price, C. C.; Pappalardo, J. A. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1950, 72, 2613.
- 5(a) Olah, G. A. Friedel–Crafts Chemistry; Wiley: New York, 1973; p 135. (b) Vol'pin, M.; Akhrem, I.; Orlinkov, A. Nouv. J. Chim. 1989, 13, 771.
- 6(a) House, H. O.; Auerbach, R. A.; Gall, M.; Peet, N. P. J. Org. Chem. 1973, 38, 514. (b) Black, T. H. Org. Prep. Proced. Int. 1989, 21, 179.
- 7(a) Burwell, R. L. Jr. Chem. Rev. 1954, 54, 615. (b) Johnson, F. Friedel–Crafts and Related Reactions; Wiley: New York, 1965; 4, p 1. (c) Bhatt, M. V.; Kulkarni, S. U. Synthesis 1983, 249.
- 8 Ishihara, K.; Kurihara, H.; Yamamoto, H. J. Org. Chem. 1993, 58, 3791.
- 9(a) Trost, B. M.; Chan, D. M. T. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1983, 105, 2315. (b) Trost, B. M.; Bonk, P. J. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1985, 107, 1778.
- 10(a)
Freudenberg, K.;
Jacob, W.
Ber. Dtsch. Chem. Ges./Chem. Ber.
1941,
74,
1001.
(b)
Riegel, B.;
Moffett, R. B.;
McIntosh, A. V.
Org. Synth.
1944,
24,
41.
(c)
Fraenkel-Conrat, H.;
Olcott, H. S.
J. Biol. Chem.
1945,
161,
259.
(d)
Baker, B. R.;
Schaub, R. E.;
Querry, M. V.;
Williams, J. H.
J. Org. Chem.
1952,
17,
77.
(e)
de Lombaert, S.;
Nemery, I.;
Roekens, B.;
Carretero, J. C.;
Kimmel, T.;
Ghosez, L.
Tetrahedron
1986,
27,
5099.
10.1016/S0040-4039(00)85143-6 Google Scholar(f) Nashed, E. M.; Glaudemans, C. P. J. J. Org. Chem. 1987, 52, 5255.
- 11(a) Chretien, A.; Oechsel, G. C.R. Hebd. Seances Acad. Sci. 1938, 206, 254. (b) Paul, R. C.; Sandhu, S. S. Proc. Chem. Soc. 1957, 262. (c) Paul, R. C.; Singh, D.; Sandhu, S. S. J. Chem. Soc 1959, 315. (d) Paul, R. C.; Singh, D.; Sandhu, S. S. J. Chem. Soc 1959, 319. (e) Maunaye, M.; Lang, J. C.R. Hebd. Seances Acad. Sci. 1965, 261, 3381, 3829.
- 12 Kaiser, G. V.; Cooper, R. D. G.; Koehler, R. E.; Murphy, C. F.; Webber, J. A.; Wright, I. G.; Van Heyningen, E. M. J. Org. Chem. 1970, 35, 2430.
- 13 Scheidmeir, W.; Bressel, U.; Hohenschutz, H. U.S. Patent 3 880 923, 1975.
- 14 Kharasch, M. S.; Hobbs, L. M. J. Org. Chem. 1941, 6, 705.
- 15(a) Collin, J.; Namy, J.-L.; Dallemer, F.; Kagan, H. B. J. Org. Chem. 1991, 56, 3118. (b) Ruder, S. M. Tetrahedron 1992, 33, 2621.
- 16 C. J. Pouchert The Aldrich Library of FT-IR Spectra, ed. I; Aldrich: Milwaukee, 1985; 1, p 723A.
- 17 Tsuchiya, S.; Kimura, M. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 1972, 45, 736.
- 18 Reagent Chemicals, 8th ed.; American Chemical Society: Washington, 1993; p 107.
- 19
Singh, J.;
Paul, R. C.;
Sandhu, S. S.
J. Chem. Soc
1959,
845.
10.1039/jr9590000845 Google Scholar
- 20(a)
Whitmore, F. C.
Recl. Trav. Chim. Pays-Bas
1938,
57,
562.
10.1002/recl.19380570519 Google Scholar(b) Cason, J.; Harman, R. E.; Goodwin, S.; Allen, C. F. J. Org. Chem. 1950, 15, 860. (c) Perrin, D. D.; Armarego, W. L. F. Purification of Laboratory Chemicals, 3rd ed.; Pergamon: Oxford, 1988; p 70.
- 21
Burton, H.;
Praill, P. F. G.
J. Chem. Soc
1952,
2546.
10.1039/jr9520002546 Google Scholar
- 22 Sax, N. I. Dangerous Properties of Industrial Materials, 6th ed.; Van Nostrand Reinhold: New York, 1984; p 106.
- 23(a) Vogel, A. I. A Text-book of Practical Organic Chemistry, 3rd ed.; Wiley: New York, 1956; p 367. (b) Damjan, J.; Benczik, J.; Kolonics, Z.; Pelyva, J.; Laborczy, R.; Szabolcs, J.; Soptei, C.; Barcza, I.; Kayos, C. Br. Patent 2 213 144, 1989. (c) Valitova, L. A.; Popova, E. V.; Ibragimov, Sh. N.; Ivanov, B. E. Bull. Acad. Sci. USSR, Div. Chem. Sci. 1990, 39, 366.
- 24 Durrans, T. H. U.S. Patent 1 326 040, 1919.
- 25 Masters, C. L. U.S. Patent 1 819 613, 1931.
- 26
Montonna, R. E.
J. Am. Chem. Soc.
1927,
49,
2114.
10.1021/ja01407a043 Google Scholar
- 27 Mugdan, M.; Wimmer, J. Ger. Patent 549 725, 1931.
- 28 Brown, H. C. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1938, 60, 1325.
- 29 Mills, L. E. U.S. Patent 1 921 767, 1933. U.S. Patent 1 965 556, 1934.
