Theory of the BOLD effect in the capillary region: An analytical approach for the determination of T*2 in the capillary network of myocardium
Corresponding Author
Wolfgang R. Bauer
Medizinische Universitätsklinik Mannheim/Heidelberg.
Medizinische Klinik, Klinikum Mannheim/Universität Heidelberg, Theodor-Kutzer Ufer 1-3, 68167 Mannheim, Germany.===Search for more papers by this authorMichael Bock
Department of Biophysics, German Cancer Research Center, Heidelberg, Germany.
Search for more papers by this authorLothar R. Schad
Department of Biophysics, German Cancer Research Center, Heidelberg, Germany.
Search for more papers by this authorAndreas Hartlep
Department of Biophysics, German Cancer Research Center, Heidelberg, Germany.
Search for more papers by this authorGeorg Ertl
Medizinische Universitätsklinik Mannheim/Heidelberg.
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Wolfgang R. Bauer
Medizinische Universitätsklinik Mannheim/Heidelberg.
Medizinische Klinik, Klinikum Mannheim/Universität Heidelberg, Theodor-Kutzer Ufer 1-3, 68167 Mannheim, Germany.===Search for more papers by this authorMichael Bock
Department of Biophysics, German Cancer Research Center, Heidelberg, Germany.
Search for more papers by this authorLothar R. Schad
Department of Biophysics, German Cancer Research Center, Heidelberg, Germany.
Search for more papers by this authorAndreas Hartlep
Department of Biophysics, German Cancer Research Center, Heidelberg, Germany.
Search for more papers by this authorGeorg Ertl
Medizinische Universitätsklinik Mannheim/Heidelberg.
Search for more papers by this authorAbstract
This article presents an analytical approach for the quantification of the blood oxygen level dependent (BOLD) effect in the capillary region. The capillary geometry of myocardium is considered. The relaxation rate R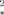 is determined as a function of the capillary radius Rc, the intracapillary volume fraction RBV, and the diffusion coefficient D. When the intracapillary volume fraction is small, the approximation R
is determined as a function of the capillary radius Rc, the intracapillary volume fraction RBV, and the diffusion coefficient D. When the intracapillary volume fraction is small, the approximation R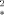 = RBV · τ−1 · (√1 + (τδω)2 − 1) is valid, with the correlation time τ = (R
= RBV · τ−1 · (√1 + (τδω)2 − 1) is valid, with the correlation time τ = (R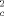 /4D) · (|ln RBV|/(1 − RBV)). The predictions of this model agree well with numerical simulations and experimental data of others and with data recently measured by our group. Magn Reson Med 41:51-62, 1999. © 1999 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
/4D) · (|ln RBV|/(1 − RBV)). The predictions of this model agree well with numerical simulations and experimental data of others and with data recently measured by our group. Magn Reson Med 41:51-62, 1999. © 1999 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
REFERENCES
- 1 Ogawa S, Lee T-M, Nayak AS, Glynn P. Oxygenation-sensitive contrast in magnetic resonance image of the rodent brain at high magnetic fields. Magn Reson Med 1990; 14: 68–78. Medline
- 2 Atalay MK, Forder JR, Chacko VP, Kawamoto S, Zerhouni EA. Oxygenation in the rabbit myocardium: assessment with susceptibility dependent MR imaging. Radiology 1993; 189: 759–764. Medline
- 3 Atalay MK, Reeder SB, Zerhouni EA, Forder JR. Blood oxygenation dependence of T1 and T2 in the isolated, perfused rabbit heart at 4.7 T Magn Reson Med 1995; 34: 623–627. Medline
- 4 Li D, Dhawale P, Rubin PJ, Haacke EM, Gropler RJ. Myocardial signal response to dipyridamol and dobutamine: demonstration of the BOLD effect using a double-echo sequence. Magn Reson Med 1996; 36: 16–20. Medline
- 5 Niemi P, Poncelet BP, Kwong KK, Weisskoff RM, Rosen BR, Brady TJ, Kantor HL. Myocardial intensity changes associated with flow stimulation in blood oxygenation sensitive magnetic resonance imaging. Magn Reson Med 1996; 38: 78–82.