- 30(a) Meder, G.; Eggert, E.; Grimm, A. U.S. Patent 2 013 988, 1935. (b) Meder, G.; Geissler, W.; Eggert, E. U.S. Patent 2 013 989, 1935. (c) Meder, G.; Bergheimer, E.; Geisler, W.; Eggert, E. Ger. Patent 638 306, 1936. (d) Eggert, E.; Grimm, A. Ger. Patent 655 683, 1938. (e) Christoph, F. J. Jr.; Parker, S. H.; Seagraves, R. L. U.S. Patent 3 318 950, 1967.
- 31(a)
Colson, A.
Bull. Soc. Claim. Fr.
1897,
17,
55.
(b)
Inoue, S.;
Hayashi, K.
Chem. Abstr.
1954,
48,
8255g.
(c)
Satchell, D. P. N.
J. Chem. Soc
1960,
1752.
10.1039/jr9600001752 Google Scholar(d) Satchell, D. P. N. Q. Rev., Chem. Soc. 1963, 17, 160.
- 32 Brown, H. C.; Marino, G.; Stock, L. M. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1959, 81, 3310.
- 33 Brown, H. C.; Marino, G. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1962, 84, 1658.
- 34(a) Brown, H. C.; Nelson, K. L. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1953, 75, 6292. (b) Olah, G. A. Friedel–Crafts Chemistry; Wiley: New York, 1973; pp 448, 452.
- 35(a) Elwood, T. A.; Flack, W. R.; Inman, K. J.; Rabideau, P. W. Tetrahedron 1974, 30, 535. (b) Todd, D.; Pickering, M. J. Chem. Educ. 1988, 65, 1100.
- 36(a)
Baddeley, G.
J. Chem. Soc
1949,
S99.
10.1039/JR9490000S99 Google Scholar(b) Bassilios, H. F.; Makar, S. M.; Salem, A. Y. Bull. Soc. Claim. Fr. 1954, 21, 72. (c) Friedman, L.; Honour, R. J. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1969, 91, 6344.
- 37(a) Girdler, R. B.; Gore, P. H.; Hoskins, J. A. J. Chem. Soc. (C) 1966, 181. (b) Arsenijevic, L.; Arsenijevic, V.; Horeau, A.; Jacques, J. Org. Synth., Coll. Vol 1988, 6, 34. (c) Magni, A.; Visentin, G. U.S. Patent 4 868 338, 1989.
- 38 Friedman, L.; Koca, R. J. Org. Chem. 1968, 33, 1255.
- 39(a) Merritt, C. Jr.; Braun, C. E. Org. Synth., Coll. Vol 1963, 4, 8. (b) Gore, P. H.; Thadani, C. K. J. Chem. Soc. (C) 1966, 1729.
- 40(a) Perrier, G. Ber. Dtsch. Chem. Ges./Chem. Ber. 1900, 33, 815. (b) Perrier, G. Bull. Soc. Claim. Fr. 1904, 31, 859.
- 41(a)
Heine, H. W.;
Cottle, D. L.;
Van Mater, H. L.
J. Am. Chem. Soc.
1946,
68,
524.
(b)
Gore, P. H.;
Hoskins, J. A.
J. Chem. Soc
1964,
5666.
10.1039/jr9640005666 Google Scholar
- 42 Johnson, J. R.; May, G. E. Org. Synth., Coll. Vol 1943, 2, 8.
- 43(a) Piccolo, O.; Visentin, G.; Blasina, P.; Spreafico, F. U.S. Patent 4 670 603, 1987. (b) Lindley, D. D.; Curtis, T. A.; Ryan, T. R.; de la Garza, E. M.; Hilton, C. B.; Kenesson, T. M. U.S. Patent 5 068 448, 1991.
- 44 Olah, G. A. Friedel–Crafts Chemistry; Wiley: New York, 1973; pp 106, 306.
- 45 Allen, C. F. H. Org. Synth., Coll. Vol 1943, 2, 3.
- 46 Olah, G. A.; Moffatt, M. E.; Kuhn, S. J.; Hardie, B. A. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1964, 86, 2198.
- 47(a) Sondheimer, F.; Woodward, R. B. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1953, 75, 5438. (b) Briner, P. H. U.S. Patent 5 124 486, 1992.
- 48(a) Kulinkovich, O. G.; Tischenko, I. G.; Sorokin, V. L. Synthesis 1985, 1058. (b) Kulinkovich, O. G.; Tischenko, I. G.; Sorokin, V. L. J. Org. Chem. USSR (Engl. Transl.) 1985, 21, 1514. (c) Mamedov, E. I.; Ismailov, A. G.; Zyk, N. V.; Kutateladze, A. G.; Zefirov, N. S. Sulfur Lett. 1991, 12, 109.
- 49(a) Nenitzescu, C. D.; Gavat, I. G. Justus Liebigs Ann. Chem./Liebigs Ann. Chem. 1935, 519, 260. (b) Johnson, W. S.; Offenhauer, R. D. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1945, 67, 1045. (c) Crosby, J. A.; Rasburn, J. W. Chem. Ind. (London) 1967, 1365.
- 50(a) Darzens, M. G. C.R. Hebd. Seances Acad. Sci. 1910, 150, 707. (b) Wieland, H.; Bettag, L. Ber. Dtsch. Chem. Ges./Chem. Ber. 1922, 55, 2246.
- 51 Royals, E. E.; Hendry, C. M. J. Org. Chem. 1950, 15, 1147.
- 52(a) Turner, R. B.; Voitle, D. M. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1951, 73, 1403. (b) Dufort, N.; Lafontaine, J. Can. J. Chem. 1968, 46, 1065.
- 53(a) Baddeley, G.; Heaton, B. G.; Rasburn, J. W. J. Chem. Soc 1960, 4713. (b) Morel-Fourrier, C.; Dulcere, J.-P.; Santelli, M. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1991, 113, 8062.
- 54 Colonge, J.; Mostafavi, K. Bull. Soc. Claim. Fr. 1939, 6, 335, 342.
- 55(a) Nenitzescu, C. D.; Ionescu, C. N. Justus Liebigs Ann. Chem./Liebigs Ann. Chem. 1931, 491, 189. (b) Baddeley, G.; Khayat, M. A. R. Proc. Chem. Soc. 1961, 382. (c) Akhrem, I. S.; Orlinkov, A. V.; Mysov, E. I.; Vol'pin, M. E. Tetrahedron 1981, 22, 3891.
- 56 Arnaud, M.; Roussel, C.; Metzger, J. Tetrahedron 1979, 1795.
- 57 Snider, B. B.; Jackson, A. C. J. Org. Chem. 1982, 47, 5393.
- 58 Shono, T.; Nishiguchi, I.; Sasaki, M.; Ikeda, H.; Kurita, M. J. Org. Chem. 1983, 48, 2503.
- 59 Baran, J.; Klein, H.; Schade, C.; Will, E.; Koschinsky, R.; Bauml, E.; Mayr, H. Tetrahedron 1988, 44, 2181.
- 60 Ruzicka, L.; Koolhaas, D. R.; Wind, A. H. Helv. Chim. Acta 1931, 14, 1151.
- 61 Hoffmann, H. M. R.; Tsushima, T. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1977, 99, 6008.
- 62(a) Smit, W. A.; Semenovsky, A. V.; Kucherov, V. F.; Chernova, T. N.; Krimer, M. Z.; Lubinskaya, O. V. Tetrahedron 1971, 3101. (b) Smit, V. A.; Semenovskii, A. V.; Lyubinskaya, O. V.; Kucherov, V. F. Dokl. Akad. Nauk SSSR 1972, 203, 272.
- 63(a) Deno, N. C.; Chafetz, H. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1952, 74, 3940. (b) Groves, J. K.; Jones, N. J. Chem. Soc. (C) 1968, 2215, 2898. (c) Beak, P.; Berger, K. R. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1980, 102, 3848.
- 64(a) Balaban, A. T.; Nenitzescu, C. D. Justus Liebigs Ann. Chem./Liebigs Ann. Chem. 1959, 625, 74. (b) Balaban, A. T.; Schroth, W.; Fischer, G. Adv. Heterocycl. Chem. 1969, 10, 241. (c) Erre, C. H.; Roussel, C. Bull. Soc. Claim. Fr., Part 2 1984, 454.
- 65 Roitburd, G. V.; Smit, W. A.; Semenovsky, A. V.; Shchegolev, A. A.; Kucherov, V. F.; Chizhov, O. S.; Kadentsev, V. I. Tetrahedron 1972, 4935.
- 66(a) Tabushi, I.; Fujita, K.; Oda, R. Tetrahedron 1968, 5455. (b) Arnaud, M.; Pedra, A.; Roussel, C.; Metzger, J. J. Org. Chem. 1979, 44, 2972.
- 67(a) Nenitzescu, C. D.; Dragan, A. Ber. Dtsch. Chem. Ges./Chem. Ber. 1933, 66, 1892. (b) Bloch, H. S.; Pines, H.; Schmerling, L. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1946, 68, 153.
- 68(a) Tabushi, I.; Fujita, K.; Oda, R.; Tsuboi, M. Tetrahedron 1969, 2581. (b) Arnaud, M.; Pedra, A.; Erre, C.; Roussel, C.; Metzger, J. Heterocycles 1983, 20, 761.
- 69 Nenitzescu, C. D.; Cantuniari, J. P. Justus Liebigs Ann. Chem./Liebigs Ann. Chem. 1934, 510, 269.
- 70 Nenitzescu, C. D.; Cioranescu, E. Ber. Dtsch. Chem. Ges./Chem. Ber. 1936, 69, 1820.
- 71
Hopff, H.
Ber. Dtsch. Chem. Ges./Chem. Ber.
1932,
65,
482.
10.1002/cber.19320650321 Google Scholar
- 72(a) Tabushi, I.; Fujita, K.; Oda, R. Tetrahedron 1968, 4247. (b) Harding, K. E.; Clement, K. S.; Gilbert, J. C.; Wiechman, B. J. Org. Chem. 1984, 49, 2049.
- 73 Gilman, H.; Van Ess, P. R. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1933, 55, 1258.
- 74 Gilman, H.; Schulze, F. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1927, 49, 2328.
- 75(a) Percival, W. C.; Wagner, R. B.; Cook, N. C. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1953, 75, 3731. (b) Fiandanese, V.; Marchese, G.; Martina, V.; Ronzini, L. Tetrahedron 1984, 25, 4805. (c) Babudri, F.; D'Ettole, A.; Fiandanese, V.; Marchese, G.; Naso, F. J. Organomet. Chem. 1991, 405, 53.
- 76(a) Hosomi, A.; Hayashida, H.; Tominaga, Y. J. Org. Chem. 1989, 54, 3254. (b) Sproesser, L.; Sperling, K.; Trautmann, W.; Smuda, H. Ger. Patent 3 744 619, 1989.
- 77 Cahiez, G.; Laboue, B. Tetrahedron 1992, 33, 4439.
- 78 Fauvarque, J.; Ducom, J.; Fauvarque, J.-F. C.R. Hebd. Seances Acad. Sci., Ser. C 1972, 275, 511.
- 79(a) Gilman, H.; Mayhue, M. L. Recl. Trav. Chim. Pays-Bas 1932, 51, 47. (b) Chan, T. H.; Chang, E.; Vinokur, E. Tetrahedron 1970, 1137. (c) Stowell, J. C. J. Org. Chem. 1976, 41, 560. (d) Sato, F.; Inoue, M.; Oguro, K.; Sato, M. Tetrahedron 1979, 4303.
- 80 Normant, J. F. Synthesis 1972, 63.
- 81(a) Marfat, A.; McGuirk, P. R.; Helquist, P. Tetrahedron 1978, 1363. (b) Fleming, I.; Newton, T. W.; Roessler, F. J. Chem. Soc., Perkin Trans. 1 1981, 2527. (c) Corriu, R. J. P.; Moreau, J. J. E.; Vernhet, C. Tetrahedron 1987, 28, 2963.