- 6 Yablonski DA, Haake EM. Theory of NMR-signal behavior in magnetically inhomogeneous tissues: the static dephasing regime. Magn Reson Med 1994; 32: 749–763. Medline
- 7 Kaul S, Jayaweera AR. Coronary and myocardial blood volumes. Circulation 1997; 96: 719–724 [Editorial]. Medline
- 8 Gillis P, Koenig SH. Transverse relaxation of solvent protons induced by magnetized spheres: application to ferritin, erythrocytes, and magnetite. Magn Reson Med 1987; 5: 323–345. Medline
- 9 Torrey HC. Bloch equations with diffusion terms. Phys Rev 1956; 104: 563–565.
- 10 Kennan RP, Zhong J, Gore JC. Intravascular susceptibility contrast mechanisms in tissues. Magn Reson Med 1994; 31: 9–21. Medline
- 11 Bassingwaighte JB, Ypintsol T, Harvey RB. Microvasculature of the dog left ventricular myocardium. Microvasc Res 1974; 7: 229–249. Medline
- 12 Donahue KM, Burstein D, Mannings WJ, Gray ML. Studies of Gd-DTPA relaxivity and proton exchange rates in tissue. Magn Reson Med 1994; 32: 66–76. Medline
- 13 Bauer WR, Schulten K. Theory of contrast agents in magnetic resonance imaging: coupling of spin relaxation and transport. Magn Reson Med 1992; 26: 16–39. Medline
- 14 Jackson DJ. “ Classical Electrodynamics,” John Wiley and Sons, New York, 1975.
- 15 Nadler W, Schulten K. Generalized moment expansion for Brownian relaxation processes. J Chem Phys 1985; 82: 151–160.
- 16 Dattagupta S, Blume M. Stochastic theory of line shape: I. Nonsecular effects in the strong collision model. Phys Rev B 1974; 10: 4540–4550.
- 17 Bauer WR, Schulten K. Nuclear spin dynamics (I = 1/2) under the influence of random perturbation fields in the strong collision approximation. Ber Bunsenges Phys Chem 1992; 96: 721–723.
- 18 Thulborn KR, Waterton JC, Mathews PM, Radda G. Oxygenation dependence of the transverse relaxation time of water protons of whole blood at high fields. Biochim Biophys Acta 1982; 714: 265–270. Medline
- 19 Groth J, Thews G. Die Bedingungen für die Sauerstoffversorgung des Herzmuskelgewebes. Pflügers Arch 1962; 276: 142–165.
- 20 Chrystal GJ, Downey HF, Bashour FA. Small vessel and total coronary blood volume during adenosine infusion. Am J Physiol 1981; 241: H194–H201. Medline
- 21 Tauchert M, Hilger HH. in “ The Pathophysiology of Myocardial Perfusion” ( W. Shaper, Ed.), p. 141, Elsevier/North Holland Biomedical Press, Amsterdam, 1979.
- 22 Bing RJ, Hammond MM, Handelsman JC, Powers SR, Spenger FC, Eckenhoff JE, Goodale WT, Hafkenschiel JH, Kety SS. The measurement of coronary blood flow, oxygen consumption, and efficiency of the left ventricle in man. Am Heart J 1949; 38: 1.
- 23 Thews G. Die Sauerstoffdrücke im Herzmuskelgewebe. Pflügers Arch 1962; 276: 166–181.
- 24 Gerdes AM, Callas G, Kasten FH. Differences in regional capillary distribution and myocyte sizes in normal and hypertrophic rat hearts. Am J Anat 1979; 156: 523–532. Medline
- 25 Boxerman JL, Bandettini PA, Kwong KK, Baker JR, Davis TL, Rosen BR, Weisskoff RM. The intravascular contribution to fMRI signal change: Monte Carlo modeling and diffusion weighted studies in vivo. Magn Reson Med 1995; 34: 4–10. Medline
- 26 Bauer WR, Roder F, Hiller K-H, Han H, Fröhlich S, Rommel E, Haase A, Ertl G. The effect of perfusion on T1 after slice-selective spin inversion in the isolated cardioplegic rat heart: measurement of a lower bound of intracapillary-extravascular water proton exchange. Magn Reson Med 1997; 38: 917–923. Medline