- 82(a) Jallabert, C.; Luong-Thi, N.-T.; Riviere, H. Bull. Soc. Claim. Fr. 1970, 797. (b) Ebert, G. W.; Rieke, R. D. J. Org. Chem. 1984, 49, 5280. (c) Ebert, G. W.; Rieke, R. D. J. Org. Chem. 1988, 53, 4482. (d) Rieke, R. D.; Wehmeyer, R. M.; Wu, T.-C.; Ebert, G. W. Tetrahedron 1989, 45, 443. (e) Zhu, L.; Wehmeyer, R. M.; Rieke, R. D. J. Org. Chem. 1991, 56, 1445. (f) Ebert, G. W.; Cheasty, J. W.; Tehrani, S. S.; Aouad, E. Organometallics 1992, 11, 1560.
- 83(a) Bourgain, M.; Normant, J.-F. Bull. Soc. Claim. Fr. 1973, 2137. (b) Logue, M. W.; Moore, G. L. J. Org. Chem. 1975, 40, 131.
- 84(a) Corriu, R. J. P.; Guerin, C.; M'Boula, J. Tetrahedron 1981, 22, 2985. (b) Fleming, I.; Pulido, F. J. Chem. Commun./J. Chem. Soc., Chem. Commun. 1986, 1010.
- 85 Negishi, E.; Bagheri, V.; Chatterjee, S.; Luo, F.-T.; Miller, J. A.; Stoll, A. T. Tetrahedron 1983, 24, 5181.
- 86(a) Tamaru, Y.; Ochiai, H.; Nakamura, T.; Yoshida, Z. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 1987, 26, 1157. (b) Jackson, R. F. W.; James, K.; Wythes, M. J.; Wood, A. Chem. Commun./J. Chem. Soc., Chem. Commun. 1989, 644. (c) Harada, T.; Kotani, Y.; Katsuhira, T.; Oku, A. Tetrahedron 1991, 32, 1573. (d) Jackson, R. F. W.; Wishart, N.; Wood, A.; James, K.; Wythes, M. J. J. Org. Chem. 1992, 57, 3397.
- 87 Grey, R. A. J. Org. Chem. 1984, 49, 2288.
- 88El
Alami, N.;
Belaud, C.;
Villieras, J.
J. Organomet. Chem.
1987,
319,
303.
10.1016/S0022-328X(00)99603-7 Google Scholar
- 89 Grondin, J.; Sebban, M.; Vottero, P.; Blancou, H.; Commeyras, A. J. Organomet. Chem. 1989, 362, 237.
- 90 Verkruijsse, H. D.; Heus-Kloos, Y. A.; Brandsma, L. J. Organomet. Chem. 1988, 338, 289.
- 91(a) Blaise, E.; Koehler, A. C.R. Hebd. Seances Acad. Sci. 1909, 148, 489. (b) Jones, R. G. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1947, 69, 2350. (c) Shirley, D. A. Org. React. 1954, 8, 28.
- 92(a) Gilman, H.; Nelson, J. F. Recl. Trav. Chim. Pays-Bas 1936, 55, 518. (b) Cason, J. Chem. Rev. 1947, 40, 15. (c) Kollonitsch, J. J. Chem. Soc. (A) 1966, 453. (d) Jones, P. R.; Desio, P. J. Chem. Rev. 1978, 78, 491. (e) Burkhardt, E. R.; Rieke, R. D. J. Org. Chem. 1985, 50, 416.
- 93 Kurts, A. L.; Beletskaya, I. P.; Savchenko, I. A.; Reutov, O. A. J. Organomet. Chem. 1969, 17, P21.
- 94(a) Larock, R. C.; Bernhardt, J. C. Tetrahedron 1976, 3097. (b) Larock, R. C.; Bernhardt, J. C. J. Org. Chem. 1978, 43, 710.
- 95(a) Bundel, Yu. G.; Rozenberg, V. I.; Kurts, A. L.; Antonova, N. D.; Reutov, O. A. J. Organomet. Chem. 1969, 18, 209. (b) Larock, R. C.; Lu, Y. Tetrahedron 1988, 29, 6761.
- 96For Pd-catalyzed coupling of Ph2Hg and Et2Hg with acyl bromides, see: Takagi, K.; Okamoto, T.; Sakakibara, Y.; Ohno, A.; Oka, S.; Hayama, N. Chem. Lett. 1975, 951.
- 97 Bumagin, N. A.; Kalinovskii, I. O.; Beletskaya, I. P. Bull. Acad. Sci. USSR, Div. Chem. Sci. 1984, 33, 2144.
- 98 Negishi, E.; Chiu, K.-W.; Yosida, T. J. Org. Chem. 1975, 40, 1676.
- 99 Negishi, E.; Abramovitch, A.; Merrill, R. E. Chem. Commun./J. Chem. Soc., Chem. Commun. 1975, 138.
- 100 Utimoto, K.; Okada, K.; Nozaki, H. Tetrahedron 1975, 4239.
- 101(a) Paetzold, P. I.; Grundke, H. Synthesis 1973, 635. (b) Naruse, M.; Tomita, T.; Utimoto, K.; Nozaki, H. Tetrahedron 1973, 795. (c) Naruse, M.; Tomita, T.; Utimoto, K.; Nozaki, H. Tetrahedron 1974, 30, 835.
- 102(a) Adkins, H.; Scanley, C. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1951, 73, 2854. (b) Carr, D. B.; Schwartz, J. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1977, 99, 638. (c) Maruoka, K.; Sano, H.; Shinoda, K.; Nakai, S.; Yamamoto, H. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1986, 108, 6036.
- 103 Takai, K.; Oshima, K.; Nozaki, H. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 1981, 54, 1281.
- 104 Sato, F.; Kodama, H.; Tomuro, Y.; Sato, M. Chem. Lett. 1979, 623.
- 105 Marko, I. E.; Southern, J. M. J. Org. Chem. 1990, 55, 3368.
- 106(a)
Frainnet, E.;
Calas, R.;
Gerval, P.
C.R. Hebd. Seances Acad. Sci.
1965,
261,
1329.
(b)
Sakurai, H.;
Tominaga, K.;
Watanabe, T.;
Kumada, M.
Tetrahedron
1966,
5493.
(c)
Grignon-Dubois, M.;
Dunogues, J.;
Calas, R.
Synthesis
1976,
737.
10.1055/s-1976-24180 Google Scholar(d) Olah, G. A.; Ho, T.-L.; Prakash, G. K. S.; Gupta, B. G. B. Synthesis 1977, 677. (e) Grignon-Dubois, M.; Dunogues, J.; Calas, R. Can. J. Chem. 1980, 58, 291. (f) Grignon-Dubois, M.; Dunogues, J. J. Organomet. Chem. 1986, 309, 35.
- 107(a) Chan, T. H.; Fleming, I. Synthesis 1979, 761. (b) Parnes, Z. N.; Bolestova, G. I. Synthesis 1984, 991.
- 108(a) Pillot, J.-P.; Dunogues, J.; Calas, R. Bull. Soc. Claim. Fr. 1975, 2143. (b) Fleming, I.; Pearce, A. J. Chem. Soc., Perkin Trans. 1 1980, 2485. (c) Babudri, F.; Fiandanese, V.; Marchese, G.; Naso, F. Chem. Commun./J. Chem. Soc., Chem. Commun. 1991, 237.
- 109 Pillot, J.-P.; Dunogues, J.; Calas, R. J. Chem. Res. (S) 1977, 268.
- 110(a) Birkofer, L.; Ritter, A.; Uhlenbrauck, H. Ber. Dtsch. Chem. Ges./Chem. Ber. 1963, 96, 3280. (b) Walton, D. R. M.; Waugh, F. J. Organomet. Chem. 1972, 37, 45.
- 111 Pillot, J.-P.; Deleris, G.; Dunogues, J.; Calas, R. J. Org. Chem. 1979, 44, 3397.
- 112 Danheiser, R. L.; Stoner, E. J.; Koyama, H.; Yamashita, D. S.; Klade, C. A. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1989, 111, 4407.
- 113 Pillot, J.-P.; Bennetau, B.; Dunogues, J.; Calas, R. Tetrahedron 1981, 22, 3401.
- 114(a) Franciotti, M.; Mordini, A.; Taddei, M. Synlett 1992, 137. (b) Franciotti, M.; Mann, A.; Mordini, A.; Taddei, M. Tetrahedron 1993, 34, 1355.
- 115 Stille, J. K. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 1986, 25, 508.
- 116(a) Soderquist, J. A.; Leong, W. W.-H. Tetrahedron 1983, 24, 2361. (b) Perez, M.; Castano, A. M.; Echavarren, A. M. J. Org. Chem. 1992, 57, 5047.
- 117(a) Milstein, D.; Stille, J. K. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1978, 100, 3636. (b) Milstein, D.; Stille, J. K. J. Org. Chem. 1979, 44, 1613. (c) Yamamoto, Y.; Yanagi, A. Heterocycles 1982, 19, 41.
- 118 Logue, M. W.; Teng, K. J. Org. Chem. 1982, 47, 2549.
- 119(a) Kosugi, M.; Shimizu, Y.; Migita, T. J. Organomet. Chem. 1977, 129, C36. (b) Andrianome, M.; Delmond, B. J. Org. Chem. 1988, 53, 542. (c) Andrianome, M.; Haberle, K.; Delmond, B. Tetrahedron 1989, 45, 1079.
- 120 Reetz, M. T.; Hois, P. Chem. Commun./J. Chem. Soc., Chem. Commun. 1989, 1081.
- 121 Gambaro, A.; Peruzzo, V.; Marton, D. J. Organomet. Chem. 1983, 258, 291.
- 122 Yano, K.; Baba, A.; Matsuda, H. Chem. Lett. 1991, 1181.
- 123(a) Barton, D. H. R.; Ozbalik, N.; Ramesh, M. Tetrahedron 1988, 44, 5661. (b) Asthana, A.; Srivastava, R. C. J. Organomet. Chem. 1989, 366, 281.
- 124 Kasatkin, A. N.; Kulak, A. N.; Tolstikov, G. A. J. Organomet. Chem. 1988, 346, 23.
- 125 Hart, D. W.; Schwartz, J. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1974, 96, 8115.
- 126 Hirao, T.; Misu, D.; Yao, K.; Agawa, T. Tetrahedron 1986, 27, 929.
- 127 Cahiez, G.; Laboue, B. Tetrahedron 1989, 30, 7369.
- 128 Normant, J.-F.; Cahiez, G. Modern Synth. Methods 1983, 3, 173.
- 129(a) Hegedus, L. S.; Kendall, P. M.; Lo, S. M.; Sheats, J. R. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1975, 97, 5448. (b) Pittman, C. U. Jr.; Hanes, R. M. J. Org. Chem. 1977, 42, 1194.
- 130 Inaba, S.; Rieke, R. D. J. Org. Chem. 1985, 50, 1373.
- 131(a) Baker, R.; Blackett, B. N.; Cookson, R. C.; Cross, R. C.; Madden, D. P. Chem. Commun./J. Chem. Soc., Chem. Commun. 1972, 343. (b) Inaba, S.; Rieke, R. D. Tetrahedron 1983, 24, 2451.
- 132(a) Tanaka, T.; Kurozumi, S.; Toru, T.; Kobayashi, M.; Miura, S.; Ishimoto, S. Tetrahedron 1975, 1535. (b) Kurozumi, S.; Toru, T.; Tanaka, T.; Miura, S.; Kobayashi, M.; Ishimoto, S. U.S. Patent 4 009 196, 1977. U.S. Patent 4 139 717, 1979. (c) Lee, S.-H.; Shih, M.-J.; Hulce, M. Tetrahedron 1992, 33, 185.
- 133 Lapkin, I. I.; Saitkulova, F. G. J. Org. Chem. USSR (Engl. Transl.) 1971, 7, 2586.
- 134For examples of acetylations of enolates in which proton transfer is not competitive, see Refs. 132a,b, and Evans, D. A.; Ennis, M. D.; Le, T.; Mandel, N.; Mandel, G. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1984, 106, 1154.
- 135(a) Rasmussen, J. K. Synthesis 1977, 91. (b) Tirpak, R. E.; Rathke, M. W. J. Org. Chem. 1982, 47, 5099.
- 136(a) Hoch, H.; Hunig, S. Ber. Dtsch. Chem. Ges./Chem. Ber. 1972, 105, 2660. (b) Nilsson, L. Acta Chem. Scand. (B) 1979, 33, 710. (c) Zhang, P.; Li, L. Synth. Commun. 1986, 16, 957.
- 137 Burlachenko, G. S.; Mal'tsev, V. V.; Baukov, Yu. I.; Lutsenko, I. F. J. Gen. Chem. USSR (Engl. Transl.) 1973, 43, 1708.
- 138 Rathke, M. W.; Sullivan, D. F. Tetrahedron 1973, 1297.
- 139 Chiba, T.; Ishizawa, T.; Sakaki, J.; Kaneko, C. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1987, 35, 4672.
- 140 Fleming, I.; Goldhill, J.; Paterson, I. Tetrahedron 1979, 3209.
- 141 Brownbridge, P.; Chan, T. H.; Brook, M. A.; Kang, G. J. Can. J. Chem. 1983, 61, 688.
- 142 Ladjama, D.; Riehl, J. J. Synthesis 1979, 504.
- 143(a) Heusler, K.; Kebrle, J.; Meystre, C.; Ueberwasser, H.; Wieland, P.; Anner, G.; Wettstein, A. Helv. Chim. Acta 1959, 42, 2043. (b) Ensley, H. E.; Parnell, C. A.; Corey, E. J. J. Org. Chem. 1978, 43, 1610.
- 144 Dauben, W. G.; Eastham, J. F.; Micheli, R. A. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1951, 73, 4496.
- 145 Snozzi, C.; Goffinet, B.; Joly, R.; Jolly, J. U.S. Patent 3 117 142, 1964.
- 146(a) Casey, C. P.; Marten, D. F. Tetrahedron 1974, 925. (b) Ouannes, C.; Langlois, Y. Tetrahedron 1975, 3461.
- 147 Ono, N.; Yoshimura, T.; Saito, T.; Tamura, R.; Tanikaga, R.; Kaji, A. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 1979, 52, 1716.
- 148 Casey, C. P.; Marten, D. F.; Boggs, R. A. Tetrahedron 1973, 2071.
- 149(a) Viscontini, M.; Merckling, N. Helv. Chim. Acta 1952, 35, 2280. (b) Rathke, M. W.; Cowan, P. J. J. Org. Chem. 1985, 50, 2622.
- 150(a) Adams, R.; Vollweiler, E. H. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1918, 40, 1732. (b) French, H. E.; Adams, R. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1921, 43, 651. (c) Ulich, L. H.; Adams, R. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1921, 43, 660. (d) Euranto, E. K.; Noponen, A.; Kujanpaa, T. Acta Chem. Scand. 1966, 20, 1273. (e) Kyburz, R.; Schaltegger, H.; Neuenschwander, M. Helv. Chim. Acta 1971, 54, 1037. (f) Neuenschwander, M.; Iseli, R. Helv. Chim. Acta 1977, 60, 1061. (g) Neuenschwander, M.; Vogeli, R.; Fahrni, H.-P.; Lehmann, H.; Ruder, J.-P. Helv. Chim. Acta 1977, 60, 1073. (h) Bigler, P.; Muhle, H.; Neuenschwander, M. Synthesis 1978, 593.
- 151 Bigler, P.; Neuenschwander, M. Helv. Chim. Acta 1978, 61, 2165.
- 152(a) Euranto, E.; Kujanpaa, T. Acta Chem. Scand. 1961, 15, 1209. (b) Euranto, E.; Leppanen, O. Acta Chem. Scand. 1963, 17, 2765. (c) Neuenschwander, M.; Bigler, P.; Christen, K.; Iseli, R.; Kyburz, R.; Muhle, H. Helv. Chim. Acta 1978, 61, 2047.
- 153(a) Bigler, P.; Schonholzer, S.; Neuenschwander, M. Helv. Chim. Acta 1978, 61, 2059. (b) Bigler, P.; Neuenschwander, M. Helv. Chim. Acta 1978, 61, 2381.
- 154(a) Chou, T.-S.; Knochel, P. J. Org. Chem. 1990, 55, 4791, 6232. (b) Knochel, P.; Chou, T.-S.; Jubert, C.; Rajagopal, D. J. Org. Chem. 1993, 58, 588.
- 155 Knochel, P.; Chou, T.-S.; Chen, H. G.; Yeh, M. C. P.; Rozema, M. J. J. Org. Chem. 1989, 54, 5202.
- 156 Enholm, E. J.; Satici, H. Tetrahedron 1991, 32, 2433.
- 157 Oku, A.; Harada, T.; Kita, K. Tetrahedron 1982, 23, 681.
- 158 Cloke, J. B.; Pilgrim, F. J. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1939, 61, 2667.
- 159 Duboudin, J.-G.; Valade, J. Bull. Soc. Claim. Fr. 1974, 272.
- 160(a) Ahmad, S.; Iqbal, J. Chem. Lett. 1987, 953. (b) Iqbal, J.; Srivastava, R. R. Tetrahedron 1991, 47, 3155.
- 161 Pri-Bar, I.; Stille, J. K. J. Org. Chem. 1982, 47, 1215.
- 162 Alper, H.; Huang, C.-C. J. Org. Chem. 1973, 38, 64.
- 163 Fitch, J. W.; Payne, W. G.; Westmoreland, D. J. Org. Chem. 1983, 48, 751.
- 164 Chang, C.; Chu, K. C.; Yue, S. Synth. Commun. 1992, 22, 1217.
- 165(a) Straus, F.; Heinze, H. Justus Liebigs Ann. Chem./Liebigs Ann. Chem. 1932, 493, 191. (b) Quintard, J.-P.; Elissondo, B.; Pereyre, M. J. Organomet. Chem. 1981, 212, C31. (c) Quintard, J.-P.; Elissondo, B.; Pereyre, M. J. Org. Chem. 1983, 48, 1559.
- 166(a) Bakos, T.; Vincze, I. Synth. Commun. 1989, 19, 523. (b) Sabharwal, A.; Vig, R.; Sharma, S.; Singh, J. Indian J. Chem., Sect. B 1990, 29, 890.
- 167(a) Pop, L.; Oprean, I.; Barabas, A.; Hodosan, F. J. Prakt. Chem. 1986, 328, 867. (b) Oprean, I.; Ciupe, H.; Gansca, L.; Hodosan, F. J. Prakt. Chem. 1987, 329, 283.
- 168 Dutka, F.; Marton, A. F. Z. Naturforsch., Tell B 1969, 24, 1664.
- 169 Hofle, G.; Steglich, W.; Vorbruggen, H. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 1978, 17, 569.
- 170(a) Vedejs, E.; Diver, S. T. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1993, 115, 3358. (b) Vedejs, E.; Bennett, N. S.; Conn, L. M.; Diver, S. T.; Gingras, M.; Lin, S.; Oliver, P. A.; Peterson, M. J. J. Org. Chem. 1993, 58, 7286.
- 1711,2-Diols can be selectively monoacetylated by conversion into the cyclic dibutylstannylidene derivative followed by treatment with AcCl: (a) Anchisi, C.; Maccioni, A.; Maccioni, A. M.; Podda, G. Gazz. Chim. Ital. 1983, 113, 73. (b) Roelens, S. J. Chem. Soc., Perkin Trans. 2 1988, 2105. (c) Anderson, W. K.; Coburn, R. A.; Gopalsamy, A.; Howe, T. J. Tetrahedron 1990, 31, 169. (d) Getman, D. P.; DeCrescenzo, G. A.; Heintz, R. M. Tetrahedron 1991, 32, 5691.
- 172 γ-Picoline might be unsuitable as a pyridine replacement because it reacts with AcCl to form N-acetyl-4-(acetylmethylidene)-1,4-dihydropyridine under standard acetylation conditions (CH2Cl2, rt, 8–16 h): Ippolito, R. M.; Vigmond, S. U.S. Patent 4 681 944, 1987.
- 173(a) Okamoto, K.; Kondo, T.; Goto, T. Tetrahedron 1987, 43, 5909. (b) McClure, K. F.; Danishefsky, S. J. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1993, 115, 6094.
- 174(a) Braun, M.; Devant, R. Tetrahedron 1984, 25, 5031. (b) Devant, R.; Mahler, U.; Braun, M. Ber. Dtsch. Chem. Ges./Chem. Ber. 1988, 121, 397.
- 175 Capek, K.; Steffkova, J.; Jary, J. Collect. Czech. Chem. Commun. 1966, 31, 1854.
- 176 Bladon, P.; Clayton, R. B.; Greenhalgh, C. W.; Henbest, H. B.; Jones, E. R. H.; Lovell, B. J.; Silverstone, G.; Wood, G. W.; Woods, G. F. J. Chem. Soc 1952, 4883.
- 177(a) Litvinenko, L. M.; Kirichenko, A. I. Dokl. Akad. Nauk SSSR 1967, 176, 763. (b) Steglich, W.; Hofle, G. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 1969, 8, 981. (c) Hofle, G.; Steglich, W. Synthesis 1972, 619. (d) Scriven, E. F. V. Chem. Soc. Rev. 1983, 12, 129.
- 178(a) Norris, J. F.; Rigby, G. W. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1932, 54, 2088. (b) Plattner, Pl. A.; Petrzilka, Th.; Lang, W. Helv. Chim. Acta 1944, 27, 513. (c) Hauser, C. R.; Hudson, B. E.; Abramovitch, B.; Shivers, J. C. Org. Synth., Coll. Vol 1955, 3, 142. (d) Ohloff, G. Helv. Chim. Acta 1958, 41, 845.
- 179(a) Plattner, Pl. A.; Furst, A.; Koller, F.; Lang, W. Helv. Chim. Acta 1948, 31, 1455. (b) Williams, K. I. H.; Rosenfeld, R. S.; Smulowitz, M.; Fukushima, D. K. Steroids 1963, 1, 377. (c) Kido, F.; Kitahara, H.; Yoshikoshi, A. J. Org. Chem. 1986, 51, 1478.
- 180(a) Takimoto, S.; Inanaga, J.; Katsuki, T.; Yamaguchi, M. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 1976, 49, 2335. (b) Amouroux, R.; Chan, T. H. Tetrahedron 1978, 4453.
- 181 Spassow, A. Org. Synth., Coll. Vol 1955, 3, 144.
- 182(a) Illi, V. O. Tetrahedron 1979, 2431. (b) Szeja, W. Synthesis 1980, 402.
- 183(a) Perriot, P.; Normant, J. F.; Villieras, J. C.R. Hebd. Seances Acad. Sci., Ser. C 1979, 289, 259. (b) Trost, B. M.; Tour, J. M. J. Org. Chem. 1989, 54, 484. (c) Corey, E. J.; Su, W. Tetrahedron 1990, 31, 2089.
- 184(a) Evans, D. D.; Evans, D. E.; Lewis, G. S.; Palmer, P. J.; Weyell, D. J. J. Chem. Soc 1963, 3578. (b) Duboudin, J. G.; Ratier, M.; Trouve, B. J. Organomet. Chem. 1987, 331, 181.
- 185 Weidert, P. J.; Geyer, E.; Horner, L. Justus Liebigs Ann. Chem./Liebigs Ann. Chem. 1989, 533.
- 186(a) Heyse, M. Ger. Patent 524 435, 1929. (b) Searles, S. Jr.; Pollart, K. A.; Block, F. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1957, 79, 952. (c) Sharma, K. K.; Torssell, K. B. G. Tetrahedron 1984, 40, 1085.
- 187 Kotsuki, H.; Kataoka, M.; Nishizawa, H. Tetrahedron 1993, 34, 4031.
- 188 Bryant, W. M. D.; Smith, D. M. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1936, 58, 1014.
- 189 Karger, M. H.; Mazur, Y. J. Org. Chem. 1971, 36, 528.
- 190(a)
Lennon, J. J.;
Perkin, W. H. Jr.
J. Chem. Soc
1928,
1513.
10.1039/JR9280001513 Google Scholar(b) Zilkha, A.; Liwschitz, Y. J. Chem. Soc 1957, 4397. (c) Bose, N. K.; Chaudhury, D. N. Tetrahedron 1964, 20, 49.
- 191(a) Turner, R. B. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1950, 72, 579. (b) Rosenmund, K. W.; Herzberg, H.; Schutt, H. Ber. Dtsch. Chem. Ges./Chem. Ber. 1954, 87, 1258. (c) Vignau, M.; Bucourt, R.; Tessier, J.; Costerousse, G.; Nedelec, L.; Gasc, J.-C.; Joly, R.; Warnant, J.; Goffinet, B. U.S. Patent 3 453 267, 1969.
- 192(a) Harada, K.; Kaji, E.; Zen, S. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1980, 28, 3296. (b) Fleming, I.; Moses, R. C.; Tercel, M.; Ziv, J. J. Chem. Soc., Perkin Trans. 1 1991, 617.
- 193 Farrissey, W. J. Jr. U.S. Patent 3 291 834, 1966.
- 194Stirring zinc dust with AcCl and CuCl (Et2O, rt → Δ) produces an active zinc couple capable of reacting with methylene bromide to form the Simmons–Smith reagent: Friedrich, E. C.; Lewis, E. J. J. Org. Chem. 1990, 55, 2491.
- 195 Watt, G. W.; Gentile, P. S.; Helvenston, E. P. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1955, 77, 2752.
- 196 Bellesia, F.; Ghelfi, F.; Pagnoni, U. M.; Pinetti, A. J. Chem. Res. (S) 1990, 188.
- 197 Nugent, W. A. Tetrahedron 1978, 3427.
- 198 Bellesia, F.; Ghelfi, F.; Pagnoni, U. M.; Pinetti, A. Synth. Commun. 1991, 21, 489.
- 199 Bellesia, F.; Ghelfi, F.; Pagnoni, U. M.; Pinetti, A. J. Chem. Res. (S) 1989, 108.
- 200 Backvall, J. E.; Young, M. W.; Sharpless, K. B. Tetrahedron 1977, 3523.
- 201 Cummins, C. H.; Coates, R. M. J. Org. Chem. 1983, 48, 2070.
- 202(a) Demerseman, P.; Guillaumel, J.; Clavel, J.-M.; Royer, R. Tetrahedron 1978, 2011. (b) Guillaumel, J.; Demerseman, P.; Clavel, J.-M.; Royer, R.; Platzer, N.; Brevard, C. Tetrahedron 1980, 36, 2459.
- 203 Numata, T.; Oae, S. Chem. Ind. (London) 1973, 277.
- 204(a) Adkins, H.; Thompson, Q. E. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1949, 71, 2242. (b) Paukstelis, J. V.; Kim, M. J. Org. Chem. 1974, 39, 1503.
- 205(a) Lang, R. W.; Hansen, H.-J. Helv. Chim. Acta 1980, 63, 438. (b) Lang, R. W.; Hansen, H.-J. Org. Synth. 1984, 62, 202. (c) Abell, A. D.; Morris, K. B.; Litten, J. C. J. Org. Chem. 1990, 55, 5217.
- 206(a) Burger, K.; Huber, E.; Sewald, N.; Partscht, H. Chem.-Ztg. 1986, 110, 83. (b) Sewald, N.; Riede, J.; Bissinger, P.; Burger, K. J. Chem. Soc., Perkin Trans. 1 1992, 267.
- 207 Maujean, A.; Chuche, J. Tetrahedron 1976, 2905.
- 208 Sauer, J. C. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1947, 69, 2444.
- 209 Hunt, C. F. U.S. Patent 2 737 528, 1956.
- 210 Matoba, K.; Tachi, M.; Itooka, T.; Yamazaki, T. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1986, 34, 2007.
- 211 Furniss, B. S.; Hannaford, A. J.; Smith, P. W. G.; Tatchell, A. R. Vogel's Textbook of Practical Organic Chemistry, 5th ed.; Longman/Wiley: New York, 1989; pp 916, 1273.
- 212(a) Sonntag, N. O. V. Chem. Rev. 1953, 52, 237. (b) To minimize the amount of hydrolysis, the acetylation should be run at pH = (x + 13.25)/2, where x is the pKa of the protonated amine: King, J. F.; Rathore, R.; Lam, J. Y. L.; Guo, Z. R.; Klassen, D. F. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1992, 114, 3028.
- 213 (a) Bohme, H.; Hartke, K. Ber. Dtsch. Chem. Ges./Chem. Ber. 1960, 93, 1305. (b) Kinast, G.; Tietze, L.-F. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 1976, 15, 239.
- 214 Kritzler, H.; Wanger, K.; Holtschmidt, H. U.S. Patent 3 242 202, 1966.
- 215(a) Ikeda, K.; Morimoto, T.; Sekiya, M. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1980, 28, 1178. (b) Ikeda, K.; Terao, Y.; Sekiya, M. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1981, 29, 1156.
- 216 Okada, I.; Takahama, T.; Sudo, R. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 1970, 43, 2591.
- 217 Caubere, P.; Madelmont, J.-C. C.R. Hebd. Seances Acad. Sci., Ser. C 1972, 275, 1305.
- 218 Comins, D. L.; Abdullah, A. H. J. Org. Chem. 1982, 47, 4315.
- 219 Corcoran, R. C.; Bang, S. H. Tetrahedron 1990, 31, 6757.
- 220(a) Oppolzer, W.; Bieber, L.; Francotte, E. Tetrahedron 1979, 981. (b) Ng, K. S.; Laycock, D. E.; Alper, H. J. Org. Chem. 1981, 46, 2899.
- 221 Ben-Ishai, D.; Katchalski, E. J. Org. Chem. 1951, 16, 1025.
- 222 Hoffmann, H. M. R.; Haase, K. Synthesis 1981, 715.
- 223 Ihara, M.; Hirabayashi, A.; Taniguchi, N.; Fukumoto, K. Heterocycles 1992, 33, 851.
- 224(a) Pump, J.; Wannagat, U. Monatsh. Chem. 1962, 93, 352. (b) Bowser, J. R.; Williams, P. J.; Kurz, K. J. Org. Chem. 1983, 48, 4111.
- 225 Ahmad, S.; Iqbal, J. Tetrahedron 1986, 27, 3791.



